Premium Only Content
ENERGY TECH NUCLEAR REACTORS
History
Small nuclear reactors originated in the 1950s for military use, such as powering submarines and aircraft carriers. The Enrico Fermi Atomic Power Plant, Unit 1, in Michigan, was an early example, operating from 1963 to 1972. Molten salt reactors (MSRs) also began in the mid-20th century with the Aircraft Reactor Experiment (ARE) and the Molten-Salt Reactor Experiment (MSRE). Micro nuclear reactors, a subset of small modular reactors (SMRs), started with the U.S. Navy's nuclear submarine project in the 1950s.
Use
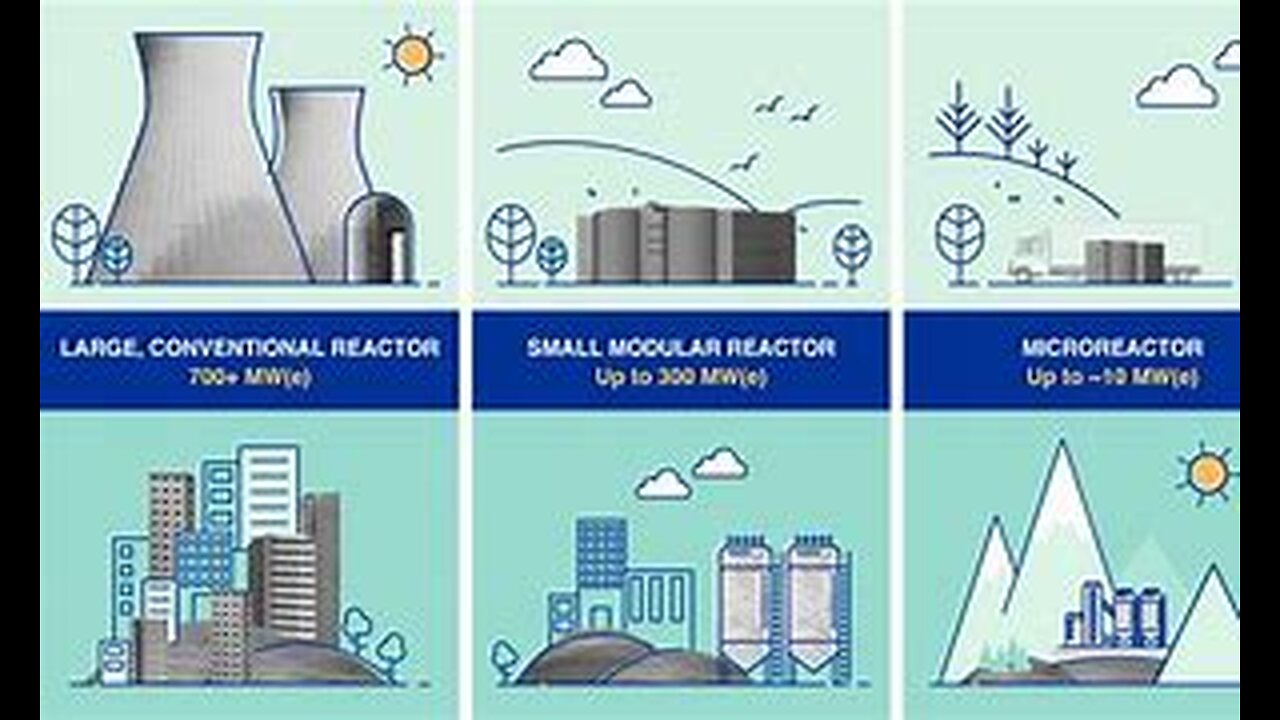
Small nuclear reactors provide flexible, scalable power solutions, ideal for remote locations and areas with limited grid infrastructure. MSRs offer high safety and efficiency, suitable for electricity generation, industrial processes, and desalination. Micro nuclear reactors are designed for rapid deployment and can operate independently of the grid, supporting resilient, non-carbon-emitting power in challenging environments.
Development
Recent interest in small nuclear reactors focuses on reducing financial risks and construction times. Companies like NuScale Power and Holtec International are leading with innovative designs. MSRs are advancing in countries like China and Russia, addressing challenges such as hot salt corrosivity. Micro nuclear reactors are being developed by various organizations, including the U.S. Department of Energy, using High-Assay Low-Enriched Uranium (HALEU) for enhanced efficiency and safety.
Latest Technology
Advancements in nuclear reactor technology aim to enhance safety, efficiency, and scalability. Third-generation reactors, like China's Hualong One, are being deployed to meet clean energy goals. Companies like NANO Nuclear Energy (NNE) are developing systems that integrate microreactors with heat storage units. The U.S. Department of Energy supports advanced reactor designs, including sodium-cooled fast reactors and very high-temperature reactors. MSRs continue to be a research focus, offering benefits for various industrial applications.
-
 12:19
12:19
Mrgunsngear
23 hours ago $6.56 earnedHUXWRX RAD 9 Suppressor Review
48.6K20 -
 LIVE
LIVE
LumpyPotatoX2
1 hour agoSub-Sunday with Casual Verdansk - #RumbleGaming
121 watching -
 23:50
23:50
marcushouse
16 hours ago $5.00 earnedStarship Is About to Do Something It’s Never Done Before - A Huge First!
47.4K17 -
 LIVE
LIVE
FrizzleMcDizzle
2 hours agoElden Ring Seamless COOP
106 watching -
 41:56
41:56
CatfishedOnline
2 days agoKinky Man Sends 401k to Romance Scammer from Ghana!
32.6K9 -
 1:53:55
1:53:55
Nick Shirley
19 hours ago $8.57 earnedIRL Confronting Anti-Trump & Anti-Elon Protesters
38.4K124 -
 16:18
16:18
Tactical Advisor
1 day agoRetiring My Patrol Rifle | Old vs New
34K2 -
 22:29
22:29
JasminLaine
20 hours agoAwkward Silence After Poilievre FACT CHECKS Reporter—Carney’s Face SAYS IT ALL
34.7K39 -
 9:48
9:48
VSOGunChannel
21 hours ago $2.35 earned25% of ATF Getting Fired? SUPER ATF on Hold?
32.9K29 -
 11:09
11:09
ariellescarcella
1 day ago"All 4 Of My Kids Are Trans" : NOOOOOO
30.7K33