Premium Only Content
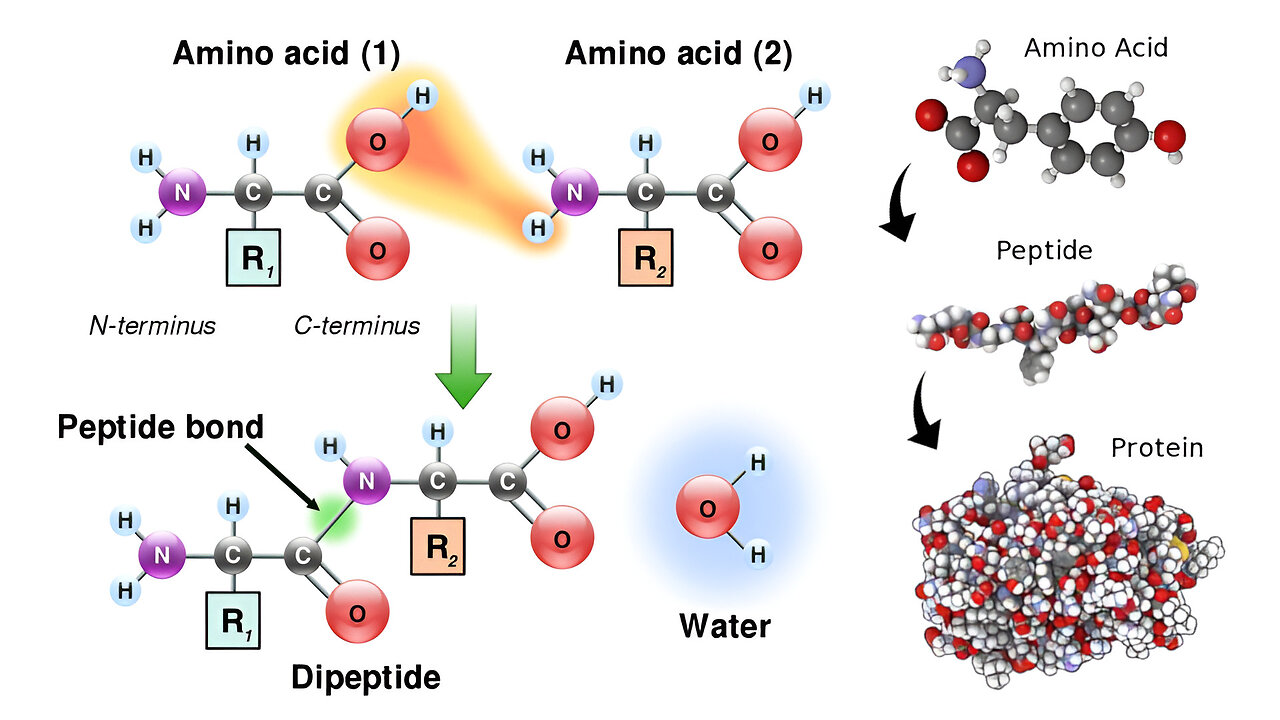
Organic Compounds: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
In this video I go over amino acids, which are derived from ammonia and carboxylate, and combine together to form peptides or longer chains as proteins. Amino acids combine via peptide bonds, which are covalent bonds that involve the loss of a water molecule. Thus, technically, peptides and proteins are made up of amino acid residues, indicating they are formed from the "residue" or leftover molecules in the peptide bond reaction (since water is lost). Further terms and definitions are listed in the timestamps below.
