Premium Only Content
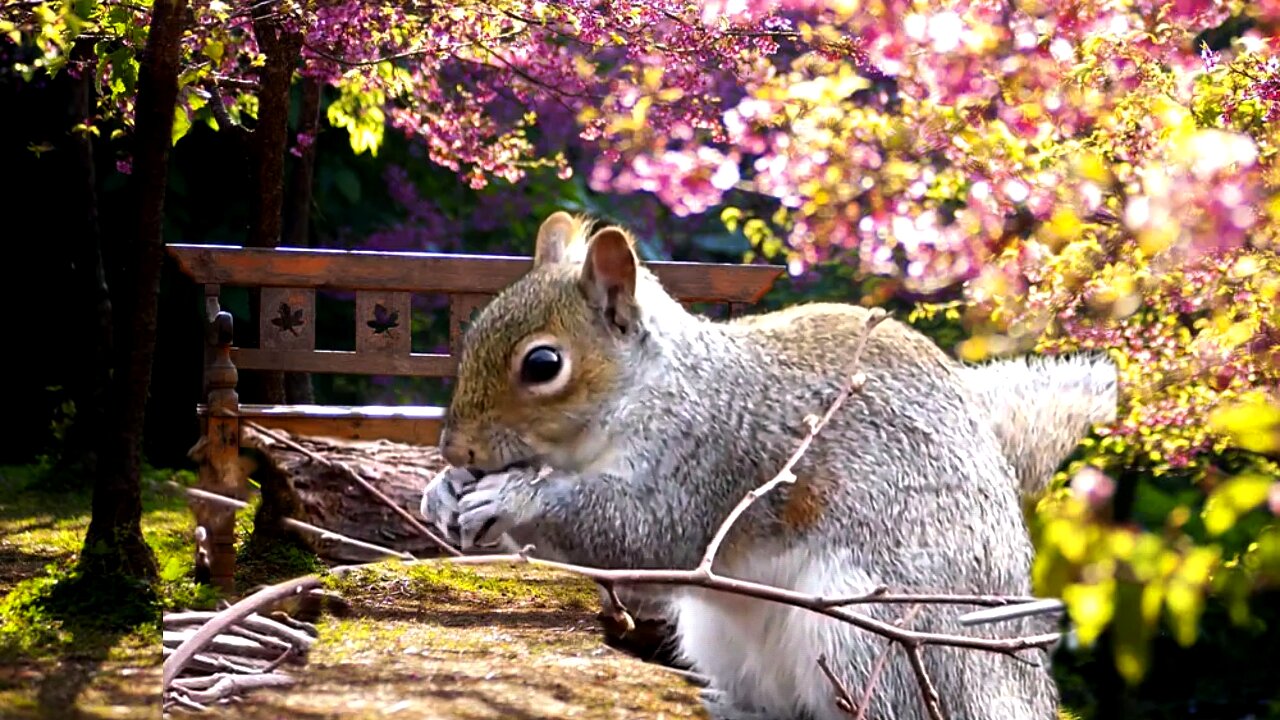

Heart-Warming Squirrel Does Plank Jacks for a Serious Core and Cardio Exercise
Do wild animals like squirrels consciously choose to work out or exercise? Surprisingly, there is very little research on this topic. I was fortunate to capture this amazing video of a wild squirrel mentally and physically preparing and training for a future athletic event of escaping a predator. It cautiously plank jumps across to the feeding station – the human equivalent of the long jump. But much more than that – just like an elite athlete – the squirrel used planning, foresight and knowledge of natural physics and basic techniques to improve his performance by designing a better launching pad, making adjustments, testing, and then adjusting again until reaching peak performance.
squirrel, (family Sciuridae), generally, any of the 50 genera and 268 species of rodents whose common name is derived from the Greek skiouros, meaning “shade tail,” which describes one of the most conspicuous and recognizable features of these small mammals. These distinctive animals occupy a range of ecological niches worldwide virtually anywhere there is vegetation. The squirrel family includes ground squirrels, chipmunks, marmots, prairie dogs, and flying squirrels, but to most people squirrel refers to the 122 species of tree squirrels, which belong to 22 genera of the subfamily Sciurinae. The North American gray squirrel (Sciurus carolinensis) has adapted to urban and suburban areas where it is regarded as aesthetic or as a minor annoyance. In northern Europe the red squirrel (S. vulgaris) is valued for its soft, thick fur. Villagers in tropical forests keep squirrels as pets. Most species are hunted for food.
