Premium Only Content
This video is only available to Rumble Premium subscribers. Subscribe to
enjoy exclusive content and ad-free viewing.
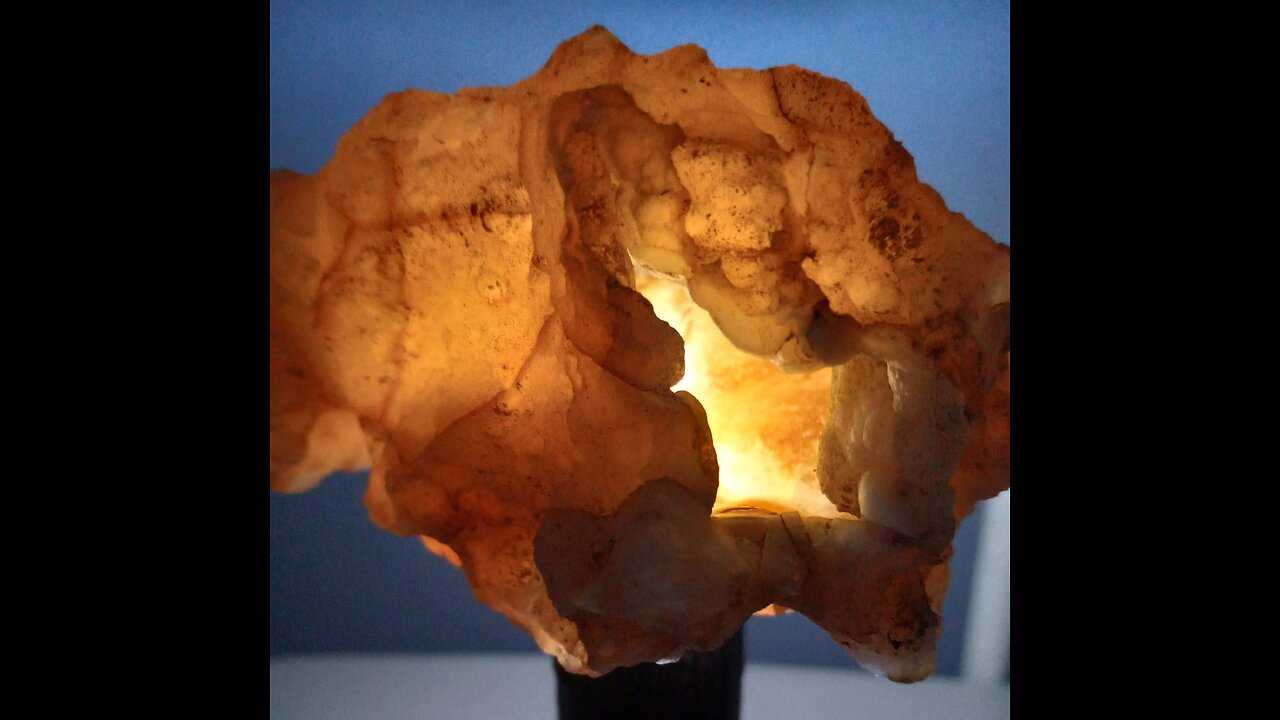

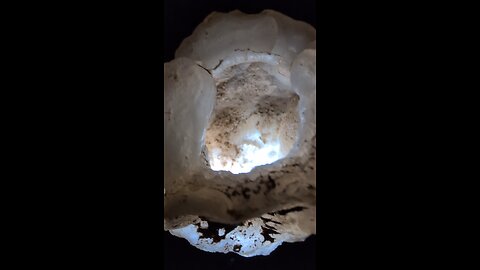
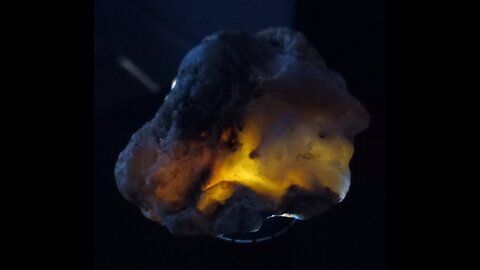
Glowrocks!
HumbleConservative
- 74 / 94
1
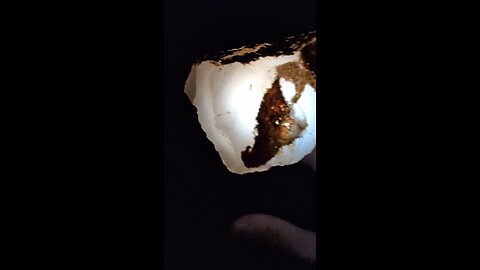
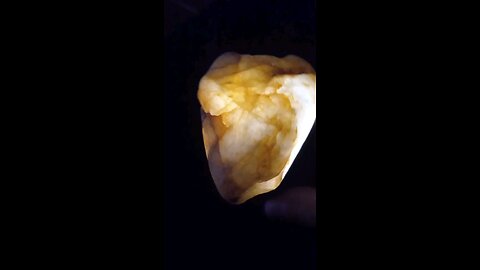
Glow Carnelean!
HumbleConservative
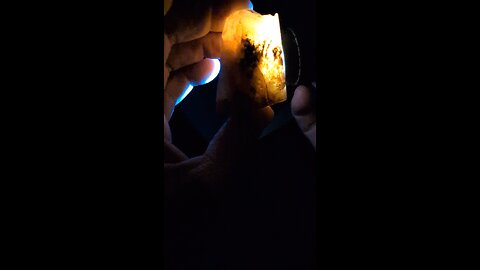
This rock houses Carnelian, a type of chalcedony known for its rich, translucent, and warm orange to red-brown color. Here's why this identification might fit:
Color: Carnelian typically exhibits a range of colors from pale orange to deep red-brown, which matches the coloration seen in the rock in the image.
Translucency: Carnelian is often translucent to semi-translucent, which aligns with the way the light passes through the rock in the image, giving it a somewhat glassy appearance.
Layering: While not as pronounced as in banded agates, carnelian can sometimes show subtle banding or layers of color, which might be seen in the varying shades of orange and brown in the rock.
Texture: Carnelian has a waxy luster when polished, much like other forms of chalcedony, which seems consistent with the appearance of the rock in the image.
Carnelian is often used in jewelry and decorative items due to its vibrant color and attractive appearance. If this rock has been polished or cut for ornamental use, it would typically enhance its color and luster, making it look like this one.
2
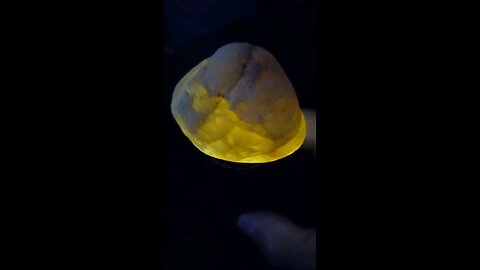
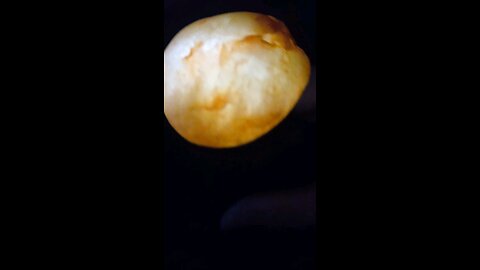
Glow Plume Nugget!
HumbleConservative
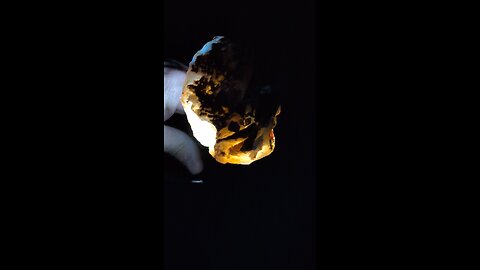
Plume agate is a distinctive variety of agate, known for its unique and intricate patterns that resemble plumes, feathers, or even landscapes. Here are some key points about plume agate:
Formation: Plume agate forms when silica-rich solutions seep into cavities in volcanic rocks. The "plumes" are created by manganese or iron oxides that get trapped in the silica, forming these feather-like patterns.
Colors: The colors of plume agate can vary widely depending on the minerals present. Common colors include reds, browns, yellows, blacks, and whites, with the plumes often contrasting against the base color of the agate.
Locations: Notable locations where plume agate is found include Oregon in the United States (specifically, the Owyhee Mountain area), Mexico, and Brazil. Each location can produce agates with unique characteristics.
Uses: Plume agate is popular among collectors and is often used in jewelry like pendants, rings, and beads due to its aesthetic appeal. It's also valued in metaphysical communities, where it's believed to enhance one's connection to the Earth, promote creativity, and aid in grounding.
Care: Like other agates, plume agate is relatively hard (about 6.5-7 on the Mohs scale), making it durable for jewelry. However, it should be protected from sharp blows or extreme temperature changes to avoid cracking.
Identification: When identifying plume agate, look for the characteristic plume-like inclusions. These inclusions should appear as if they are floating within the stone, giving a 3D effect when viewed from different angles.
Plume agate's beauty lies in its natural patterns, which can look like trees, clouds, or even abstract art, making each piece unique.
3
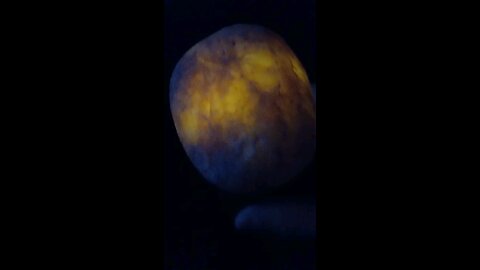
Glow Plume Slab!
HumbleConservative
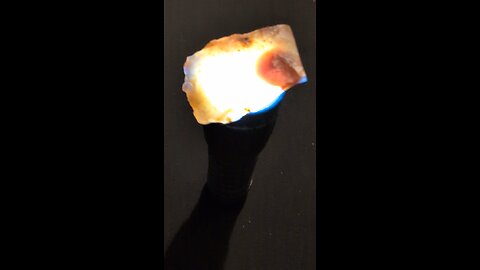
Plume agate is a distinctive variety of agate, known for its unique and intricate patterns that resemble plumes, feathers, or even landscapes. Here are some key points about plume agate:
Formation: Plume agate forms when silica-rich solutions seep into cavities in volcanic rocks. The "plumes" are created by manganese or iron oxides that get trapped in the silica, forming these feather-like patterns.
Colors: The colors of plume agate can vary widely depending on the minerals present. Common colors include reds, browns, yellows, blacks, and whites, with the plumes often contrasting against the base color of the agate.
Locations: Notable locations where plume agate is found include Oregon in the United States (specifically, the Owyhee Mountain area), Mexico, and Brazil. Each location can produce agates with unique characteristics.
Uses: Plume agate is popular among collectors and is often used in jewelry like pendants, rings, and beads due to its aesthetic appeal. It's also valued in metaphysical communities, where it's believed to enhance one's connection to the Earth, promote creativity, and aid in grounding.
Care: Like other agates, plume agate is relatively hard (about 6.5-7 on the Mohs scale), making it durable for jewelry. However, it should be protected from sharp blows or extreme temperature changes to avoid cracking.
Identification: When identifying plume agate, look for the characteristic plume-like inclusions. These inclusions should appear as if they are floating within the stone, giving a 3D effect when viewed from different angles.
Plume agate's beauty lies in its natural patterns, which can look like trees, clouds, or even abstract art, making each piece unique.
4
Glowing Plume!
HumbleConservative
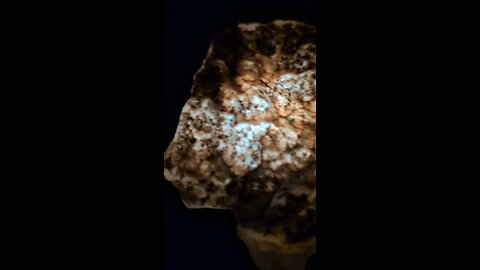
Plume agate is a distinctive variety of agate, known for its unique and intricate patterns that resemble plumes, feathers, or even landscapes. Here are some key points about plume agate:
Formation: Plume agate forms when silica-rich solutions seep into cavities in volcanic rocks. The "plumes" are created by manganese or iron oxides that get trapped in the silica, forming these feather-like patterns.
Colors: The colors of plume agate can vary widely depending on the minerals present. Common colors include reds, browns, yellows, blacks, and whites, with the plumes often contrasting against the base color of the agate.
Locations: Notable locations where plume agate is found include Oregon in the United States (specifically, the Owyhee Mountain area), Mexico, and Brazil. Each location can produce agates with unique characteristics.
Uses: Plume agate is popular among collectors and is often used in jewelry like pendants, rings, and beads due to its aesthetic appeal. It's also valued in metaphysical communities, where it's believed to enhance one's connection to the Earth, promote creativity, and aid in grounding.
Care: Like other agates, plume agate is relatively hard (about 6.5-7 on the Mohs scale), making it durable for jewelry. However, it should be protected from sharp blows or extreme temperature changes to avoid cracking.
Identification: When identifying plume agate, look for the characteristic plume-like inclusions. These inclusions should appear as if they are floating within the stone, giving a 3D effect when viewed from different angles.
Plume agate's beauty lies in its natural patterns, which can look like trees, clouds, or even abstract art, making each piece unique.
5
Carnelean Glow!
HumbleConservative
This rock houses Carnelian, a type of chalcedony known for its rich, translucent, and warm orange to red-brown color. Here's why this identification might fit:
Color: Carnelian typically exhibits a range of colors from pale orange to deep red-brown, which matches the coloration seen in the rock in the image.
Translucency: Carnelian is often translucent to semi-translucent, which aligns with the way the light passes through the rock in the image, giving it a somewhat glassy appearance.
Layering: While not as pronounced as in banded agates, carnelian can sometimes show subtle banding or layers of color, which might be seen in the varying shades of orange and brown in the rock.
Texture: Carnelian has a waxy luster when polished, much like other forms of chalcedony, which seems consistent with the appearance of the rock in the image.