Timestamps:
- Ammonia (NH3) is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen: 0:00
- Amines have a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair of electrons: 1:09
- Amino group is the substituent -NH2: 2:25
- Amino acids contained charged amino (ammonio), carboxylate, and a side chain: 3:05
- Every amino acid contains carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen: 4:20
- Structure of generic L-amino acid used for systematic naming: 4:45
- L- vs D- amino acids are left and right handed (chiral) configurations: 5:21
- A molecule or ion is chiral if it can't be superposed on its mirror image by any combination of rotations, translation, some conformational changes: 6:30
- A chiral molecule or ion exists in 2 stereoisomers that are mirror images, called enantiomers: 7:14
- Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds (covalent bond that releases a water molecule): 8:36
- Oligopeptide consists of 2 to 20 amino acids: 9:44
- Polypeptide is a longer continuous unbranched peptide chain: 10:08
- Protein is a polypeptide with more than approximately 50 amino acids: 10:22
- Proteins consists of 1+ polypeptides arranged in a biologically functional way: 11:09
- Ligand forms a complex (surrounding a central atom or ion) with a biomolecule: 11:39
- Cofactor is required for an enzyme's activity as a catalyst (increases rate of reaction): 13:08
- Amino acid residues refer to the amino acids left over from peptide bonds which removes a water molecule: 13:51
- Condensation reaction combines two molecules into one: 15:54
- Protein sequence is the linear sequence of amino acids, reported from amino-terminal (N) end to carboxyl-terminal (C) end: 16:02
Full video below:
- #MESScience 3: Overview of Biology: https://youtu.be/WX_qzT0nZFY
- HIVE video notes: https://peakd.com/hive-128780/@mes/messcience-3-overview-of-biology
- Video sections playlist: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLai3U8-WIK0FYO6bxFbBAtVJ9sDOJnH72
- #MESScience playlist: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLai3U8-WIK0FjJpwnxwdrOR7L8Ul8VZoZ .
------------------------------------------------------
Become a MES Super Fan! https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCUUBq1GPBvvGNz7dpgO14Ow/join
DONATE! ʕ •ᴥ•ʔ https://mes.fm/donate
SUBSCRIBE via EMAIL: https://mes.fm/subscribe
MES Links: https://mes.fm/links
MES Truth: https://mes.fm/truth
Official Website: https://MES.fm
Hive: https://peakd.com/@mes
Email me: contact@mes.fm
Free Calculators: https://mes.fm/calculators
BMI Calculator: https://bmicalculator.mes.fm
Grade Calculator: https://gradecalculator.mes.fm
Mortgage Calculator: https://mortgagecalculator.mes.fm
Percentage Calculator: https://percentagecalculator.mes.fm
Free Online Tools: https://mes.fm/tools
iPhone and Android Apps: https://mes.fm/mobile-apps
-
 2:15:38
2:15:38
Math Easy Solutions
3 days agoMES Math Q/A 6: What Lab Equipment is Needed for the Hutchison Effect?
1441 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Right Side Broadcasting Network
5 days agoLIVE: CPAC 2025 Day Three with President Donald J. Trump - 2/22/25
19,236 watching -
 1:05:34
1:05:34
The Big Mig™
9 hours agoConfirmed Kash Patel New FBI Director, Bring On The Pain |EP483
27.1K13 -
 53:59
53:59
Tactical Advisor
5 hours agoThe Vault Room Podcast 009 | Everyone Getting $5000?!
30.1K6 -
 2:04:44
2:04:44
TheAlecLaceShow
16 hours agoLive at CPAC | Interviews with Dean Cain, Rep. Comer and more! | The Alec Lace Show
41.3K3 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Major League Fishing
2 days agoLIVE Tackle Warehouse Invitationals, Stop 1, Day 2
241 watching -
 3:12:37
3:12:37
I_Came_With_Fire_Podcast
13 hours agoNOC Spy: CIA uses SATANIC RITUAL ABUSE to make SLEEPER Cells
29.4K5 -
 28:42
28:42
CatfishedOnline
1 day ago $1.67 earnedWoman Insists Morgan Wallen Relationship Isn't a Romance Scam!
24.6K -
 16:25
16:25
TSPLY
1 day agoNew CNN / MSNBC Meltdown Moments Of Getting Mad At Donald Trump In February
30.8K22 -
 8:33
8:33
scoutthedoggie
6 hours agoAirsoft War Games Scotland
45.8K5