General features
Tree squirrels have slender, lanky bodies, long, muscular limbs, and furred feet. The forefeet have four long digits plus a short, stubby thumb, and the five-toed hind feet are narrow or moderately wide. The bald soles of the feet take the form of prominent, fleshy pads. Because the ankle joints are flexible and can be rotated, squirrels can rapidly descend trees headfirst with the hind feet splayed flat against the trunk. Their large, bright eyes convey an alert demeanour, and the broad, short head tapers to a blunt muzzle adorned with long whiskers. The rounded ears, small in relation to body size, are densely covered with short, fine hairs, which form a long tuft at the tips of the ears in some species. The tail is about as long as head and body or appreciably longer. Furred from base to tip, the tail appears bushy and cylindrical when the hairs grow evenly around the tail; the tail appears flatter if the fur originates only from opposite sides. Claws are large, strong, curved, and very sharp, which enables tree squirrels to navigate vertical surfaces and slim branches.
Variation in body size is considerable. Largest are the four species of Oriental giant squirrels (genus Ratufa) native to the tropical forests of Southeast Asia. Weighing 1.5 to 3 kg (3 to almost 7 pounds), it has a body length of 25 to 46 cm (about 10 to 18 inches) and a tail about as long. Two species of pygmy squirrels are the smallest: the neotropical pygmy squirrel (Sciurillus pusillus) of the Amazon Basin weighs 33 to 45 grams (1 to 1.5 ounces), with a body 9 to 12 cm long and an equally long tail; but the African pygmy squirrel (Myosciurus pumilio) of the West African tropical forests is even smaller, at 13 to 20 grams, with a body length of 6 to 8 cm and a somewhat shorter tail.
Squirrels’ soft, dense fur is moderately long in most species but can be very long and almost shaggy in some. Colour is extraordinarily variable. Some species are plain, covered in one or two solid shades of brown or gray. A few species are striped along the sides and back; sometimes the head is also striped. Tropical species exhibit combinations of white, gray, yellow, orange, red, maroon, brown, and black, yielding a variety of complex coat patterns.
Giraffe standing in grass, Kenya.
Britannica Quiz
Know Your Mammals Quiz
Natural history
All tree squirrels are diurnal and arboreal, but the range of vertical activity in species differs widely, especially among those living in tropical rainforests. Some, such as the Oriental giant squirrels (genus Ratufa) and the African giant squirrels (genus Protoxerus), rarely descend from the high canopy. Others, like the pygmy squirrel of Sulawesi (Prosciurillus murinus), travel and forage at intermediate levels between ground and canopy. Some large tropical squirrels, such as the Sulawesi giant squirrel (Rubrisciurus rubriventer) and the northern Amazon red squirrel (Sciurus igniventris), nest at middle levels but travel and forage low in the understory or on the ground. The African palm squirrels (genus Epixerus) are long-legged runners that forage only on the ground. Certain species, such as the red-tailed squirrel (S. granatensis) of the American tropics and the African pygmy squirrel, are active from ground to canopy. In the United States, the Eastern fox squirrel (S. niger) runs along the ground from tree to tree, but others, including the Eastern gray squirrel (S. carolinensis), prefer to travel through the treetops and regularly cross rivers by swimming with the head up and tail flat on the water’s surface. Thomas’s rope squirrel (Funisciurus anerythrus) of Africa even submerges itself and swims underwater.
Discover whether squirrels forget where they bury half of their food
Discover whether squirrels forget where they bury half of their foodSee all videos for this article
Most tree squirrels have strong chisel-like incisors and powerful jaws, which are required for gnawing open the hard nuts that, along with fruits, are a primary component of their diet. They also eat seeds, fungi, insects and other arthropods, the cambium layer of tree bark, nectar, leaves, buds, flowers, and sometimes bird eggs, nestlings, and carrion. Some red squirrels (genus Tamiasciurus) and Sciurus species of temperate climates will stalk, kill, and eat other squirrels, mice, and adult birds and rabbits for food, but such predation in tropical tree squirrels seems rare.
Get a Britannica Premium subscription and gain access to exclusive content.
Nests are constructed among branches in the forest canopy or at lower levels in tree crowns, vine tangles, tree hollows, or undergrowth near the ground. Some species of tropical tree squirrels produce several litters per year; breeding season in the Northern Hemisphere may extend from December to September and may result in one or two litters that average three to seven young, depending upon the species.
In the New World, tree squirrels range from the boreal forests of Canada and Alaska southward through coniferous and deciduous woodlands in the United States to the tropical rainforests of South America. In Africa, tree squirrels are native to rainforests and some woodland savannas. Their distribution in the remainder of the Old World extends from the northern boreal forests of Europe and Asia to the Indonesian tropical rainforests. East of the Asian continental margin, tree squirrels inhabit the forests of Taiwan, some islands in the Philippines, and Sulawesi, but they do not occur naturally anywhere east of those islands. Most of the species in 20 of the 22 genera are found in tropical rainforests.