Carnelian is often used in jewelry and decorative items due to its vibrant color and attractive appearance. If this rock has been polished or cut for ornamental use, it would typically enhance its color and luster, making it look like this one.
Plume Agate is a captivating variety of agate, renowned for its intricate and delicate feather-like inclusions. These mesmerizing formations resemble ethereal plumes or wisps suspended within the stone, creating a stunning visual effect. It belongs to the chalcedony family, characterized by its microcrystalline structure and vibrant colors.
Plume Agate derives its name from the feathery patterns that adorn its surface. These patterns are typically composed of mineral deposits, often in striking hues such as white, cream, pink, or red, contrasting against a translucent or opaque background. These intricate formations are formed through the slow crystallization of silica-rich solutions within cavities or fissures in volcanic rocks.
Each piece of Plume Agate is unique, showcasing a kaleidoscope of colors and patterns. The delicate plumes within the stone evoke a sense of tranquility and beauty, making it a highly sought-after gemstone among collectors and jewelry enthusiasts alike.
Plume Agate holds significant importance in the world of gemstones and jewelry for several reasons:
Aesthetic Appeal: Plume Agate’s captivating patterns and vibrant colors make it a favorite among jewelry designers and collectors. Its unique beauty adds an element of elegance and individuality to any piece of jewelry.
Metaphysical Properties: In addition to its visual allure, Plume Agate is believed to possess metaphysical properties that promote harmony, balance, and emotional healing. It is often used in alternative healing practices and spiritual rituals.
Collectibility: Due to its rarity and unique characteristics, Plume Agate is highly prized by gemstone collectors. Specimens with exceptional plume formations or intense colors can command high prices in the market.
Versatility: Plume Agate’s diverse color palette and patterns make it a versatile gemstone for jewelry design. It can be fashioned into various shapes and sizes, including cabochons, beads, and carvings, allowing for creativity and innovation in jewelry making.
Historical Significance: Throughout history, agates have been revered for their beauty and perceived mystical properties. Plume Agate, with its distinct plume-like inclusions, has been admired and utilized in adornments and talismans by ancient civilizations.
Plume Agate stands out as a gemstone of exceptional beauty, imbued with both aesthetic and metaphysical significance. Its popularity in the world of gemstones and jewelry continues to endure, captivating admirers with its mesmerizing patterns and timeless allure.
6
Agate Glow!
HumbleConservative
Agate is a microcrystalline variety of quartz, specifically a form of chalcedony, known for its fine grain and bright color patterns. Here are some key points about agate:
Formation: Agate forms in volcanic and sedimentary rocks. It often begins as a cavity in the rock, which then gets filled with layers of silica-rich water. Over time, this solution deposits minerals in layers, creating the characteristic banding of agate. This process can take millions of years.
Appearance: Agate is famous for its beautiful, often banded patterns of color, which can range from translucent to opaque. Colors include white, blue, red, black, yellow, and brown among others, with the patterns formed by the successive layers of chalcedony being deposited. Sometimes, agates can be found with inclusions like moss (moss agate) or even fossils.
Types of Agate:
Banded Agate: Shows clear, concentric bands of color.
Moss Agate: Contains mineral inclusions that look like moss or foliage.
Dendritic Agate: Similar to moss agate but with tree-like or branch-like patterns.
Fire Agate: Contains iridescent layers that appear to glow with fiery colors.
Lace Agate: Features lace-like patterns, most notably in Blue Lace Agate from Namibia.
Crazy Lace Agate: Known for its wild, chaotic patterns of colors.
Locations: Agates are found worldwide, but some of the most famous locations include Brazil, Uruguay, Mexico, Germany, Madagascar, and the United States (particularly in Oregon, Washington, and Idaho).
Uses:
Jewelry: Due to its beauty when polished, agate is widely used in jewelry like rings, pendants, and beads.
Decorative Items: Larger pieces or slices are used for decorative objects, bookends, or as display pieces.
Metaphysical: In metaphysical practices, agate is believed to have various healing properties, like balancing physical, emotional, and intellectual energy, and promoting strength and courage.
Cultural Significance: Agate has been used since ancient times; it was prized in Ancient Egypt for amulets and seals, in Greece and Rome for intaglios and cameos, and by many other cultures for its beauty and supposed protective qualities.
Cutting and Polishing: When cutting agate for jewelry or display, lapidaries look for the most visually appealing patterns. The process involves sawing, grinding, and polishing to bring out the internal beauty of the stone.
Agate's diversity in color and pattern, combined with its durability, makes it one of the most sought-after stones in the world of gemology and mineral collecting.
1
comment
7
Plume Glow!
HumbleConservative
Plume agate is a distinctive variety of agate, known for its unique and intricate patterns that resemble plumes, feathers, or even landscapes. Here are some key points about plume agate:
Formation: Plume agate forms when silica-rich solutions seep into cavities in volcanic rocks. The "plumes" are created by manganese or iron oxides that get trapped in the silica, forming these feather-like patterns.
Colors: The colors of plume agate can vary widely depending on the minerals present. Common colors include reds, browns, yellows, blacks, and whites, with the plumes often contrasting against the base color of the agate.
Locations: Notable locations where plume agate is found include Oregon in the United States (specifically, the Owyhee Mountain area), Mexico, and Brazil. Each location can produce agates with unique characteristics.
Uses: Plume agate is popular among collectors and is often used in jewelry like pendants, rings, and beads due to its aesthetic appeal. It's also valued in metaphysical communities, where it's believed to enhance one's connection to the Earth, promote creativity, and aid in grounding.
Care: Like other agates, plume agate is relatively hard (about 6.5-7 on the Mohs scale), making it durable for jewelry. However, it should be protected from sharp blows or extreme temperature changes to avoid cracking.
Identification: When identifying plume agate, look for the characteristic plume-like inclusions. These inclusions should appear as if they are floating within the stone, giving a 3D effect when viewed from different angles.
Plume agate's beauty lies in its natural patterns, which can look like trees, clouds, or even abstract art, making each piece unique.
1
comment
8
Chalcedony glow!
HumbleConservative
This rock appears to be a type of agate, specifically a form known as Banded Agate or Fortification Agate. Here are some key characteristics that led to this identification:
Banded Structure: The rock shows clear banding, which is characteristic of agates formed in cavities where silica-rich solutions deposit in layers over time.
Translucency: Parts of the rock are translucent, which is typical for agate due to its chalcedony composition.
Color Variations: The presence of various shades like white, brown, and hints of yellow or orange indicates different mineral inclusions or variations in the silica deposition process.
Patterns: The patterns resemble a fortification or landscape, which is common in fortification agates where the bands follow the outline of the cavity in which they formed.
Agates are a variety of chalcedony, which is a cryptocrystalline form of silica, and they often contain colorful bands or layers due to changes in the composition of the depositing fluids or the presence of different minerals. This particular specimen seems to have been polished or naturally smoothed, enhancing its translucency and the visibility of its internal structures.
If you're interested in further identification or more detailed information, I could suggest searching for similar examples or consulting with a mineralogist or gemologist.
9
Plume Agate Glow!
HumbleConservative
Plume agate is a distinctive variety of agate, known for its unique and intricate patterns that resemble plumes, feathers, or even landscapes. Here are some key points about plume agate:
Formation: Plume agate forms when silica-rich solutions seep into cavities in volcanic rocks. The "plumes" are created by manganese or iron oxides that get trapped in the silica, forming these feather-like patterns.
Colors: The colors of plume agate can vary widely depending on the minerals present. Common colors include reds, browns, yellows, blacks, and whites, with the plumes often contrasting against the base color of the agate.
Locations: Notable locations where plume agate is found include Oregon in the United States (specifically, the Owyhee Mountain area), Mexico, and Brazil. Each location can produce agates with unique characteristics.
Uses: Plume agate is popular among collectors and is often used in jewelry like pendants, rings, and beads due to its aesthetic appeal. It's also valued in metaphysical communities, where it's believed to enhance one's connection to the Earth, promote creativity, and aid in grounding.
Care: Like other agates, plume agate is relatively hard (about 6.5-7 on the Mohs scale), making it durable for jewelry. However, it should be protected from sharp blows or extreme temperature changes to avoid cracking.
Identification: When identifying plume agate, look for the characteristic plume-like inclusions. These inclusions should appear as if they are floating within the stone, giving a 3D effect when viewed from different angles.
Plume agate's beauty lies in its natural patterns, which can look like trees, clouds, or even abstract art, making each piece unique. If you're interested in seeing or acquiring plume agate, looking into local gem shows, mineral clubs, or reputable online gem dealers would be a good start.
10
Carnelean Glow!
HumbleConservative
This rock houses Carnelian, a type of chalcedony known for its rich, translucent, and warm orange to red-brown color. Here's why this identification might fit:
Color: Carnelian typically exhibits a range of colors from pale orange to deep red-brown, which matches the coloration seen in the rock in the image.
Translucency: Carnelian is often translucent to semi-translucent, which aligns with the way the light passes through the rock in the image, giving it a somewhat glassy appearance.
Layering: While not as pronounced as in banded agates, carnelian can sometimes show subtle banding or layers of color, which might be seen in the varying shades of orange and brown in the rock.
Texture: Carnelian has a waxy luster when polished, much like other forms of chalcedony, which seems consistent with the appearance of the rock in the image.
Carnelian is often used in jewelry and decorative items due to its vibrant color and attractive appearance. If this rock has been polished or cut for ornamental use, it would typically enhance its color and luster, making it look like this one.
Plume Agate is a captivating variety of agate, renowned for its intricate and delicate feather-like inclusions. These mesmerizing formations resemble ethereal plumes or wisps suspended within the stone, creating a stunning visual effect. It belongs to the chalcedony family, characterized by its microcrystalline structure and vibrant colors.
Plume Agate derives its name from the feathery patterns that adorn its surface. These patterns are typically composed of mineral deposits, often in striking hues such as white, cream, pink, or red, contrasting against a translucent or opaque background. These intricate formations are formed through the slow crystallization of silica-rich solutions within cavities or fissures in volcanic rocks.
Each piece of Plume Agate is unique, showcasing a kaleidoscope of colors and patterns. The delicate plumes within the stone evoke a sense of tranquility and beauty, making it a highly sought-after gemstone among collectors and jewelry enthusiasts alike.
Plume Agate holds significant importance in the world of gemstones and jewelry for several reasons:
Aesthetic Appeal: Plume Agate’s captivating patterns and vibrant colors make it a favorite among jewelry designers and collectors. Its unique beauty adds an element of elegance and individuality to any piece of jewelry.
Metaphysical Properties: In addition to its visual allure, Plume Agate is believed to possess metaphysical properties that promote harmony, balance, and emotional healing. It is often used in alternative healing practices and spiritual rituals.
Collectibility: Due to its rarity and unique characteristics, Plume Agate is highly prized by gemstone collectors. Specimens with exceptional plume formations or intense colors can command high prices in the market.
Versatility: Plume Agate’s diverse color palette and patterns make it a versatile gemstone for jewelry design. It can be fashioned into various shapes and sizes, including cabochons, beads, and carvings, allowing for creativity and innovation in jewelry making.
Historical Significance: Throughout history, agates have been revered for their beauty and perceived mystical properties. Plume Agate, with its distinct plume-like inclusions, has been admired and utilized in adornments and talismans by ancient civilizations.
Plume Agate stands out as a gemstone of exceptional beauty, imbued with both aesthetic and metaphysical significance. Its popularity in the world of gemstones and jewelry continues to endure, captivating admirers with its mesmerizing patterns and timeless allure.
1
comment
11
Plume botryoidal chalcedony nugget!
HumbleConservative
Plume Agate is a captivating variety of agate, renowned for its intricate and delicate feather-like inclusions. These mesmerizing formations resemble ethereal plumes or wisps suspended within the stone, creating a stunning visual effect. It belongs to the chalcedony family, characterized by its microcrystalline structure and vibrant colors.
Plume Agate derives its name from the feathery patterns that adorn its surface. These patterns are typically composed of mineral deposits, often in striking hues such as white, cream, pink, or red, contrasting against a translucent or opaque background. These intricate formations are formed through the slow crystallization of silica-rich solutions within cavities or fissures in volcanic rocks.
Each piece of Plume Agate is unique, showcasing a kaleidoscope of colors and patterns. The delicate plumes within the stone evoke a sense of tranquility and beauty, making it a highly sought-after gemstone among collectors and jewelry enthusiasts alike.
Plume Agate holds significant importance in the world of gemstones and jewelry for several reasons:
Aesthetic Appeal: Plume Agate’s captivating patterns and vibrant colors make it a favorite among jewelry designers and collectors. Its unique beauty adds an element of elegance and individuality to any piece of jewelry.
Metaphysical Properties: In addition to its visual allure, Plume Agate is believed to possess metaphysical properties that promote harmony, balance, and emotional healing. It is often used in alternative healing practices and spiritual rituals.
Collectibility: Due to its rarity and unique characteristics, Plume Agate is highly prized by gemstone collectors. Specimens with exceptional plume formations or intense colors can command high prices in the market.
Versatility: Plume Agate’s diverse color palette and patterns make it a versatile gemstone for jewelry design. It can be fashioned into various shapes and sizes, including cabochons, beads, and carvings, allowing for creativity and innovation in jewelry making.
Historical Significance: Throughout history, agates have been revered for their beauty and perceived mystical properties. Plume Agate, with its distinct plume-like inclusions, has been admired and utilized in adornments and talismans by ancient civilizations.
Plume Agate stands out as a gemstone of exceptional beauty, imbued with both aesthetic and metaphysical significance. Its popularity in the world of gemstones and jewelry continues to endure, captivating admirers with its mesmerizing patterns and timeless allure.
- https://geologyscience.com/gemstone/plume-agate/
12
Plume slice!
HumbleConservative
Plume Agate is a captivating variety of agate, renowned for its intricate and delicate feather-like inclusions. These mesmerizing formations resemble ethereal plumes or wisps suspended within the stone, creating a stunning visual effect. It belongs to the chalcedony family, characterized by its microcrystalline structure and vibrant colors.
