Premium Only Content
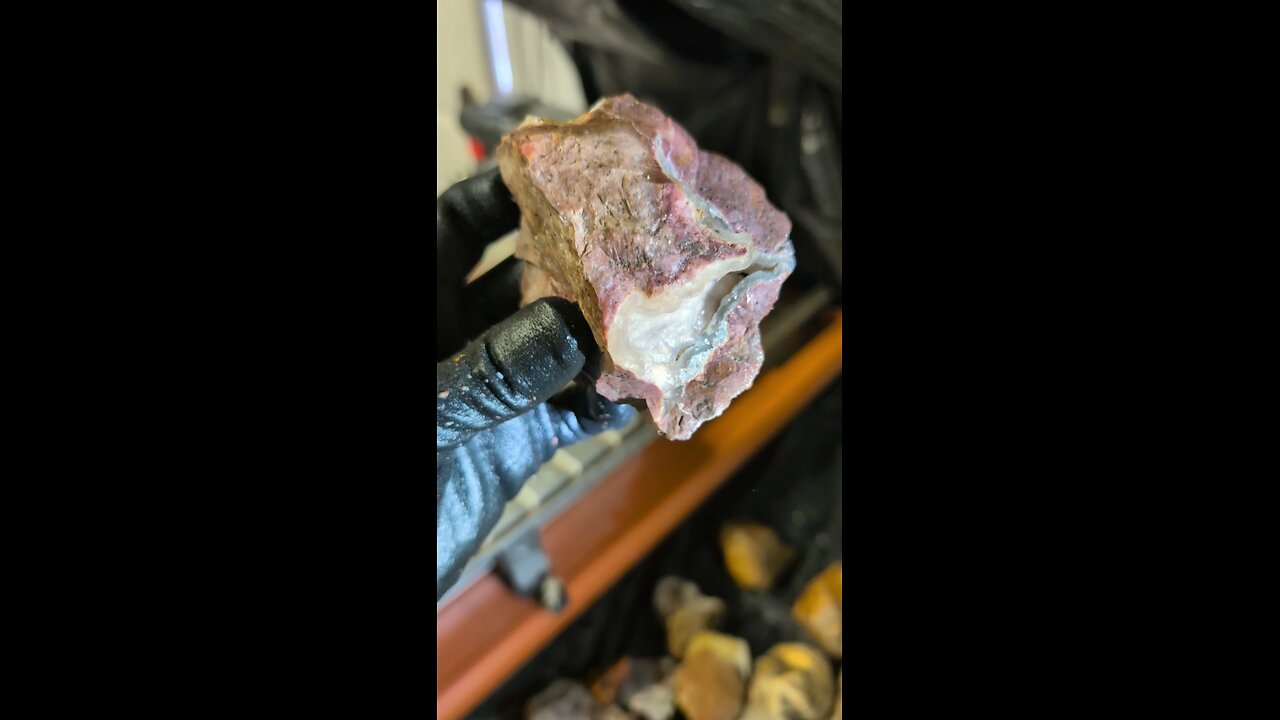

Botryoidal cut!
Botryoidal is a term used in mineralogy to describe a mineral or rock formation that has a rounded, grape-like, or botryoidal (from the Greek word "botryoeidēs" meaning "like a bunch of grapes") shape. Here are some key points about botryoidal formations:
Formation: Botryoidal structures form when minerals precipitate from solution in a way that creates rounded, nodular surfaces. This often happens in cavities or vugs within rocks where mineral-rich solutions slowly deposit layers of minerals, building up in a manner that mimics the shape of grapes.
Common Minerals: Some minerals commonly found in botryoidal forms include:
Hematite: Often forms botryoidal shapes with a metallic luster.
Malachite: Known for its vibrant green botryoidal formations.
Goethite: Can exhibit botryoidal textures, usually in brown or yellow hues.
Chalcedony: Including varieties like agate, which can form botryoidal layers within geodes.
Psilomelane: A manganese oxide mineral often found in botryoidal shapes.
Texture: The texture of botryoidal minerals is smooth and rounded, with a surface that looks like clusters of small spheres or nodules. This texture is due to the slow, even deposition of mineral material from solution.
Uses:
Jewelry and Decoration: Botryoidal minerals are prized for their unique shapes and are often polished or cut into cabochons for use in jewelry. They can also be used as decorative stones.
Collectors: Due to their distinctive appearance, botryoidal specimens are popular among mineral collectors.
Art: Their natural beauty makes them suitable for artistic endeavors, including sculptures or inlays.
Geological Significance: Botryoidal formations can provide insights into the conditions under which the minerals precipitated, often indicating slow, stable conditions conducive to this type of growth. They are also indicators of the fluid dynamics and chemistry in the environment where they formed.
-
![[Ep 630] Election Integrity w/ Guest Steve Stern! | Sam Anthony [your]NEWS | Laura Loomer Delivers!](https://1a-1791.com/video/fww1/23/s8/1/G/S/8/t/GS8ty.0kob-small-Ep-630-Election-Integrity-w.jpg) 3:04:33
3:04:33
The Nunn Report - w/ Dan Nunn
17 hours ago[Ep 630] Election Integrity w/ Guest Steve Stern! | Sam Anthony [your]NEWS | Laura Loomer Delivers!
13.6K11 -
 11:33
11:33
Russell Brand
19 hours agoThe Democratic Party is Becoming A Parody
110K259 -
 26:17
26:17
The Brett Cooper Show
1 day agoWhy Trans Activists Are Attacking This Gym Owner | Episode 14
95.6K83 -
 42:04
42:04
Film Threat
21 hours agoSNOW WHITE EARLY REACTIONS! | Film Threat After Dark
58.6K12 -
 2:57:45
2:57:45
GoodLawgic
10 hours agoThe Following Program: Day 57 Recap: JF Files Realeased; Russo-Ukrainian Cease Fire?
35.5K10 -
 2:42:22
2:42:22
Badlands Media
1 day agoEye of the Storm Ep. 240
127K41 -
 8:15:45
8:15:45
MyronGainesX
1 day ago $41.81 earnedJFK Files Exposed With Cory Hughes! Israel Ends Ceasefire!
111K21 -
 1:19:34
1:19:34
Awaken With JP
19 hours agoJFK Files FINALLY Released - LIES Ep 83
112K99 -
 22:41
22:41
Stephen Gardner
12 hours ago🔥I Can't BELIEVE What JUST HAPPENED to Trump!
76.3K184 -
 2:37:35
2:37:35
TimcastIRL
12 hours agoJFK FILES RELEASED, Shocking Documents Released By Trump DROPPED w/Amber Duke | Timcast IRL
269K199