Classification and evolutionary history
Tree squirrels belong to the subfamily Sciurinae; it and the subfamily Pteromyinae (flying squirrels) constitute the family Sciuridae of the order Rodentia. Fossils record the evolutionary history of tree squirrels back to the Late Eocene Epoch (41.3 million to 33.7 million years ago) in North America and the Miocene Epoch (23.8 million to 5.3 million years ago) in Africa and Eurasia.
FAMILY SCIURIDAE (squirrels)
2 subfamilies comprising 272 species in 51 genera found worldwide. See flying squirrel for 15 genera and 42 species of subfamily Pteromyinae. See also ground squirrel.
Subfamily Sciurinae
230 species in 36 genera, including ground squirrels (10 genera, 62 species), marmots (1 genus, 14 species), chipmunks (1 genus, 25 species), Asian rock squirrels (1 genus, 2 species), and prairie dogs (1 genus, 5 species).
Tree squirrels
122 species in 22 genera.
Genus Sciurus (tree squirrels)
28 non-African species.
Genus Callosciurus (Oriental, or tricoloured, tree squirrels)
15 Southeast Asian species.
Genus Sundasciurus (Sunda squirrels)
15 Southeast Asian species.
Genus Paraxerus (bush squirrels)
11 African species.
Genus Funisciurus (rope, or African striped, squirrels)
9 African species.
Genus Heliosciurus (sun squirrels)
6 African species.
Genus Funambulus (Asiatic palm squirrels)
5 Asian species.
Genus Microsciurus (dwarf squirrels)
4 Central and South American species.
Genus Prosciurillus (Sulawesi dwarf squirrels)
4 Southeast Asian species.
Genus Ratufa (Oriental giant squirrels)
4 Indian and Southeast Asian species.
Genus Tamiops (Asiatic striped squirrels)
4 Southeast Asian species.
Genus Tamiasciurus (red squirrels or chickarees)
3 North American species.
Genus Exilisciurus (pygmy squirrels)
3 Southeast Asian species.
Genus Epixerus (African palm squirrels)
2 West African species.
Genus Protoxerus (oil palm squirrels or African giant squirrels)
2 African species.
Genus Sciurillus (neotropical pygmy squirrel)
1 Amazonian species.
Genus Rubrisciurus (Sulawesi giant squirrel)
1 Southeast Asian species.
Genus Nannosciurus (black-eared squirrel)
1 Southeast Asian species.
Genus Myosciurus (African pygmy squirrel)
1 West African species.
Genus Rheithrosciurus (tufted, or groove-toothed, ground squirrel)
1 Southeast Asian species found only on Borneo.
Genus Glyphotes (sculptor squirrel)
1 Southeast Asian species found only on Borneo.
Genus Syntheosciurus (Bang’s mountain squirrel)
1 species found only in Costa Rica and Panama.
Guy Musser.
-
 4:10
4:10
PerpetualHealthCo
17 hours agoFDA Bans Red Dye No.3
4.13K1 -
 59:57
59:57
Trumpet Daily
20 hours ago $3.73 earnedRemembering Herbert W. Armstrong - Trumpet Daily | Jan. 16, 2025
6.91K12 -
 26:07
26:07
The Lou Holtz Show
13 hours agoThe Lou Holtz Show S 2 Ep 1 | Tony Rice on Championship Leadership and Notre Dame Legacy #podcast
14.3K -
 53:37
53:37
Weberz Way
13 hours agoGOODBYE JOE, TRUMPS CABINET, LA FIRES, & KEEP TIKTOK
8.48K -
 3:07:17
3:07:17
Alex Zedra
10 hours agoLIVE! New Game | Exorcism!??
36K4 -
 6:00:06
6:00:06
SpartakusLIVE
13 hours agoThe Conqueror of Corona || Delta Force LATER
86.8K3 -
 2:17:30
2:17:30
barstoolsports
16 hours ago$250k Winner Revealed With Final Votes And Reunion | Surviving Barstool S4 Finale
136K9 -
 2:05:49
2:05:49
Kim Iversen
14 hours agoTikTok Ban BACKFIRES: Millions Flee To New App Showing The REAL China
123K189 -
 1:35:12
1:35:12
Glenn Greenwald
16 hours agoCNN And Jake Tapper In Deep Trouble In Defamation Lawsuit: With Jonathan Turley; TikTok Ban, Trump's China Policy, And More With Arnaud Bertrand | SYSTEM UPDATE SHOW #390
116K87 -
 12:24
12:24
Dan Bongino Show Clips
16 hours agoPresident Trump Full Interview - 01/16/25
139K307