Plume Agate derives its name from the feathery patterns that adorn its surface. These patterns are typically composed of mineral deposits, often in striking hues such as white, cream, pink, or red, contrasting against a translucent or opaque background. These intricate formations are formed through the slow crystallization of silica-rich solutions within cavities or fissures in volcanic rocks.
Each piece of Plume Agate is unique, showcasing a kaleidoscope of colors and patterns. The delicate plumes within the stone evoke a sense of tranquility and beauty, making it a highly sought-after gemstone among collectors and jewelry enthusiasts alike.
Plume Agate holds significant importance in the world of gemstones and jewelry for several reasons:
Aesthetic Appeal: Plume Agate’s captivating patterns and vibrant colors make it a favorite among jewelry designers and collectors. Its unique beauty adds an element of elegance and individuality to any piece of jewelry.
Metaphysical Properties: In addition to its visual allure, Plume Agate is believed to possess metaphysical properties that promote harmony, balance, and emotional healing. It is often used in alternative healing practices and spiritual rituals.
Collectibility: Due to its rarity and unique characteristics, Plume Agate is highly prized by gemstone collectors. Specimens with exceptional plume formations or intense colors can command high prices in the market.
Versatility: Plume Agate’s diverse color palette and patterns make it a versatile gemstone for jewelry design. It can be fashioned into various shapes and sizes, including cabochons, beads, and carvings, allowing for creativity and innovation in jewelry making.
Historical Significance: Throughout history, agates have been revered for their beauty and perceived mystical properties. Plume Agate, with its distinct plume-like inclusions, has been admired and utilized in adornments and talismans by ancient civilizations.
Plume Agate stands out as a gemstone of exceptional beauty, imbued with both aesthetic and metaphysical significance. Its popularity in the world of gemstones and jewelry continues to endure, captivating admirers with its mesmerizing patterns and timeless allure.
- https://geologyscience.com/gemstone/plume-agate/
13
Botryoidal slice!
HumbleConservative
Plume Agate is a captivating variety of agate, renowned for its intricate and delicate feather-like inclusions. These mesmerizing formations resemble ethereal plumes or wisps suspended within the stone, creating a stunning visual effect. It belongs to the chalcedony family, characterized by its microcrystalline structure and vibrant colors.
Plume Agate derives its name from the feathery patterns that adorn its surface. These patterns are typically composed of mineral deposits, often in striking hues such as white, cream, pink, or red, contrasting against a translucent or opaque background. These intricate formations are formed through the slow crystallization of silica-rich solutions within cavities or fissures in volcanic rocks.
Each piece of Plume Agate is unique, showcasing a kaleidoscope of colors and patterns. The delicate plumes within the stone evoke a sense of tranquility and beauty, making it a highly sought-after gemstone among collectors and jewelry enthusiasts alike.
Plume Agate holds significant importance in the world of gemstones and jewelry for several reasons:
Aesthetic Appeal: Plume Agate’s captivating patterns and vibrant colors make it a favorite among jewelry designers and collectors. Its unique beauty adds an element of elegance and individuality to any piece of jewelry.
Metaphysical Properties: In addition to its visual allure, Plume Agate is believed to possess metaphysical properties that promote harmony, balance, and emotional healing. It is often used in alternative healing practices and spiritual rituals.
Collectibility: Due to its rarity and unique characteristics, Plume Agate is highly prized by gemstone collectors. Specimens with exceptional plume formations or intense colors can command high prices in the market.
Versatility: Plume Agate’s diverse color palette and patterns make it a versatile gemstone for jewelry design. It can be fashioned into various shapes and sizes, including cabochons, beads, and carvings, allowing for creativity and innovation in jewelry making.
Historical Significance: Throughout history, agates have been revered for their beauty and perceived mystical properties. Plume Agate, with its distinct plume-like inclusions, has been admired and utilized in adornments and talismans by ancient civilizations.
Plume Agate stands out as a gemstone of exceptional beauty, imbued with both aesthetic and metaphysical significance. Its popularity in the world of gemstones and jewelry continues to endure, captivating admirers with its mesmerizing patterns and timeless allure.
- https://geologyscience.com/gemstone/plume-agate/
14
Plume flow!
HumbleConservative
Plume Agate is a captivating variety of agate, renowned for its intricate and delicate feather-like inclusions. These mesmerizing formations resemble ethereal plumes or wisps suspended within the stone, creating a stunning visual effect. It belongs to the chalcedony family, characterized by its microcrystalline structure and vibrant colors.
Plume Agate derives its name from the feathery patterns that adorn its surface. These patterns are typically composed of mineral deposits, often in striking hues such as white, cream, pink, or red, contrasting against a translucent or opaque background. These intricate formations are formed through the slow crystallization of silica-rich solutions within cavities or fissures in volcanic rocks.
Each piece of Plume Agate is unique, showcasing a kaleidoscope of colors and patterns. The delicate plumes within the stone evoke a sense of tranquility and beauty, making it a highly sought-after gemstone among collectors and jewelry enthusiasts alike.
Plume Agate holds significant importance in the world of gemstones and jewelry for several reasons:
Aesthetic Appeal: Plume Agate’s captivating patterns and vibrant colors make it a favorite among jewelry designers and collectors. Its unique beauty adds an element of elegance and individuality to any piece of jewelry.
Metaphysical Properties: In addition to its visual allure, Plume Agate is believed to possess metaphysical properties that promote harmony, balance, and emotional healing. It is often used in alternative healing practices and spiritual rituals.
Collectibility: Due to its rarity and unique characteristics, Plume Agate is highly prized by gemstone collectors. Specimens with exceptional plume formations or intense colors can command high prices in the market.
Versatility: Plume Agate’s diverse color palette and patterns make it a versatile gemstone for jewelry design. It can be fashioned into various shapes and sizes, including cabochons, beads, and carvings, allowing for creativity and innovation in jewelry making.
Historical Significance: Throughout history, agates have been revered for their beauty and perceived mystical properties. Plume Agate, with its distinct plume-like inclusions, has been admired and utilized in adornments and talismans by ancient civilizations.
Plume Agate stands out as a gemstone of exceptional beauty, imbued with both aesthetic and metaphysical significance. Its popularity in the world of gemstones and jewelry continues to endure, captivating admirers with its mesmerizing patterns and timeless allure.
- https://geologyscience.com/gemstone/plume-agate/
15
Playing with color!
HumbleConservative
Plume agate is a variety of chalcedony, a microcrystalline quartz, characterized by delicate, plume-like inclusions of various colors and minerals. These inclusions often resemble feathers, flowers, or flames, giving the agate a unique and visually appealing appearance.
Plume agate only forms in hotsprings with the help of thermophiles and extremophiles (microscopic organisms that like harsh and hot environments) collecting silica and other dissolved particles in silica rich hotsprings and depositing them in wild patterns within the agate.
A combination of clays, metals and minerals make up the cool colors and textures we experience.
There are many famous deposits of plume, flame and other varieties of textures made with the assistance of microbes.
1
comment
16
Botryoidal Glow!
HumbleConservative
This rock appears to be an example of an open geode. Geodes are typically characterized by their hollow or partially hollow interiors, which are often lined with crystals or minerals. Here's why:
Texture and Appearance: The rock in the image has a rough exterior with a somewhat nodular surface, which is typical for geodes. The interior seems to contain a liquid or a crystalline substance, which is consistent with the internal structure of many geodes.
Possible Mineral Content: The yellowish-brown coloration and the appearance of liquid or crystalline material suggest the presence of minerals like quartz or calcite, which are common in geodes.
Formation: Geodes form when gas bubbles are trapped in volcanic rocks or sedimentary layers. Over time, minerals precipitate from water seeping through the rock, lining the cavity with crystals.
17
Plume chunk glow!
HumbleConservative
Plume agate is a variety of chalcedony, a microcrystalline quartz, characterized by delicate, plume-like inclusions of various colors and minerals. These inclusions often resemble feathers, flowers, or flames, giving the agate a unique and visually appealing appearance.
Plume agate only forms in hotsprings with the help of thermophiles and extremophiles (microscopic organisms that like harsh and hot environments) collecting silica and other dissolved particles in silica rich hotsprings and depositing them in wild patterns within the agate.
A combination of clays, metals and minerals make up the cool colors and textures we experience.
There are many famous deposits of plume, flame and other varieties of textures made with the assistance of microbes.
18
Red dot glow slice!
HumbleConservative
Plume agate is a variety of chalcedony, a microcrystalline quartz, characterized by delicate, plume-like inclusions of various colors and minerals. These inclusions often resemble feathers, flowers, or flames, giving the agate a unique and visually appealing appearance.
Plume agate only forms in hotsprings with the help of thermophiles and extremophiles (microscopic organisms that like harsh and hot environments) collecting silica and other dissolved particles in silica rich hotsprings and depositing them in wild patterns within the agate.
A combination of clays, metals and minerals make up the cool colors and textures we experience.
There are many famous deposits of plume, flame and other varieties of textures made with the assistance of microbes.
19
Glow plume!
HumbleConservative
Plume agate is a variety of chalcedony, a microcrystalline quartz, characterized by delicate, plume-like inclusions of various colors and minerals. These inclusions often resemble feathers, flowers, or flames, giving the agate a unique and visually appealing appearance.
Plume agate only forms in hotsprings with the help of thermophiles and extremophiles (microscopic organisms that like harsh and hot environments) collecting silica and other dissolved particles in silica rich hotsprings and depositing them in wild patterns within the agate.
A combination of clays, metals and minerals make up the cool colors and textures we experience.
There are many famous deposits of plume, flame and other varieties of textures made with the assistance of microbes.
20
Carnelean Glow!
HumbleConservative
Plume agate is a variety of chalcedony, a microcrystalline quartz, characterized by delicate, plume-like inclusions of various colors and minerals. These inclusions often resemble feathers, flowers, or flames, giving the agate a unique and visually appealing appearance.
Plume agate only forms in hotsprings with the help of thermophiles and extremophiles (microscopic organisms that like harsh and hot environments) collecting silica and other dissolved particles in silica rich hotsprings and depositing them in wild patterns within the agate.
A combination of clays, metals and minerals make up the cool colors and textures we experience.
There are many famous deposits of plume, flame and other varieties of textures made with the assistance of microbes.
21
Jasper glow!
HumbleConservative
Plume agate is a variety of chalcedony, a microcrystalline quartz, characterized by delicate, plume-like inclusions of various colors and minerals. These inclusions often resemble feathers, flowers, or flames, giving the agate a unique and visually appealing appearance.
Plume agate only forms in hotsprings with the help of thermophiles and extremophiles (microscopic organisms that like harsh and hot environments) collecting silica and other dissolved particles in silica rich hotsprings and depositing them in wild patterns within the agate.
A combination of clays, metals and minerals make up the cool colors and textures we experience.
There are many famous deposits of plume, flame and other varieties of textures made with the assistance of microbes.
1
comment
22
Glow Plume!
HumbleConservative
Plume agate is a variety of chalcedony, a microcrystalline quartz, characterized by delicate, plume-like inclusions of various colors and minerals. These inclusions often resemble feathers, flowers, or flames, giving the agate a unique and visually appealing appearance.
Plume agate only forms in hotsprings with the help of thermophiles and extremophiles (microscopic organisms that like harsh and hot environments) collecting silica and other dissolved particles in silica rich hotsprings and depositing them in wild patterns within the agate.
A combination of clays, metals and minerals make up the cool colors and textures we experience.
There are many famous deposits of plume, flame and other varieties of textures made with the assistance of microbes.
23
Thundercup glow!
HumbleConservative
These rocks appears to be a type of **thunder egg**. Here's why:
1. **Coloration and Banding**: The rock shows a combination of colors, including brown, white, green, and possibly some hints of other colors, which is typical for agates and thunder eggs. The banding pattern is also characteristic of agates, which form in cavities of volcanic rocks.
2. **Translucency**: Some parts of the rock are translucent, which is common in agates due to their chalcedony composition.
3. **Texture**: The rock's texture looks somewhat waxy or glassy, which is typical for agates that have been polished or naturally worn smooth.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish or brownish areas could be due to iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which are often found in agates. Thunder eggs are nodules of agate found in volcanic rocks, and they often have a hollow or partially hollow interior filled with crystals or banded agate.
24
Thunderegg glow!
HumbleConservative
These rocks appears to be a type of **thunder egg**. Here's why:
1. **Coloration and Banding**: The rock shows a combination of colors, including brown, white, green, and possibly some hints of other colors, which is typical for agates and thunder eggs. The banding pattern is also characteristic of agates, which form in cavities of volcanic rocks.
2. **Translucency**: Some parts of the rock are translucent, which is common in agates due to their chalcedony composition.
3. **Texture**: The rock's texture looks somewhat waxy or glassy, which is typical for agates that have been polished or naturally worn smooth.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish or brownish areas could be due to iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which are often found in agates. Thunder eggs are nodules of agate found in volcanic rocks, and they often have a hollow or partially hollow interior filled with crystals or banded agate.
1
comment
25
Plume chunk glow!
HumbleConservative
Plume Agate is a captivating variety of agate, renowned for its intricate and delicate feather-like inclusions. These mesmerizing formations resemble ethereal plumes or wisps suspended within the stone, creating a stunning visual effect. It belongs to the chalcedony family, characterized by its microcrystalline structure and vibrant colors.
Plume Agate derives its name from the feathery patterns that adorn its surface. These patterns are typically composed of mineral deposits, often in striking hues such as white, cream, pink, or red, contrasting against a translucent or opaque background. These intricate formations are formed through the slow crystallization of silica-rich solutions within cavities or fissures in volcanic rocks.
Each piece of Plume Agate is unique, showcasing a kaleidoscope of colors and patterns. The delicate plumes within the stone evoke a sense of tranquility and beauty, making it a highly sought-after gemstone among collectors and jewelry enthusiasts alike.
Plume Agate holds significant importance in the world of gemstones and jewelry for several reasons:
Aesthetic Appeal: Plume Agate’s captivating patterns and vibrant colors make it a favorite among jewelry designers and collectors. Its unique beauty adds an element of elegance and individuality to any piece of jewelry.
