Premium Only Content
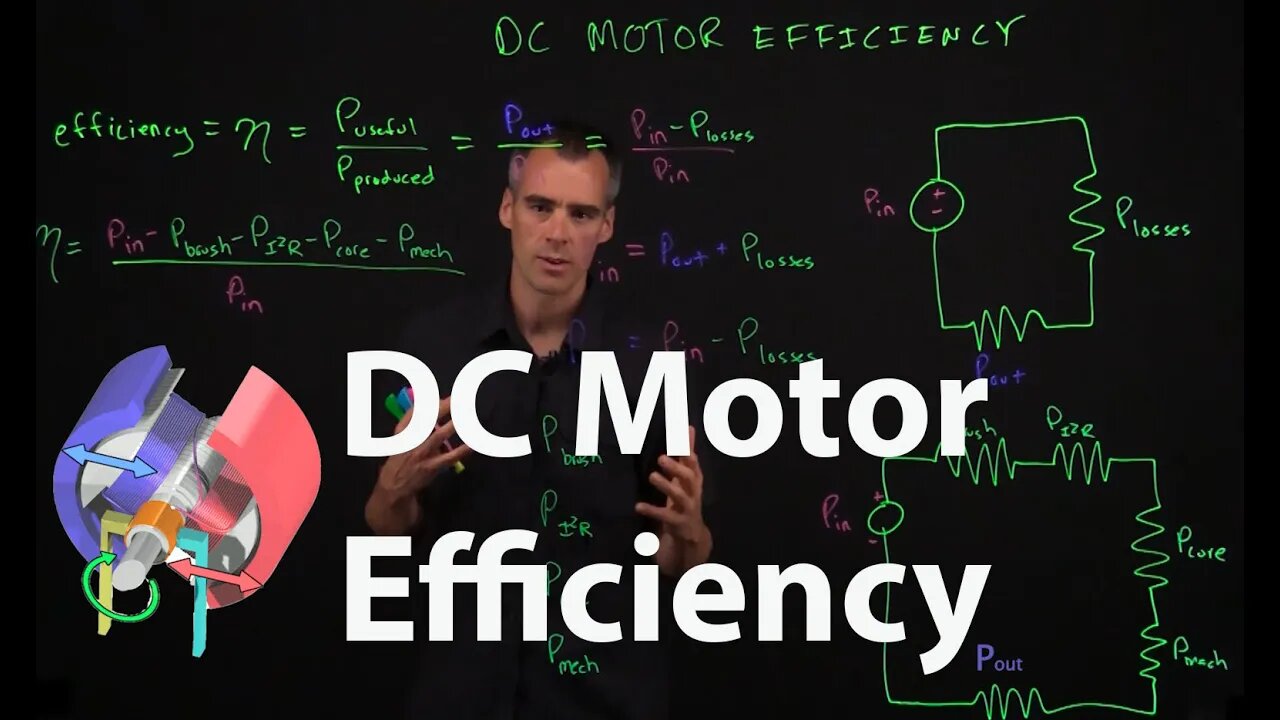
Calculating efficiency of a DC motor
Let's take a look at the efficiency of the DC motor we just discussed
Like almost anything in the real world, the motor won't be 100% efficient
The power generated by the motor will be less than the power we input, and the efficiency can be defined as
𝜂=P{useful}P{produced}
or
𝜂=PoutPin
We could also look at this like a circuit in series where the power in is our source power and the power lost and power generated are modeled as resistors.
In this case we'd have a circuit like this
And due to the conservation of power, the Power in would have to equal the combination of the Power out and the Power lost.
Another way you could look at this is the power generated, or output power, as the power in minus the power lost, or
𝜂=Pin−PlossPin
In the case of our motor we have several sources of loss.
Loss from the brush, which we can call
Pbrush
There is typically some electrical loss here with sparking as well as the frictional loss of the brush going against the commutator
There is a lot of current going through a lot of wire wrapped around the rotor, so there will be
I2R
losses, or
Pheat
as the current heats up the wire a little
There are some losses,
Pcore
, in the core of the magnet due to the electromagnetics involved
And lastly, there is some loss due to air resistance and the friction of the rotor turning, or
Pmech
, similar to the reasons your skateboard stops coasting even when you're not going up a hill.
Given that nomenclature, our efficiency of the motor could simply be found as:
𝜂=Pin−Pbrush−Pheat−Pcore−PmechPin
Typicall efficiency for a DC motor might be in the range of 70-85%, which Isn't too bad.
But that was just a brief overview of how one might go about calculating the efficiency of a DC motor based on it's various types of losses.
-
![🔴LIVE : THE FINALS Season5 [The World's STRONGEST Gamer] 1080p 60fps](https://1a-1791.com/video/s8/1/4/m/-/L/4m-Lv.0kob-small-LIVE-THE-FINALS-Season5-The.jpg) 2:14:36
2:14:36
PacPowerTV
5 hours ago🔴LIVE : THE FINALS Season5 [The World's STRONGEST Gamer] 1080p 60fps
37.9K9 -
 5:11:27
5:11:27
Joe Donuts Gaming
5 hours ago🟢Live : City Boy Inherits A Ranch 😧😓
22.8K2 -
 3:41:12
3:41:12
Fresh and Fit
11 hours agoDaniel Penny ACQUITTED & BLM Meltdown
78.7K22 -
 42:46
42:46
barstoolsports
9 hours agoThe Shred Line with Coach Gruden, Dave Portnoy and Steven Cheah | Week 15
54.3K4 -
 3:43:53
3:43:53
EricJohnPizzaArtist
5 hours agoAwesome Sauce PIZZA ART LIVE Ep. #27: Christmas Special! Dr. Disrespect is Coming to Town!
31.8K8 -
 1:42:14
1:42:14
TheDozenPodcast
12 hours agoConnor McGregor, Raoul Moat, Burglary, BKFC Heavyweight Champion: Mick Terrill
43.5K3 -
 2:10:02
2:10:02
vivafrei
15 hours agoEp. 241: Stephanopoulos PAYS for Defamation! Accused CEO Shooter Gets ELITE Attorney! Drone Madness
164K93 -
 6:05:13
6:05:13
Right Side Broadcasting Network
6 days agoLIVE REPLAY: NYYRC 112th Annual Gala Ft. Steve Bannon, Nigel Farage, and Dan Scavino - 12/15/24
216K15 -
 1:22:45
1:22:45
Josh Pate's College Football Show
9 hours ago $3.43 earnedCFP First Round Predictions | Travis Hunter Heisman | Transfer Portal Intel | Biggest Misses In 2024
36.4K -
 LIVE
LIVE
Vigilant News Network
9 hours agoTsunami of Devastating News Crashes Down on COVID Vaccines | Media Blackout
1,719 watching