Premium Only Content
THIS CAN SAVE YOUR LIFE || WATCH THIS FRIST THING IN THE MORNING
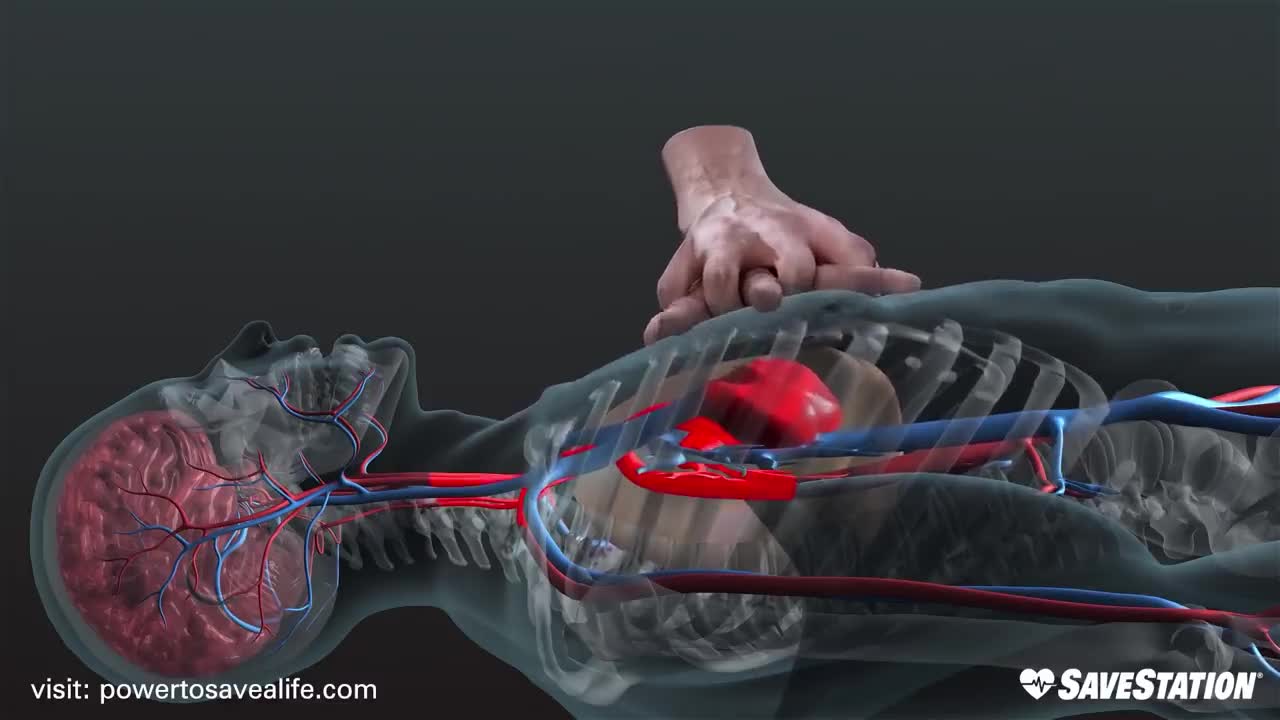
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is an emergency procedure consisting of chest compressions often combined with artificial ventilation in an effort to manually preserve intact brain function until further measures are taken to restore spontaneous blood circulation and breathing in a person who is in cardiac arrest. It is recommended in those who are unresponsive with no breathing or abnormal breathing, for example, agonal respirations.
CPR involves chest compressions for adults between 5 cm (2.0 in) and 6 cm (2.4 in) deep and at a rate of at least 100 to 120 per minute. The rescuer may also provide artificial ventilation by either exhaling air into the subject's mouth or nose (mouth-to-mouth resuscitation) or using a device that pushes air into the subject's lungs (mechanical ventilation). Current recommendations place emphasis on early and high-quality chest compressions over artificial ventilation; a simplified CPR method involving only chest compressions is recommended for untrained rescuers. In children, however, only doing compressions may result in worse outcomes because, in children, the problem normally arises from respiratory, rather than cardiac, problems. Chest compression to breathing ratios is set at 30 to 2 in adults.
CPR alone is unlikely to restart the heart. Its main purpose is to restore the partial flow of oxygenated blood to the brain and heart. The objective is to delay tissue death and to extend the brief window of opportunity for a successful resuscitation without permanent brain damage. Administration of an electric shock to the subject's heart, termed defibrillation, is usually needed in order to restore a viable, or "perfusing", heart rhythm. Defibrillation is effective only for certain heart rhythms, namely ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia, rather than asystole or pulseless electrical activity, which usually require the treatment of underlying conditions to restore cardiac function. Early shock, when appropriate, is recommended. CPR may succeed in inducing a heart rhythm that may be shockable. In general, CPR is continued until the person has a return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) or is declared dead.
-
 0:51
0:51
Chrisfocused
3 years agoA must watch | 8 things that can your life forever
66 -
 1:11:10
1:11:10
Steve-O's Wild Ride! Podcast
5 days ago $9.30 earnedDusty Slay Went From Selling Pesticides To Having A Netflix Special - Wild Ride #244
38.3K3 -
 1:16:02
1:16:02
CocktailsConsoles
7 hours agoBE PART OF THE GAME!!| Death Road to Canada | Cocktails & Consoles Livestream
26.8K2 -
 8:19:28
8:19:28
Phyxicx
9 hours agoWe're streaming again! - 11/26/2024
22.9K -
 6:49:31
6:49:31
GamingWithHemp
9 hours agoHanging with Hemp #103
41.3K3 -
 21:24
21:24
DeVory Darkins
1 day ago $11.40 earnedElon Musk and Tucker Carlson SHATTER Left Wing Media
41.4K42 -
 15:13
15:13
Stephen Gardner
6 hours ago🔥Breaking: Trump JUST DID the UNEXPECTED | Tucker Carlson WARNS America!
37.2K80 -
 1:18:01
1:18:01
Glenn Greenwald
11 hours agoWill Trump's Second Term Promote Economic Populism? Matt Stoller On Cabinet Picks To Fight Corporate Power; Should Liberals Cut Off Pro-Trump Friends & Family? | SYSTEM UPDATE #372
177K225 -
 2:26:30
2:26:30
WeAreChange
11 hours agoTrump To Subdue Deranged Opposition! ARRESTS Planned
137K59 -
 1:19:04
1:19:04
JustPearlyThings
12 hours agoWhy MODERN WOMEN Keep REJECTING The Redpill! | Pearl Daily
105K58