Metaphysical Properties: In addition to its visual allure, Plume Agate is believed to possess metaphysical properties that promote harmony, balance, and emotional healing. It is often used in alternative healing practices and spiritual rituals.
Collectibility: Due to its rarity and unique characteristics, Plume Agate is highly prized by gemstone collectors. Specimens with exceptional plume formations or intense colors can command high prices in the market.
Versatility: Plume Agate’s diverse color palette and patterns make it a versatile gemstone for jewelry design. It can be fashioned into various shapes and sizes, including cabochons, beads, and carvings, allowing for creativity and innovation in jewelry making.
Historical Significance: Throughout history, agates have been revered for their beauty and perceived mystical properties. Plume Agate, with its distinct plume-like inclusions, has been admired and utilized in adornments and talismans by ancient civilizations.
Plume Agate stands out as a gemstone of exceptional beauty, imbued with both aesthetic and metaphysical significance. Its popularity in the world of gemstones and jewelry continues to endure, captivating admirers with its mesmerizing patterns and timeless allure.
- https://geologyscience.com/gemstone/plume-agate/
26
Slab o' Plume Glow!
HumbleConservative
Plume Agate is a captivating variety of agate, renowned for its intricate and delicate feather-like inclusions. These mesmerizing formations resemble ethereal plumes or wisps suspended within the stone, creating a stunning visual effect. It belongs to the chalcedony family, characterized by its microcrystalline structure and vibrant colors.
Plume Agate derives its name from the feathery patterns that adorn its surface. These patterns are typically composed of mineral deposits, often in striking hues such as white, cream, pink, or red, contrasting against a translucent or opaque background. These intricate formations are formed through the slow crystallization of silica-rich solutions within cavities or fissures in volcanic rocks.
Each piece of Plume Agate is unique, showcasing a kaleidoscope of colors and patterns. The delicate plumes within the stone evoke a sense of tranquility and beauty, making it a highly sought-after gemstone among collectors and jewelry enthusiasts alike.
Plume Agate holds significant importance in the world of gemstones and jewelry for several reasons:
Aesthetic Appeal: Plume Agate’s captivating patterns and vibrant colors make it a favorite among jewelry designers and collectors. Its unique beauty adds an element of elegance and individuality to any piece of jewelry.
Metaphysical Properties: In addition to its visual allure, Plume Agate is believed to possess metaphysical properties that promote harmony, balance, and emotional healing. It is often used in alternative healing practices and spiritual rituals.
Collectibility: Due to its rarity and unique characteristics, Plume Agate is highly prized by gemstone collectors. Specimens with exceptional plume formations or intense colors can command high prices in the market.
Versatility: Plume Agate’s diverse color palette and patterns make it a versatile gemstone for jewelry design. It can be fashioned into various shapes and sizes, including cabochons, beads, and carvings, allowing for creativity and innovation in jewelry making.
Historical Significance: Throughout history, agates have been revered for their beauty and perceived mystical properties. Plume Agate, with its distinct plume-like inclusions, has been admired and utilized in adornments and talismans by ancient civilizations.
Plume Agate stands out as a gemstone of exceptional beauty, imbued with both aesthetic and metaphysical significance. Its popularity in the world of gemstones and jewelry continues to endure, captivating admirers with its mesmerizing patterns and timeless allure.
- https://geologyscience.com/gemstone/plume-agate/
27
Glow chunk!
HumbleConservative
Plume Agate is a captivating variety of agate, renowned for its intricate and delicate feather-like inclusions. These mesmerizing formations resemble ethereal plumes or wisps suspended within the stone, creating a stunning visual effect. It belongs to the chalcedony family, characterized by its microcrystalline structure and vibrant colors.
Plume Agate derives its name from the feathery patterns that adorn its surface. These patterns are typically composed of mineral deposits, often in striking hues such as white, cream, pink, or red, contrasting against a translucent or opaque background. These intricate formations are formed through the slow crystallization of silica-rich solutions within cavities or fissures in volcanic rocks.
Each piece of Plume Agate is unique, showcasing a kaleidoscope of colors and patterns. The delicate plumes within the stone evoke a sense of tranquility and beauty, making it a highly sought-after gemstone among collectors and jewelry enthusiasts alike.
Plume Agate holds significant importance in the world of gemstones and jewelry for several reasons:
Aesthetic Appeal: Plume Agate’s captivating patterns and vibrant colors make it a favorite among jewelry designers and collectors. Its unique beauty adds an element of elegance and individuality to any piece of jewelry.
Metaphysical Properties: In addition to its visual allure, Plume Agate is believed to possess metaphysical properties that promote harmony, balance, and emotional healing. It is often used in alternative healing practices and spiritual rituals.
Collectibility: Due to its rarity and unique characteristics, Plume Agate is highly prized by gemstone collectors. Specimens with exceptional plume formations or intense colors can command high prices in the market.
Versatility: Plume Agate’s diverse color palette and patterns make it a versatile gemstone for jewelry design. It can be fashioned into various shapes and sizes, including cabochons, beads, and carvings, allowing for creativity and innovation in jewelry making.
Historical Significance: Throughout history, agates have been revered for their beauty and perceived mystical properties. Plume Agate, with its distinct plume-like inclusions, has been admired and utilized in adornments and talismans by ancient civilizations.
Plume Agate stands out as a gemstone of exceptional beauty, imbued with both aesthetic and metaphysical significance. Its popularity in the world of gemstones and jewelry continues to endure, captivating admirers with its mesmerizing patterns and timeless allure.
- https://geologyscience.com/gemstone/plume-agate/
1
comment
28
Plume agate glow!
HumbleConservative
Plume Agate is a captivating variety of agate, renowned for its intricate and delicate feather-like inclusions. These mesmerizing formations resemble ethereal plumes or wisps suspended within the stone, creating a stunning visual effect. It belongs to the chalcedony family, characterized by its microcrystalline structure and vibrant colors.
Plume Agate derives its name from the feathery patterns that adorn its surface. These patterns are typically composed of mineral deposits, often in striking hues such as white, cream, pink, or red, contrasting against a translucent or opaque background. These intricate formations are formed through the slow crystallization of silica-rich solutions within cavities or fissures in volcanic rocks.
Each piece of Plume Agate is unique, showcasing a kaleidoscope of colors and patterns. The delicate plumes within the stone evoke a sense of tranquility and beauty, making it a highly sought-after gemstone among collectors and jewelry enthusiasts alike.
Plume Agate holds significant importance in the world of gemstones and jewelry for several reasons:
Aesthetic Appeal: Plume Agate’s captivating patterns and vibrant colors make it a favorite among jewelry designers and collectors. Its unique beauty adds an element of elegance and individuality to any piece of jewelry.
Metaphysical Properties: In addition to its visual allure, Plume Agate is believed to possess metaphysical properties that promote harmony, balance, and emotional healing. It is often used in alternative healing practices and spiritual rituals.
Collectibility: Due to its rarity and unique characteristics, Plume Agate is highly prized by gemstone collectors. Specimens with exceptional plume formations or intense colors can command high prices in the market.
Versatility: Plume Agate’s diverse color palette and patterns make it a versatile gemstone for jewelry design. It can be fashioned into various shapes and sizes, including cabochons, beads, and carvings, allowing for creativity and innovation in jewelry making.
Historical Significance: Throughout history, agates have been revered for their beauty and perceived mystical properties. Plume Agate, with its distinct plume-like inclusions, has been admired and utilized in adornments and talismans by ancient civilizations.
Plume Agate stands out as a gemstone of exceptional beauty, imbued with both aesthetic and metaphysical significance. Its popularity in the world of gemstones and jewelry continues to endure, captivating admirers with its mesmerizing patterns and timeless allure.
- https://geologyscience.com/gemstone/plume-agate/
1
comment
29
Beautiful Opal Glow!
HumbleConservative
Opal is a hydrated amorphous form of silica, with a water content typically between 3 and 21% by weight, most commonly around 6-10%. It's deposited at relatively low temperatures and can be found in the fissures of various rock types, including limonite, sandstone, rhyolite, marl, and basalt. Here's a deeper look into opal:
Types of Opal:
Precious Opal: Known for its "play-of-color," which is an optical phenomenon where colors flash or change as the angle of light or observation changes. This effect is due to the diffraction of light through the microscopic silica spheres within the opal.
Common Opal: Lacks the play-of-color and can come in a variety of colors like white, black, grey, yellow, orange, red, or brown. It's often referred to as "potch" when not gem-quality.
Fire Opal: Typically ranges in color from yellow to orange to red and can be transparent to translucent. Fire opals can exhibit play-of-color, but their name comes from the fiery body color.
Boulder Opal: A type of opal naturally attached to its host rock. It's often cut with the host rock to provide stability and to enhance the visual appeal.
Matrix Opal: The opal fills the cracks and cavities within the host rock, creating a network of opal that's visible on the surface.
Formation:
Primary Opal: Forms through the slow deposition of silica from groundwater in cavities or fractures of rocks.
Secondary Opal: Can form by weathering or alteration of other minerals, often in more superficial environments or through the action of silica-rich waters.
Locations:
Australia: The world's leading source, especially for precious opal, with significant deposits in places like Coober Pedy, Lightning Ridge, and White Cliffs.
Ethiopia: Known for its black opals and more recently discovered opal fields.
Mexico: Famous for fire opals.
Brazil: Produces a variety of opals, including crystal opal.
Properties:
Hardness: Typically ranges between 5.5 to 6.5 on the Mohs scale, though it can be softer if less hydrated or harder if more silica-rich.
Luster: Can range from waxy to resinous to vitreous.
Transparency: Varies from opaque to semi-translucent to transparent.
1
comment
30
Quartz!
HumbleConservative
If we consider the rock in the image to be quartz or a variety of quartz, here's how it might fit:
1. **Chalcedony**: As mentioned earlier, chalcedony is a type of quartz, specifically microcrystalline quartz. Its appearance can range from translucent to opaque, with colors influenced by impurities. The smooth, somewhat waxy luster and the mix of white with yellowish-brown in your rock could indeed fit chalcedony.
2. **Agate**: If there's any subtle banding not clearly visible in the image, it could be agate, a variety of chalcedony known for its fine grain and bright, attractive colors, often with bands or layers.
3. **Opal**: While not typically classified as quartz, opal can be associated with quartz deposits. However, its characteristic feature is its play-of-color, which isn't evident here. If it's common opal or opalite, it might lack this feature but still be related to quartz in geological context.
4. **Quartzite**: This is a metamorphic rock derived from sandstone, which is primarily quartz grains. If your rock has been subjected to metamorphism, the texture and color could be consistent with quartzite, especially if there's been some iron staining or if it's not fully recrystallized.
5. **Milky Quartz**: If the rock has a significant white component, it could be milky quartz, which is quartz with microscopic inclusions that give it a cloudy appearance. Given the context of quartz: -
**Chalcedony or Agate** seem like the most fitting categories for your rock if we're considering varieties of quartz. The smooth texture, potential for banding (even if not clearly visible in the image), and the color variation are all consistent with these forms.
Your rock's appearance aligns well with being a variety of quartz, particularly something like chalcedony or agate, based on its visual characteristics.
31
Iron Stained Quartz!
HumbleConservative
If we consider the rock in the image to be quartz or a variety of quartz, here's how it might fit:
1. **Chalcedony**: As mentioned earlier, chalcedony is a type of quartz, specifically microcrystalline quartz. Its appearance can range from translucent to opaque, with colors influenced by impurities. The smooth, somewhat waxy luster and the mix of white with yellowish-brown in your rock could indeed fit chalcedony.
2. **Agate**: If there's any subtle banding not clearly visible in the image, it could be agate, a variety of chalcedony known for its fine grain and bright, attractive colors, often with bands or layers.
3. **Opal**: While not typically classified as quartz, opal can be associated with quartz deposits. However, its characteristic feature is its play-of-color, which isn't evident here. If it's common opal or opalite, it might lack this feature but still be related to quartz in geological context.
4. **Quartzite**: This is a metamorphic rock derived from sandstone, which is primarily quartz grains. If your rock has been subjected to metamorphism, the texture and color could be consistent with quartzite, especially if there's been some iron staining or if it's not fully recrystallized.
5. **Milky Quartz**: If the rock has a significant white component, it could be milky quartz, which is quartz with microscopic inclusions that give it a cloudy appearance. Given the context of quartz: -
**Chalcedony or Agate** seem like the most fitting categories for your rock if we're considering varieties of quartz. The smooth texture, potential for banding (even if not clearly visible in the image), and the color variation are all consistent with these forms.
Your rock's appearance aligns well with being a variety of quartz, particularly something like chalcedony or agate, based on its visual characteristics.
32
Quartz!
HumbleConservative
If we consider the rock in the image to be quartz or a variety of quartz, here's how it might fit:
1. **Chalcedony**: As mentioned earlier, chalcedony is a type of quartz, specifically microcrystalline quartz. Its appearance can range from translucent to opaque, with colors influenced by impurities. The smooth, somewhat waxy luster and the mix of white with yellowish-brown in your rock could indeed fit chalcedony.
2. **Agate**: If there's any subtle banding not clearly visible in the image, it could be agate, a variety of chalcedony known for its fine grain and bright, attractive colors, often with bands or layers.
3. **Opal**: While not typically classified as quartz, opal can be associated with quartz deposits. However, its characteristic feature is its play-of-color, which isn't evident here. If it's common opal or opalite, it might lack this feature but still be related to quartz in geological context.
4. **Quartzite**: This is a metamorphic rock derived from sandstone, which is primarily quartz grains. If your rock has been subjected to metamorphism, the texture and color could be consistent with quartzite, especially if there's been some iron staining or if it's not fully recrystallized.
5. **Milky Quartz**: If the rock has a significant white component, it could be milky quartz, which is quartz with microscopic inclusions that give it a cloudy appearance. Given the context of quartz: -
**Chalcedony or Agate** seem like the most fitting categories for your rock if we're considering varieties of quartz. The smooth texture, potential for banding (even if not clearly visible in the image), and the color variation are all consistent with these forms.
Your rock's appearance aligns well with being a variety of quartz, particularly something like chalcedony or agate, based on its visual characteristics.
33
Beautiful!
HumbleConservative
The rock in the image appears to be a type of quartzite. Quartzite is a metamorphic rock that forms from the metamorphism of quartz sandstone. It's primarily composed of quartz grains that have been recrystallized under heat and pressure, giving it a hard, durable nature and often a somewhat glassy luster.
The colors and patterns you see, with light colors and darker veins, are typical of quartzite, which often retains some of the original sedimentary layering or banding from its sandstone precursor but in a more compact and crystalline form.
The presence of different shades like white, beige, and possibly some iron staining or other mineral inclusions could give it the varied coloration seen here.
1
comment
34
White/Grey Quartz!
HumbleConservative
If we consider the rock in the image to be quartz or a variety of quartz, here's how it might fit:
1. **Chalcedony**: As mentioned earlier, chalcedony is a type of quartz, specifically microcrystalline quartz. Its appearance can range from translucent to opaque, with colors influenced by impurities. The smooth, somewhat waxy luster and the mix of white with yellowish-brown in your rock could indeed fit chalcedony.
2. **Agate**: If there's any subtle banding not clearly visible in the image, it could be agate, a variety of chalcedony known for its fine grain and bright, attractive colors, often with bands or layers.
3. **Opal**: While not typically classified as quartz, opal can be associated with quartz deposits. However, its characteristic feature is its play-of-color, which isn't evident here. If it's common opal or opalite, it might lack this feature but still be related to quartz in geological context.
4. **Quartzite**: This is a metamorphic rock derived from sandstone, which is primarily quartz grains. If your rock has been subjected to metamorphism, the texture and color could be consistent with quartzite, especially if there's been some iron staining or if it's not fully recrystallized.
5. **Milky Quartz**: If the rock has a significant white component, it could be milky quartz, which is quartz with microscopic inclusions that give it a cloudy appearance. Given the context of quartz: -
**Chalcedony or Agate** seem like the most fitting categories for your rock if we're considering varieties of quartz. The smooth texture, potential for banding (even if not clearly visible in the image), and the color variation are all consistent with these forms.
Your rock's appearance aligns well with being a variety of quartz, particularly something like chalcedony or agate, based on its visual characteristics.
35
Nice!
HumbleConservative
If we consider the rock in the image to be quartz or a variety of quartz, here's how it might fit:
1. **Chalcedony**: As mentioned earlier, chalcedony is a type of quartz, specifically microcrystalline quartz. Its appearance can range from translucent to opaque, with colors influenced by impurities. The smooth, somewhat waxy luster and the mix of white with yellowish-brown in your rock could indeed fit chalcedony.
2. **Agate**: If there's any subtle banding not clearly visible in the image, it could be agate, a variety of chalcedony known for its fine grain and bright, attractive colors, often with bands or layers.
3. **Opal**: While not typically classified as quartz, opal can be associated with quartz deposits. However, its characteristic feature is its play-of-color, which isn't evident here. If it's common opal or opalite, it might lack this feature but still be related to quartz in geological context.
4. **Quartzite**: This is a metamorphic rock derived from sandstone, which is primarily quartz grains. If your rock has been subjected to metamorphism, the texture and color could be consistent with quartzite, especially if there's been some iron staining or if it's not fully recrystallized.
5. **Milky Quartz**: If the rock has a significant white component, it could be milky quartz, which is quartz with microscopic inclusions that give it a cloudy appearance. Given the context of quartz: -
**Chalcedony or Agate** seem like the most fitting categories for your rock if we're considering varieties of quartz. The smooth texture, potential for banding (even if not clearly visible in the image), and the color variation are all consistent with these forms.
Your rock's appearance aligns well with being a variety of quartz, particularly something like chalcedony or agate, based on its visual characteristics.
36
Mostly Quartz!
HumbleConservative
If we consider the rock in the image to be quartz or a variety of quartz, here's how it might fit:
1. **Chalcedony**: As mentioned earlier, chalcedony is a type of quartz, specifically microcrystalline quartz. Its appearance can range from translucent to opaque, with colors influenced by impurities. The smooth, somewhat waxy luster and the mix of white with yellowish-brown in your rock could indeed fit chalcedony.
2. **Agate**: If there's any subtle banding not clearly visible in the image, it could be agate, a variety of chalcedony known for its fine grain and bright, attractive colors, often with bands or layers.
3. **Opal**: While not typically classified as quartz, opal can be associated with quartz deposits. However, its characteristic feature is its play-of-color, which isn't evident here. If it's common opal or opalite, it might lack this feature but still be related to quartz in geological context.
4. **Quartzite**: This is a metamorphic rock derived from sandstone, which is primarily quartz grains. If your rock has been subjected to metamorphism, the texture and color could be consistent with quartzite, especially if there's been some iron staining or if it's not fully recrystallized.
5. **Milky Quartz**: If the rock has a significant white component, it could be milky quartz, which is quartz with microscopic inclusions that give it a cloudy appearance. Given the context of quartz: -
**Chalcedony or Agate** seem like the most fitting categories for your rock if we're considering varieties of quartz. The smooth texture, potential for banding (even if not clearly visible in the image), and the color variation are all consistent with these forms.
Your rock's appearance aligns well with being a variety of quartz, particularly something like chalcedony or agate, based on its visual characteristics.
37
Beautiful Quartz!
HumbleConservative
If we consider the rock in the image to be quartz or a variety of quartz, here's how it might fit:
1. **Chalcedony**: As mentioned earlier, chalcedony is a type of quartz, specifically microcrystalline quartz. Its appearance can range from translucent to opaque, with colors influenced by impurities. The smooth, somewhat waxy luster and the mix of white with yellowish-brown in your rock could indeed fit chalcedony.
2. **Agate**: If there's any subtle banding not clearly visible in the image, it could be agate, a variety of chalcedony known for its fine grain and bright, attractive colors, often with bands or layers.
3. **Opal**: While not typically classified as quartz, opal can be associated with quartz deposits. However, its characteristic feature is its play-of-color, which isn't evident here. If it's common opal or opalite, it might lack this feature but still be related to quartz in geological context.
4. **Quartzite**: This is a metamorphic rock derived from sandstone, which is primarily quartz grains. If your rock has been subjected to metamorphism, the texture and color could be consistent with quartzite, especially if there's been some iron staining or if it's not fully recrystallized.
5. **Milky Quartz**: If the rock has a significant white component, it could be milky quartz, which is quartz with microscopic inclusions that give it a cloudy appearance. Given the context of quartz: -
**Chalcedony or Agate** seem like the most fitting categories for your rock if we're considering varieties of quartz. The smooth texture, potential for banding (even if not clearly visible in the image), and the color variation are all consistent with these forms.
Your rock's appearance aligns well with being a variety of quartz, particularly something like chalcedony or agate, based on its visual characteristics.
38
Quartz Nugget!
HumbleConservative
If we consider the rock in the image to be quartz or a variety of quartz, here's how it might fit:
1. **Chalcedony**: As mentioned earlier, chalcedony is a type of quartz, specifically microcrystalline quartz. Its appearance can range from translucent to opaque, with colors influenced by impurities. The smooth, somewhat waxy luster and the mix of white with yellowish-brown in your rock could indeed fit chalcedony.
2. **Agate**: If there's any subtle banding not clearly visible in the image, it could be agate, a variety of chalcedony known for its fine grain and bright, attractive colors, often with bands or layers.
3. **Opal**: While not typically classified as quartz, opal can be associated with quartz deposits. However, its characteristic feature is its play-of-color, which isn't evident here. If it's common opal or opalite, it might lack this feature but still be related to quartz in geological context.
4. **Quartzite**: This is a metamorphic rock derived from sandstone, which is primarily quartz grains. If your rock has been subjected to metamorphism, the texture and color could be consistent with quartzite, especially if there's been some iron staining or if it's not fully recrystallized.
5. **Milky Quartz**: If the rock has a significant white component, it could be milky quartz, which is quartz with microscopic inclusions that give it a cloudy appearance. Given the context of quartz: -
**Chalcedony or Agate** seem like the most fitting categories for your rock if we're considering varieties of quartz. The smooth texture, potential for banding (even if not clearly visible in the image), and the color variation are all consistent with these forms.
Your rock's appearance aligns well with being a variety of quartz, particularly something like chalcedony or agate, based on its visual characteristics.
39
Beauty!
HumbleConservative
The rock in the image appears to be a type of chalcedony, possibly an agate or a similar variety. Here's why:
1. **Coloration and Banding**: The rock has a predominantly white or light gray color with some yellowish-brown inclusions. This kind of coloration and banding is typical for agates, which are a variety of chalcedony.
2. **Translucency**: Chalcedony, including agate, often has a translucent quality, which seems to be present in parts of this rock.
3. **Texture**: The rock's texture looks somewhat waxy or greasy, which is characteristic of chalcedony due to its fine-grained silica composition.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish-brown areas could be iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which are common in agates and give them their varied colors. However, without specific tests like a hardness test, streak test, or chemical analysis, this identification remains speculative. For a more precise identification: - **Hardness Test**: Chalcedony has a hardness of around 7 on the Mohs scale, meaning it should scratch glass but not be scratched by a knife. - **Streak Test**: The streak of chalcedony (if it could be powdered) would typically be white or colorless. - **Microscopic Analysis**: Looking at thin sections under a microscope could reveal the mineral composition more clearly. - **Consulting a Geologist or Using Spectroscopy**: For a definitive identification, especially if this rock might be of value or scientific interest.
40
Chalcedony?
HumbleConservative
The rock in the image appears to be a type of chalcedony, possibly an agate or a similar variety. Here's why:
1. **Coloration and Banding**: The rock has a predominantly white or light gray color with some yellowish-brown inclusions. This kind of coloration and banding is typical for agates, which are a variety of chalcedony.
2. **Translucency**: Chalcedony, including agate, often has a translucent quality, which seems to be present in parts of this rock.
3. **Texture**: The rock's texture looks somewhat waxy or greasy, which is characteristic of chalcedony due to its fine-grained silica composition.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish-brown areas could be iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which are common in agates and give them their varied colors. However, without specific tests like a hardness test, streak test, or chemical analysis, this identification remains speculative. For a more precise identification: - **Hardness Test**: Chalcedony has a hardness of around 7 on the Mohs scale, meaning it should scratch glass but not be scratched by a knife. - **Streak Test**: The streak of chalcedony (if it could be powdered) would typically be white or colorless. - **Microscopic Analysis**: Looking at thin sections under a microscope could reveal the mineral composition more clearly. - **Consulting a Geologist or Using Spectroscopy**: For a definitive identification, especially if this rock might be of value or scientific interest.
41
Purdy!
HumbleConservative
If we consider the rock in the image to be quartz or a variety of quartz, here's how it might fit:
1. **Chalcedony**: As mentioned earlier, chalcedony is a type of quartz, specifically microcrystalline quartz. Its appearance can range from translucent to opaque, with colors influenced by impurities. The smooth, somewhat waxy luster and the mix of white with yellowish-brown in your rock could indeed fit chalcedony.
2. **Agate**: If there's any subtle banding not clearly visible in the image, it could be agate, a variety of chalcedony known for its fine grain and bright, attractive colors, often with bands or layers.
3. **Opal**: While not typically classified as quartz, opal can be associated with quartz deposits. However, its characteristic feature is its play-of-color, which isn't evident here. If it's common opal or opalite, it might lack this feature but still be related to quartz in geological context.
4. **Quartzite**: This is a metamorphic rock derived from sandstone, which is primarily quartz grains. If your rock has been subjected to metamorphism, the texture and color could be consistent with quartzite, especially if there's been some iron staining or if it's not fully recrystallized.
5. **Milky Quartz**: If the rock has a significant white component, it could be milky quartz, which is quartz with microscopic inclusions that give it a cloudy appearance. Given the context of quartz: -
**Chalcedony or Agate** seem like the most fitting categories for your rock if we're considering varieties of quartz. The smooth texture, potential for banding (even if not clearly visible in the image), and the color variation are all consistent with these forms.
Your rock's appearance aligns well with being a variety of quartz, particularly something like chalcedony or agate, based on its visual characteristics.
42
Chalcedony!
HumbleConservative
The rock in the image appears to be a type of chalcedony, possibly an agate or a similar variety. Here's why:
1. **Coloration and Banding**: The rock has a predominantly white or light gray color with some yellowish-brown inclusions. This kind of coloration and banding is typical for agates, which are a variety of chalcedony.
2. **Translucency**: Chalcedony, including agate, often has a translucent quality, which seems to be present in parts of this rock.
3. **Texture**: The rock's texture looks somewhat waxy or greasy, which is characteristic of chalcedony due to its fine-grained silica composition.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish-brown areas could be iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which are common in agates and give them their varied colors. However, without specific tests like a hardness test, streak test, or chemical analysis, this identification remains speculative. For a more precise identification: - **Hardness Test**: Chalcedony has a hardness of around 7 on the Mohs scale, meaning it should scratch glass but not be scratched by a knife. - **Streak Test**: The streak of chalcedony (if it could be powdered) would typically be white or colorless. - **Microscopic Analysis**: Looking at thin sections under a microscope could reveal the mineral composition more clearly. - **Consulting a Geologist or Using Spectroscopy**: For a definitive identification, especially if this rock might be of value or scientific interest.
43
Iron Stained!
HumbleConservative
If we consider the rock in the image to be quartz or a variety of quartz, here's how it might fit:
1. **Chalcedony**: As mentioned earlier, chalcedony is a type of quartz, specifically microcrystalline quartz. Its appearance can range from translucent to opaque, with colors influenced by impurities. The smooth, somewhat waxy luster and the mix of white with yellowish-brown in your rock could indeed fit chalcedony.
2. **Agate**: If there's any subtle banding not clearly visible in the image, it could be agate, a variety of chalcedony known for its fine grain and bright, attractive colors, often with bands or layers.
3. **Opal**: While not typically classified as quartz, opal can be associated with quartz deposits. However, its characteristic feature is its play-of-color, which isn't evident here. If it's common opal or opalite, it might lack this feature but still be related to quartz in geological context.
4. **Quartzite**: This is a metamorphic rock derived from sandstone, which is primarily quartz grains. If your rock has been subjected to metamorphism, the texture and color could be consistent with quartzite, especially if there's been some iron staining or if it's not fully recrystallized.
5. **Milky Quartz**: If the rock has a significant white component, it could be milky quartz, which is quartz with microscopic inclusions that give it a cloudy appearance. Given the context of quartz: -
**Chalcedony or Agate** seem like the most fitting categories for your rock if we're considering varieties of quartz. The smooth texture, potential for banding (even if not clearly visible in the image), and the color variation are all consistent with these forms.
Your rock's appearance aligns well with being a variety of quartz, particularly something like chalcedony or agate, based on its visual characteristics.
44
Quartz or Chalcedony!?!?
HumbleConservative
If we consider the rock in the image to be quartz or a variety of quartz, here's how it might fit:
1. **Chalcedony**: As mentioned earlier, chalcedony is a type of quartz, specifically microcrystalline quartz. Its appearance can range from translucent to opaque, with colors influenced by impurities. The smooth, somewhat waxy luster and the mix of white with yellowish-brown in your rock could indeed fit chalcedony.
2. **Agate**: If there's any subtle banding not clearly visible in the image, it could be agate, a variety of chalcedony known for its fine grain and bright, attractive colors, often with bands or layers.
3. **Opal**: While not typically classified as quartz, opal can be associated with quartz deposits. However, its characteristic feature is its play-of-color, which isn't evident here. If it's common opal or opalite, it might lack this feature but still be related to quartz in geological context.
4. **Quartzite**: This is a metamorphic rock derived from sandstone, which is primarily quartz grains. If your rock has been subjected to metamorphism, the texture and color could be consistent with quartzite, especially if there's been some iron staining or if it's not fully recrystallized.
5. **Milky Quartz**: If the rock has a significant white component, it could be milky quartz, which is quartz with microscopic inclusions that give it a cloudy appearance. Given the context of quartz: -
**Chalcedony or Agate** seem like the most fitting categories for your rock if we're considering varieties of quartz. The smooth texture, potential for banding (even if not clearly visible in the image), and the color variation are all consistent with these forms.
Your rock's appearance aligns well with being a variety of quartz, particularly something like chalcedony or agate, based on its visual characteristics.
45
Chalcedony from a Thunderegg!
HumbleConservative
The rock in the image appears to be a type of chalcedony, possibly an agate or a similar variety. Here's why:
1. **Coloration and Banding**: The rock has a predominantly white or light gray color with some yellowish-brown inclusions. This kind of coloration and banding is typical for agates, which are a variety of chalcedony.
2. **Translucency**: Chalcedony, including agate, often has a translucent quality, which seems to be present in parts of this rock.
3. **Texture**: The rock's texture looks somewhat waxy or greasy, which is characteristic of chalcedony due to its fine-grained silica composition.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish-brown areas could be iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which are common in agates and give them their varied colors. However, without specific tests like a hardness test, streak test, or chemical analysis, this identification remains speculative. For a more precise identification: - **Hardness Test**: Chalcedony has a hardness of around 7 on the Mohs scale, meaning it should scratch glass but not be scratched by a knife. - **Streak Test**: The streak of chalcedony (if it could be powdered) would typically be white or colorless. - **Microscopic Analysis**: Looking at thin sections under a microscope could reveal the mineral composition more clearly. - **Consulting a Geologist or Using Spectroscopy**: For a definitive identification, especially if this rock might be of value or scientific interest.
46
Quartz +!
HumbleConservative
@RyanzRocks #noob #rockhound #rockformation #sandstone #tumbling #agates #rocks #rockhounders #rockstructure #metamorphicrocks #metamorphic #igneousrocks #igneous #quartz #quartzite #geology #nodules #minerals #crystals #glowrocks #idahorockhunting #idahogems #rockcutting #thundereggs #chalcedony #opal #lavarock #rigidtools #ryobitools #riverrocks #translucentrocks #translucent #rockgarden #flow #vevortools #jasper #granite #caves #marble #carnelian #gneiss #limestone #calcite #gold #silver #botryoidal #geodes
47
Chalcedony!
HumbleConservative
If we consider the rock in the image to be quartz or a variety of quartz, here's how it might fit:
1. **Chalcedony**: As mentioned earlier, chalcedony is a type of quartz, specifically microcrystalline quartz. Its appearance can range from translucent to opaque, with colors influenced by impurities. The smooth, somewhat waxy luster and the mix of white with yellowish-brown in your rock could indeed fit chalcedony.
2. **Agate**: If there's any subtle banding not clearly visible in the image, it could be agate, a variety of chalcedony known for its fine grain and bright, attractive colors, often with bands or layers.
3. **Opal**: While not typically classified as quartz, opal can be associated with quartz deposits. However, its characteristic feature is its play-of-color, which isn't evident here. If it's common opal or opalite, it might lack this feature but still be related to quartz in geological context.
4. **Quartzite**: This is a metamorphic rock derived from sandstone, which is primarily quartz grains. If your rock has been subjected to metamorphism, the texture and color could be consistent with quartzite, especially if there's been some iron staining or if it's not fully recrystallized.
5. **Milky Quartz**: If the rock has a significant white component, it could be milky quartz, which is quartz with microscopic inclusions that give it a cloudy appearance. Given the context of quartz: -
**Chalcedony or Agate** seem like the most fitting categories for your rock if we're considering varieties of quartz. The smooth texture, potential for banding (even if not clearly visible in the image), and the color variation are all consistent with these forms.
Your rock's appearance aligns well with being a variety of quartz, particularly something like chalcedony or agate, based on its visual characteristics.
48
Rose Quartz!
HumbleConservative
If we consider the rock in the image to be quartz or a variety of quartz, here's how it might fit:
1. **Chalcedony**: As mentioned earlier, chalcedony is a type of quartz, specifically microcrystalline quartz. Its appearance can range from translucent to opaque, with colors influenced by impurities. The smooth, somewhat waxy luster and the mix of white with yellowish-brown in your rock could indeed fit chalcedony.
2. **Agate**: If there's any subtle banding not clearly visible in the image, it could be agate, a variety of chalcedony known for its fine grain and bright, attractive colors, often with bands or layers.
3. **Opal**: While not typically classified as quartz, opal can be associated with quartz deposits. However, its characteristic feature is its play-of-color, which isn't evident here. If it's common opal or opalite, it might lack this feature but still be related to quartz in geological context.
4. **Quartzite**: This is a metamorphic rock derived from sandstone, which is primarily quartz grains. If your rock has been subjected to metamorphism, the texture and color could be consistent with quartzite, especially if there's been some iron staining or if it's not fully recrystallized.
5. **Milky Quartz**: If the rock has a significant white component, it could be milky quartz, which is quartz with microscopic inclusions that give it a cloudy appearance. Given the context of quartz: -
**Chalcedony or Agate** seem like the most fitting categories for your rock if we're considering varieties of quartz. The smooth texture, potential for banding (even if not clearly visible in the image), and the color variation are all consistent with these forms.
Your rock's appearance aligns well with being a variety of quartz, particularly something like chalcedony or agate, based on its visual characteristics.
49
Yellow Quartz!
HumbleConservative
If we consider the rock in the image to be quartz or a variety of quartz, here's how it might fit:
1. **Chalcedony**: As mentioned earlier, chalcedony is a type of quartz, specifically microcrystalline quartz. Its appearance can range from translucent to opaque, with colors influenced by impurities. The smooth, somewhat waxy luster and the mix of white with yellowish-brown in your rock could indeed fit chalcedony.
2. **Agate**: If there's any subtle banding not clearly visible in the image, it could be agate, a variety of chalcedony known for its fine grain and bright, attractive colors, often with bands or layers.
3. **Opal**: While not typically classified as quartz, opal can be associated with quartz deposits. However, its characteristic feature is its play-of-color, which isn't evident here. If it's common opal or opalite, it might lack this feature but still be related to quartz in geological context.
4. **Quartzite**: This is a metamorphic rock derived from sandstone, which is primarily quartz grains. If your rock has been subjected to metamorphism, the texture and color could be consistent with quartzite, especially if there's been some iron staining or if it's not fully recrystallized.
5. **Milky Quartz**: If the rock has a significant white component, it could be milky quartz, which is quartz with microscopic inclusions that give it a cloudy appearance. Given the context of quartz: -
**Chalcedony or Agate** seem like the most fitting categories for your rock if we're considering varieties of quartz. The smooth texture, potential for banding (even if not clearly visible in the image), and the color variation are all consistent with these forms.
Your rock's appearance aligns well with being a variety of quartz, particularly something like chalcedony or agate, based on its visual characteristics.
50
Quartz n' Iron!
HumbleConservative
If we consider the rock in the image to be quartz or a variety of quartz, here's how it might fit:
1. **Chalcedony**: As mentioned earlier, chalcedony is a type of quartz, specifically microcrystalline quartz. Its appearance can range from translucent to opaque, with colors influenced by impurities. The smooth, somewhat waxy luster and the mix of white with yellowish-brown in your rock could indeed fit chalcedony.
2. **Agate**: If there's any subtle banding not clearly visible in the image, it could be agate, a variety of chalcedony known for its fine grain and bright, attractive colors, often with bands or layers.
3. **Opal**: While not typically classified as quartz, opal can be associated with quartz deposits. However, its characteristic feature is its play-of-color, which isn't evident here. If it's common opal or opalite, it might lack this feature but still be related to quartz in geological context.
4. **Quartzite**: This is a metamorphic rock derived from sandstone, which is primarily quartz grains. If your rock has been subjected to metamorphism, the texture and color could be consistent with quartzite, especially if there's been some iron staining or if it's not fully recrystallized.
5. **Milky Quartz**: If the rock has a significant white component, it could be milky quartz, which is quartz with microscopic inclusions that give it a cloudy appearance. Given the context of quartz: -
**Chalcedony or Agate** seem like the most fitting categories for your rock if we're considering varieties of quartz. The smooth texture, potential for banding (even if not clearly visible in the image), and the color variation are all consistent with these forms.
Your rock's appearance aligns well with being a variety of quartz, particularly something like chalcedony or agate, based on its visual characteristics.
51
Beautiful Glow Nodule!
HumbleConservative
If we consider the rock in the image to be quartz or a variety of quartz, here's how it might fit:
1. **Chalcedony**: As mentioned earlier, chalcedony is a type of quartz, specifically microcrystalline quartz. Its appearance can range from translucent to opaque, with colors influenced by impurities. The smooth, somewhat waxy luster and the mix of white with yellowish-brown in your rock could indeed fit chalcedony.
2. **Agate**: If there's any subtle banding not clearly visible in the image, it could be agate, a variety of chalcedony known for its fine grain and bright, attractive colors, often with bands or layers.
3. **Opal**: While not typically classified as quartz, opal can be associated with quartz deposits. However, its characteristic feature is its play-of-color, which isn't evident here. If it's common opal or opalite, it might lack this feature but still be related to quartz in geological context.
4. **Quartzite**: This is a metamorphic rock derived from sandstone, which is primarily quartz grains. If your rock has been subjected to metamorphism, the texture and color could be consistent with quartzite, especially if there's been some iron staining or if it's not fully recrystallized.
5. **Milky Quartz**: If the rock has a significant white component, it could be milky quartz, which is quartz with microscopic inclusions that give it a cloudy appearance. Given the context of quartz: -
**Chalcedony or Agate** seem like the most fitting categories for your rock if we're considering varieties of quartz. The smooth texture, potential for banding (even if not clearly visible in the image), and the color variation are all consistent with these forms.
Your rock's appearance aligns well with being a variety of quartz, particularly something like chalcedony or agate, based on its visual characteristics.
52
Big ol' Quartzite Glowrock!
HumbleConservative
The rock in the image appears to be a type of quartzite. Quartzite is a metamorphic rock that forms from the metamorphism of quartz sandstone. It's primarily composed of quartz grains that have been recrystallized under heat and pressure, giving it a hard, durable nature and often a somewhat glassy luster.
The colors and patterns you see, with light colors and darker veins, are typical of quartzite, which often retains some of the original sedimentary layering or banding from its sandstone precursor but in a more compact and crystalline form.
The presence of different shades like white, beige, and possibly some iron staining or other mineral inclusions could give it the varied coloration seen here.
53
Yellow Quartz Glow!
HumbleConservative
If we consider the rock in the image to be quartz or a variety of quartz, here's how it might fit:
1. **Chalcedony**: As mentioned earlier, chalcedony is a type of quartz, specifically microcrystalline quartz. Its appearance can range from translucent to opaque, with colors influenced by impurities. The smooth, somewhat waxy luster and the mix of white with yellowish-brown in your rock could indeed fit chalcedony.
2. **Agate**: If there's any subtle banding not clearly visible in the image, it could be agate, a variety of chalcedony known for its fine grain and bright, attractive colors, often with bands or layers.
3. **Opal**: While not typically classified as quartz, opal can be associated with quartz deposits. However, its characteristic feature is its play-of-color, which isn't evident here. If it's common opal or opalite, it might lack this feature but still be related to quartz in geological context.
4. **Quartzite**: This is a metamorphic rock derived from sandstone, which is primarily quartz grains. If your rock has been subjected to metamorphism, the texture and color could be consistent with quartzite, especially if there's been some iron staining or if it's not fully recrystallized.
5. **Milky Quartz**: If the rock has a significant white component, it could be milky quartz, which is quartz with microscopic inclusions that give it a cloudy appearance. Given the context of quartz: -
**Chalcedony or Agate** seem like the most fitting categories for your rock if we're considering varieties of quartz. The smooth texture, potential for banding (even if not clearly visible in the image), and the color variation are all consistent with these forms.
Your rock's appearance aligns well with being a variety of quartz, particularly something like chalcedony or agate, based on its visual characteristics.
54
Beautiful Aqua Marine Glow!
HumbleConservative
This rock appears to be a piece of **malachite**, possibly with some chrysocolla or other copper minerals. Here's why:
1. **Coloration**: The green color is characteristic of malachite, which is a copper carbonate hydroxide mineral. The blue-green hue is typical for malachite when it's mixed with chrysocolla or other copper minerals. 2. **Banding and Texture**: Malachite often forms in banded patterns due to its fibrous crystal structure. The rock in the image shows some banding and a waxy to vitreous luster, which is consistent with malachite.
3. **Translucency**: Parts of the rock appear somewhat translucent, which can be a feature of malachite, especially in thinner sections.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish or brownish areas could be due to iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which can sometimes be found associated with malachite.
However, without specific tests like a hardness test, streak test, or chemical analysis, this identification remains speculative. For a more precise identification: - **Hardness Test**: Malachite has a hardness of around 3.5 to 4 on the Mohs scale, meaning it can be scratched by a knife but not by a fingernail. - **Streak Test**: The streak of malachite would be green, which can help distinguish it from other minerals. - **Acid Test**: Malachite will effervesce (fizz) in hydrochloric acid due to its carbonate content.
55
Beautiful Aqua Blue/Green Marine!
HumbleConservative
This rock appears to be a piece of **malachite**, possibly with some chrysocolla or other copper minerals. Here's why:
1. **Coloration**: The green color is characteristic of malachite, which is a copper carbonate hydroxide mineral. The blue-green hue is typical for malachite when it's mixed with chrysocolla or other copper minerals. 2. **Banding and Texture**: Malachite often forms in banded patterns due to its fibrous crystal structure. The rock in the image shows some banding and a waxy to vitreous luster, which is consistent with malachite.
3. **Translucency**: Parts of the rock appear somewhat translucent, which can be a feature of malachite, especially in thinner sections.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish or brownish areas could be due to iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which can sometimes be found associated with malachite.
However, without specific tests like a hardness test, streak test, or chemical analysis, this identification remains speculative. For a more precise identification: - **Hardness Test**: Malachite has a hardness of around 3.5 to 4 on the Mohs scale, meaning it can be scratched by a knife but not by a fingernail. - **Streak Test**: The streak of malachite would be green, which can help distinguish it from other minerals. - **Acid Test**: Malachite will effervesce (fizz) in hydrochloric acid due to its carbonate content.
1
comment
56
Pink Quartz!
HumbleConservative
If we consider the rock in the image to be quartz or a variety of quartz, here's how it might fit:
1. **Chalcedony**: As mentioned earlier, chalcedony is a type of quartz, specifically microcrystalline quartz. Its appearance can range from translucent to opaque, with colors influenced by impurities. The smooth, somewhat waxy luster and the mix of white with yellowish-brown in your rock could indeed fit chalcedony.
2. **Agate**: If there's any subtle banding not clearly visible in the image, it could be agate, a variety of chalcedony known for its fine grain and bright, attractive colors, often with bands or layers.
3. **Opal**: While not typically classified as quartz, opal can be associated with quartz deposits. However, its characteristic feature is its play-of-color, which isn't evident here. If it's common opal or opalite, it might lack this feature but still be related to quartz in geological context.
4. **Quartzite**: This is a metamorphic rock derived from sandstone, which is primarily quartz grains. If your rock has been subjected to metamorphism, the texture and color could be consistent with quartzite, especially if there's been some iron staining or if it's not fully recrystallized.
5. **Milky Quartz**: If the rock has a significant white component, it could be milky quartz, which is quartz with microscopic inclusions that give it a cloudy appearance. Given the context of quartz: -
**Chalcedony or Agate** seem like the most fitting categories for your rock if we're considering varieties of quartz. The smooth texture, potential for banding (even if not clearly visible in the image), and the color variation are all consistent with these forms.
Your rock's appearance aligns well with being a variety of quartz, particularly something like chalcedony or agate, based on its visual characteristics.
1
comment
57
Beautiful Glow Quartz!
HumbleConservative
If we consider the rock in the image to be quartz or a variety of quartz, here's how it might fit:
1. **Chalcedony**: As mentioned earlier, chalcedony is a type of quartz, specifically microcrystalline quartz. Its appearance can range from translucent to opaque, with colors influenced by impurities. The smooth, somewhat waxy luster and the mix of white with yellowish-brown in your rock could indeed fit chalcedony.
2. **Agate**: If there's any subtle banding not clearly visible in the image, it could be agate, a variety of chalcedony known for its fine grain and bright, attractive colors, often with bands or layers.
3. **Opal**: While not typically classified as quartz, opal can be associated with quartz deposits. However, its characteristic feature is its play-of-color, which isn't evident here. If it's common opal or opalite, it might lack this feature but still be related to quartz in geological context.
4. **Quartzite**: This is a metamorphic rock derived from sandstone, which is primarily quartz grains. If your rock has been subjected to metamorphism, the texture and color could be consistent with quartzite, especially if there's been some iron staining or if it's not fully recrystallized.
5. **Milky Quartz**: If the rock has a significant white component, it could be milky quartz, which is quartz with microscopic inclusions that give it a cloudy appearance. Given the context of quartz: -
**Chalcedony or Agate** seem like the most fitting categories for your rock if we're considering varieties of quartz. The smooth texture, potential for banding (even if not clearly visible in the image), and the color variation are all consistent with these forms.
Your rock's appearance aligns well with being a variety of quartz, particularly something like chalcedony or agate, based on its visual characteristics.
58
Iron Stained Quartz!
HumbleConservative
If we consider the rock in the image to be quartz or a variety of quartz, here's how it might fit:
1. **Chalcedony**: As mentioned earlier, chalcedony is a type of quartz, specifically microcrystalline quartz. Its appearance can range from translucent to opaque, with colors influenced by impurities. The smooth, somewhat waxy luster and the mix of white with yellowish-brown in your rock could indeed fit chalcedony.
2. **Agate**: If there's any subtle banding not clearly visible in the image, it could be agate, a variety of chalcedony known for its fine grain and bright, attractive colors, often with bands or layers.
3. **Opal**: While not typically classified as quartz, opal can be associated with quartz deposits. However, its characteristic feature is its play-of-color, which isn't evident here. If it's common opal or opalite, it might lack this feature but still be related to quartz in geological context.
4. **Quartzite**: This is a metamorphic rock derived from sandstone, which is primarily quartz grains. If your rock has been subjected to metamorphism, the texture and color could be consistent with quartzite, especially if there's been some iron staining or if it's not fully recrystallized.
5. **Milky Quartz**: If the rock has a significant white component, it could be milky quartz, which is quartz with microscopic inclusions that give it a cloudy appearance. Given the context of quartz: -
**Chalcedony or Agate** seem like the most fitting categories for your rock if we're considering varieties of quartz. The smooth texture, potential for banding (even if not clearly visible in the image), and the color variation are all consistent with these forms.
Your rock's appearance aligns well with being a variety of quartz, particularly something like chalcedony or agate, based on its visual characteristics.
59
Beautiful Yellow Quartz!
HumbleConservative
If we consider the rock in the image to be quartz or a variety of quartz, here's how it might fit:
1. **Chalcedony**: As mentioned earlier, chalcedony is a type of quartz, specifically microcrystalline quartz. Its appearance can range from translucent to opaque, with colors influenced by impurities. The smooth, somewhat waxy luster and the mix of white with yellowish-brown in your rock could indeed fit chalcedony.
2. **Agate**: If there's any subtle banding not clearly visible in the image, it could be agate, a variety of chalcedony known for its fine grain and bright, attractive colors, often with bands or layers.
3. **Opal**: While not typically classified as quartz, opal can be associated with quartz deposits. However, its characteristic feature is its play-of-color, which isn't evident here. If it's common opal or opalite, it might lack this feature but still be related to quartz in geological context.
4. **Quartzite**: This is a metamorphic rock derived from sandstone, which is primarily quartz grains. If your rock has been subjected to metamorphism, the texture and color could be consistent with quartzite, especially if there's been some iron staining or if it's not fully recrystallized.
5. **Milky Quartz**: If the rock has a significant white component, it could be milky quartz, which is quartz with microscopic inclusions that give it a cloudy appearance. Given the context of quartz: -
**Chalcedony or Agate** seem like the most fitting categories for your rock if we're considering varieties of quartz. The smooth texture, potential for banding (even if not clearly visible in the image), and the color variation are all consistent with these forms.
Your rock's appearance aligns well with being a variety of quartz, particularly something like chalcedony or agate, based on its visual characteristics.
1
comment
60
Yellow Agate Nodule!
HumbleConservative
If we consider the rock in the image to be quartz or a variety of quartz, here's how it might fit:
1. **Chalcedony**: As mentioned earlier, chalcedony is a type of quartz, specifically microcrystalline quartz. Its appearance can range from translucent to opaque, with colors influenced by impurities. The smooth, somewhat waxy luster and the mix of white with yellowish-brown in your rock could indeed fit chalcedony.
2. **Agate**: If there's any subtle banding not clearly visible in the image, it could be agate, a variety of chalcedony known for its fine grain and bright, attractive colors, often with bands or layers.
3. **Opal**: While not typically classified as quartz, opal can be associated with quartz deposits. However, its characteristic feature is its play-of-color, which isn't evident here. If it's common opal or opalite, it might lack this feature but still be related to quartz in geological context.
4. **Quartzite**: This is a metamorphic rock derived from sandstone, which is primarily quartz grains. If your rock has been subjected to metamorphism, the texture and color could be consistent with quartzite, especially if there's been some iron staining or if it's not fully recrystallized.
5. **Milky Quartz**: If the rock has a significant white component, it could be milky quartz, which is quartz with microscopic inclusions that give it a cloudy appearance. Given the context of quartz: -
**Chalcedony or Agate** seem like the most fitting categories for your rock if we're considering varieties of quartz. The smooth texture, potential for banding (even if not clearly visible in the image), and the color variation are all consistent with these forms.
Your rock's appearance aligns well with being a variety of quartz, particularly something like chalcedony or agate, based on its visual characteristics.
61
White Iron Stained Quartz!
HumbleConservative
If we consider the rock in the image to be quartz or a variety of quartz, here's how it might fit:
1. **Chalcedony**: As mentioned earlier, chalcedony is a type of quartz, specifically microcrystalline quartz. Its appearance can range from translucent to opaque, with colors influenced by impurities. The smooth, somewhat waxy luster and the mix of white with yellowish-brown in your rock could indeed fit chalcedony.
2. **Agate**: If there's any subtle banding not clearly visible in the image, it could be agate, a variety of chalcedony known for its fine grain and bright, attractive colors, often with bands or layers.
3. **Opal**: While not typically classified as quartz, opal can be associated with quartz deposits. However, its characteristic feature is its play-of-color, which isn't evident here. If it's common opal or opalite, it might lack this feature but still be related to quartz in geological context.
4. **Quartzite**: This is a metamorphic rock derived from sandstone, which is primarily quartz grains. If your rock has been subjected to metamorphism, the texture and color could be consistent with quartzite, especially if there's been some iron staining or if it's not fully recrystallized.
5. **Milky Quartz**: If the rock has a significant white component, it could be milky quartz, which is quartz with microscopic inclusions that give it a cloudy appearance. Given the context of quartz: -
**Chalcedony or Agate** seem like the most fitting categories for your rock if we're considering varieties of quartz. The smooth texture, potential for banding (even if not clearly visible in the image), and the color variation are all consistent with these forms.
Your rock's appearance aligns well with being a variety of quartz, particularly something like chalcedony or agate, based on its visual characteristics.
62
White Quartz!
HumbleConservative
If we consider the rock in the image to be quartz or a variety of quartz, here's how it might fit:
1. **Chalcedony**: As mentioned earlier, chalcedony is a type of quartz, specifically microcrystalline quartz. Its appearance can range from translucent to opaque, with colors influenced by impurities. The smooth, somewhat waxy luster and the mix of white with yellowish-brown in your rock could indeed fit chalcedony.
2. **Agate**: If there's any subtle banding not clearly visible in the image, it could be agate, a variety of chalcedony known for its fine grain and bright, attractive colors, often with bands or layers.
3. **Opal**: While not typically classified as quartz, opal can be associated with quartz deposits. However, its characteristic feature is its play-of-color, which isn't evident here. If it's common opal or opalite, it might lack this feature but still be related to quartz in geological context.
4. **Quartzite**: This is a metamorphic rock derived from sandstone, which is primarily quartz grains. If your rock has been subjected to metamorphism, the texture and color could be consistent with quartzite, especially if there's been some iron staining or if it's not fully recrystallized.
5. **Milky Quartz**: If the rock has a significant white component, it could be milky quartz, which is quartz with microscopic inclusions that give it a cloudy appearance. Given the context of quartz: -
**Chalcedony or Agate** seem like the most fitting categories for your rock if we're considering varieties of quartz. The smooth texture, potential for banding (even if not clearly visible in the image), and the color variation are all consistent with these forms.
Your rock's appearance aligns well with being a variety of quartz, particularly something like chalcedony or agate, based on its visual characteristics.
63
Iron Stained Quartz!
HumbleConservative
If we consider the rock in the image to be quartz or a variety of quartz, here's how it might fit:
1. **Chalcedony**: As mentioned earlier, chalcedony is a type of quartz, specifically microcrystalline quartz. Its appearance can range from translucent to opaque, with colors influenced by impurities. The smooth, somewhat waxy luster and the mix of white with yellowish-brown in your rock could indeed fit chalcedony.
2. **Agate**: If there's any subtle banding not clearly visible in the image, it could be agate, a variety of chalcedony known for its fine grain and bright, attractive colors, often with bands or layers.
3. **Opal**: While not typically classified as quartz, opal can be associated with quartz deposits. However, its characteristic feature is its play-of-color, which isn't evident here. If it's common opal or opalite, it might lack this feature but still be related to quartz in geological context.
4. **Quartzite**: This is a metamorphic rock derived from sandstone, which is primarily quartz grains. If your rock has been subjected to metamorphism, the texture and color could be consistent with quartzite, especially if there's been some iron staining or if it's not fully recrystallized.
5. **Milky Quartz**: If the rock has a significant white component, it could be milky quartz, which is quartz with microscopic inclusions that give it a cloudy appearance. Given the context of quartz: -
**Chalcedony or Agate** seem like the most fitting categories for your rock if we're considering varieties of quartz. The smooth texture, potential for banding (even if not clearly visible in the image), and the color variation are all consistent with these forms.
Your rock's appearance aligns well with being a variety of quartz, particularly something like chalcedony or agate, based on its visual characteristics.
64
Pretty Yellow Glow Nodule!
HumbleConservative
The rock in the image appears to be a type of chalcedony, possibly an agate or a similar variety. Here's why:
1. **Coloration and Banding**: The rock has a predominantly white or light gray color with some yellowish-brown inclusions. This kind of coloration and banding is typical for agates, which are a variety of chalcedony.
2. **Translucency**: Chalcedony, including agate, often has a translucent quality, which seems to be present in parts of this rock.
3. **Texture**: The rock's texture looks somewhat waxy or greasy, which is characteristic of chalcedony due to its fine-grained silica composition.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish-brown areas could be iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which are common in agates and give them their varied colors. However, without specific tests like a hardness test, streak test, or chemical analysis, this identification remains speculative. For a more precise identification: - **Hardness Test**: Chalcedony has a hardness of around 7 on the Mohs scale, meaning it should scratch glass but not be scratched by a knife. - **Streak Test**: The streak of chalcedony (if it could be powdered) would typically be white or colorless. - **Microscopic Analysis**: Looking at thin sections under a microscope could reveal the mineral composition more clearly. - **Consulting a Geologist or Using Spectroscopy**: For a definitive identification, especially if this rock might be of value or scientific interest.
65
Yellow Chalcedony!
HumbleConservative
The rock in the image appears to be a type of chalcedony, possibly an agate or a similar variety. Here's why:
1. **Coloration and Banding**: The rock has a predominantly white or light gray color with some yellowish-brown inclusions. This kind of coloration and banding is typical for agates, which are a variety of chalcedony.
2. **Translucency**: Chalcedony, including agate, often has a translucent quality, which seems to be present in parts of this rock.
3. **Texture**: The rock's texture looks somewhat waxy or greasy, which is characteristic of chalcedony due to its fine-grained silica composition.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish-brown areas could be iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which are common in agates and give them their varied colors. However, without specific tests like a hardness test, streak test, or chemical analysis, this identification remains speculative. For a more precise identification: - **Hardness Test**: Chalcedony has a hardness of around 7 on the Mohs scale, meaning it should scratch glass but not be scratched by a knife. - **Streak Test**: The streak of chalcedony (if it could be powdered) would typically be white or colorless. - **Microscopic Analysis**: Looking at thin sections under a microscope could reveal the mineral composition more clearly. - **Consulting a Geologist or Using Spectroscopy**: For a definitive identification, especially if this rock might be of value or scientific interest.
66
White Quartz Shard!
HumbleConservative
If we consider the rock in the image to be quartz or a variety of quartz, here's how it might fit:
1. **Chalcedony**: As mentioned earlier, chalcedony is a type of quartz, specifically microcrystalline quartz. Its appearance can range from translucent to opaque, with colors influenced by impurities. The smooth, somewhat waxy luster and the mix of white with yellowish-brown in your rock could indeed fit chalcedony.
2. **Agate**: If there's any subtle banding not clearly visible in the image, it could be agate, a variety of chalcedony known for its fine grain and bright, attractive colors, often with bands or layers.
3. **Opal**: While not typically classified as quartz, opal can be associated with quartz deposits. However, its characteristic feature is its play-of-color, which isn't evident here. If it's common opal or opalite, it might lack this feature but still be related to quartz in geological context.
4. **Quartzite**: This is a metamorphic rock derived from sandstone, which is primarily quartz grains. If your rock has been subjected to metamorphism, the texture and color could be consistent with quartzite, especially if there's been some iron staining or if it's not fully recrystallized.
5. **Milky Quartz**: If the rock has a significant white component, it could be milky quartz, which is quartz with microscopic inclusions that give it a cloudy appearance. Given the context of quartz: -
**Chalcedony or Agate** seem like the most fitting categories for your rock if we're considering varieties of quartz. The smooth texture, potential for banding (even if not clearly visible in the image), and the color variation are all consistent with these forms.
Your rock's appearance aligns well with being a variety of quartz, particularly something like chalcedony or agate, based on its visual characteristics.
67
Glow Shard!
HumbleConservative
The rock in the image appears to be a type of chalcedony, possibly an agate or a similar variety. Here's why:
1. **Coloration and Banding**: The rock has a predominantly white or light gray color with some yellowish-brown inclusions. This kind of coloration and banding is typical for agates, which are a variety of chalcedony.
2. **Translucency**: Chalcedony, including agate, often has a translucent quality, which seems to be present in parts of this rock.
3. **Texture**: The rock's texture looks somewhat waxy or greasy, which is characteristic of chalcedony due to its fine-grained silica composition.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish-brown areas could be iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which are common in agates and give them their varied colors. However, without specific tests like a hardness test, streak test, or chemical analysis, this identification remains speculative. For a more precise identification: - **Hardness Test**: Chalcedony has a hardness of around 7 on the Mohs scale, meaning it should scratch glass but not be scratched by a knife. - **Streak Test**: The streak of chalcedony (if it could be powdered) would typically be white or colorless. - **Microscopic Analysis**: Looking at thin sections under a microscope could reveal the mineral composition more clearly. - **Consulting a Geologist or Using Spectroscopy**: For a definitive identification, especially if this rock might be of value or scientific interest.
68
Nice Glow!
HumbleConservative
The rock in the image appears to be a type of chalcedony, possibly an agate or a similar variety. Here's why:
1. **Coloration and Banding**: The rock has a predominantly white or light gray color with some yellowish-brown inclusions. This kind of coloration and banding is typical for agates, which are a variety of chalcedony.
2. **Translucency**: Chalcedony, including agate, often has a translucent quality, which seems to be present in parts of this rock.
3. **Texture**: The rock's texture looks somewhat waxy or greasy, which is characteristic of chalcedony due to its fine-grained silica composition.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish-brown areas could be iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which are common in agates and give them their varied colors. However, without specific tests like a hardness test, streak test, or chemical analysis, this identification remains speculative. For a more precise identification: - **Hardness Test**: Chalcedony has a hardness of around 7 on the Mohs scale, meaning it should scratch glass but not be scratched by a knife. - **Streak Test**: The streak of chalcedony (if it could be powdered) would typically be white or colorless. - **Microscopic Analysis**: Looking at thin sections under a microscope could reveal the mineral composition more clearly. - **Consulting a Geologist or Using Spectroscopy**: For a definitive identification, especially if this rock might be of value or scientific interest.
69
Half Glow!
HumbleConservative
The rock in the image appears to be a type of chalcedony, possibly an agate or a similar variety. Here's why:
1. **Coloration and Banding**: The rock has a predominantly white or light gray color with some yellowish-brown inclusions. This kind of coloration and banding is typical for agates, which are a variety of chalcedony.
2. **Translucency**: Chalcedony, including agate, often has a translucent quality, which seems to be present in parts of this rock.
3. **Texture**: The rock's texture looks somewhat waxy or greasy, which is characteristic of chalcedony due to its fine-grained silica composition.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish-brown areas could be iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which are common in agates and give them their varied colors. However, without specific tests like a hardness test, streak test, or chemical analysis, this identification remains speculative. For a more precise identification: - **Hardness Test**: Chalcedony has a hardness of around 7 on the Mohs scale, meaning it should scratch glass but not be scratched by a knife. - **Streak Test**: The streak of chalcedony (if it could be powdered) would typically be white or colorless. - **Microscopic Analysis**: Looking at thin sections under a microscope could reveal the mineral composition more clearly. - **Consulting a Geologist or Using Spectroscopy**: For a definitive identification, especially if this rock might be of value or scientific interest.
70
Banded Glow!
HumbleConservative
The rock in the image appears to be a type of quartzite. Quartzite is a metamorphic rock that forms from the metamorphism of quartz sandstone. It's primarily composed of quartz grains that have been recrystallized under heat and pressure, giving it a hard, durable nature and often a somewhat glassy luster.
The colors and patterns you see, with light colors and darker veins, are typical of quartzite, which often retains some of the original sedimentary layering or banding from its sandstone precursor but in a more compact and crystalline form.
The presence of different shades like white, beige, and possibly some iron staining or other mineral inclusions could give it the varied coloration seen here.
71
Bright White!
HumbleConservative
The rock in the image appears to be a type of chalcedony, possibly an agate or a similar variety. Here's why:
1. **Coloration and Banding**: The rock has a predominantly white or light gray color with some yellowish-brown inclusions. This kind of coloration and banding is typical for agates, which are a variety of chalcedony.
2. **Translucency**: Chalcedony, including agate, often has a translucent quality, which seems to be present in parts of this rock.
3. **Texture**: The rock's texture looks somewhat waxy or greasy, which is characteristic of chalcedony due to its fine-grained silica composition.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish-brown areas could be iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which are common in agates and give them their varied colors. However, without specific tests like a hardness test, streak test, or chemical analysis, this identification remains speculative. For a more precise identification: - **Hardness Test**: Chalcedony has a hardness of around 7 on the Mohs scale, meaning it should scratch glass but not be scratched by a knife. - **Streak Test**: The streak of chalcedony (if it could be powdered) would typically be white or colorless. - **Microscopic Analysis**: Looking at thin sections under a microscope could reveal the mineral composition more clearly. - **Consulting a Geologist or Using Spectroscopy**: For a definitive identification, especially if this rock might be of value or scientific interest.
72
Glow Blob!
HumbleConservative
The rock in the image appears to be a type of chalcedony, possibly an agate or a similar variety. Here's why:
1. **Coloration and Banding**: The rock has a predominantly white or light gray color with some yellowish-brown inclusions. This kind of coloration and banding is typical for agates, which are a variety of chalcedony.
2. **Translucency**: Chalcedony, including agate, often has a translucent quality, which seems to be present in parts of this rock.
3. **Texture**: The rock's texture looks somewhat waxy or greasy, which is characteristic of chalcedony due to its fine-grained silica composition.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish-brown areas could be iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which are common in agates and give them their varied colors. However, without specific tests like a hardness test, streak test, or chemical analysis, this identification remains speculative. For a more precise identification: - **Hardness Test**: Chalcedony has a hardness of around 7 on the Mohs scale, meaning it should scratch glass but not be scratched by a knife. - **Streak Test**: The streak of chalcedony (if it could be powdered) would typically be white or colorless. - **Microscopic Analysis**: Looking at thin sections under a microscope could reveal the mineral composition more clearly. - **Consulting a Geologist or Using Spectroscopy**: For a definitive identification, especially if this rock might be of value or scientific interest.
73
Glow cave!
HumbleConservative
@RyanzRocks #noob #rockhound #rockformation #tumbling #agates #rocks #rockhounders #rockstructure #metamorphicrocks #metamorphic #igneousrocks #igneous #quartz #quartzite #geology #nodules #minerals #crystals #glowrocks #idahorockhunting #idahogems #rockcutting #thundereggs #chalcedony #opal #lavarock #rigidtools #ryobitools #riverrocks #translucentrocks #translucent #rockgarden #flow #vevortools #jasper #granite #caves #marble #carnelian #gneiss #limestone #calcite #gold #silver #botryoidal
75
77
78
79
80
81
84
85
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
Glow cave!
7 months ago
3
@RyanzRocks #noob #rockhound #rockformation #tumbling #agates #rocks #rockhounders #rockstructure #metamorphicrocks #metamorphic #igneousrocks #igneous #quartz #quartzite #geology #nodules #minerals #crystals #glowrocks #idahorockhunting #idahogems #rockcutting #thundereggs #chalcedony #opal #lavarock #rigidtools #ryobitools #riverrocks #translucentrocks #translucent #rockgarden #flow #vevortools #jasper #granite #caves #marble #carnelian #gneiss #limestone #calcite #gold #silver #botryoidal
Loading comments...
-
 1:08:36
1:08:36
Man in America
14 hours agoUS, China, Israel & the Battle for the New World Order w/ Boone Cutler
81.4K54 -
 2:37:49
2:37:49
The Connect: With Johnny Mitchell
1 day ago $8.00 earnedBlackwater Mercenary EXPOSES Private Military War Secrets From The Middle East, Fueling Terrorism
38.7K38 -
 2:54:21
2:54:21
Total Horse Channel
2 days ago2025 Scottsdale Arabian Horse Show | Saturday Evening Session
80K6 -
 22:39
22:39
The Mel K Show
10 hours agoMel K & Representative Brandon Gill | Our Constitutional Republic is Being Restored | 4-26-25
59.3K48 -
 4:17:17
4:17:17
VapinGamers
10 hours ago $5.64 earned📣 Fortnite Family Night! - Games and Dubs with BrianZGame - !rumbot
49.1K3 -
 4:27:48
4:27:48
ThePope_Live
8 hours agoLIVE - First time playing The Finals in over a YEAR! Still good? with @Arrowthorn
37.6K1 -
 3:06:26
3:06:26
TruthStream with Joe and Scott
14 hours agoRoundtable with Patriot Underground and News Treason Live 4/26 5pm pacific 8pm Eastern
61.5K37 -
 8:52
8:52
Tundra Tactical
12 hours ago $10.30 earnedSCOTUS Denies Appeal, Minnesota Courts Deal 2a Win!
59.4K12 -
 10:36:01
10:36:01
a12cat34dog
14 hours agoONE WITH THE DARK & SHADOWS :: The Elder Scrolls IV: Oblivion Remastered :: FIRST-TIME PLAYING {18+}
82.8K7 -
 22:27
22:27
Exploring With Nug
21 hours ago $13.00 earnedSwamp Yields a Chilling Discovery in 40-Year Search for Missing Man!
71.2K25