Premium Only Content
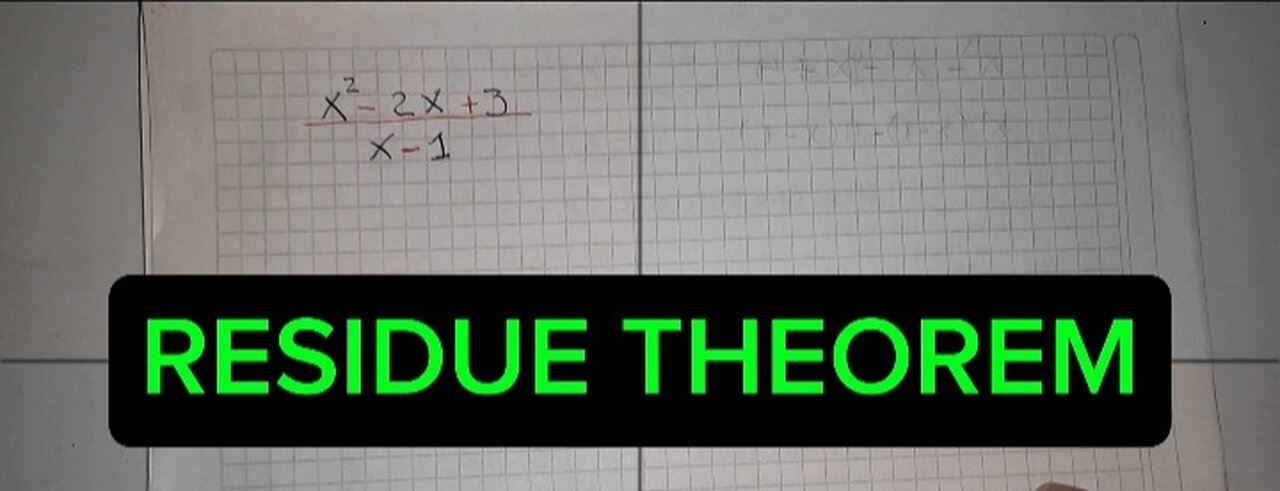
RESIDUE THEOREM
The remainder theorem in algebra is a fundamental theorem that states that if a polynomial f(x) is divided by a linear polynomial (x - a), then the remainder is equal to the value of f(a).
Statement of the theorem
If f(x) is a polynomial and a is a number, then the remainder of f(x) divided by (x - a) is equal to f(a).
Proof of the theorem
The proof of the remainder theorem is based on polynomial division. If f(x) is divided by (x - a), then we can write:
f(x) = q(x)(x - a) + r
where q(x) is the quotient and r is the remainder.
Substituting x = a in the previous equation, we obtain:
f(a) = q(a)(a - a) + r
f(a) = r
Therefore, the remainder is equal to the value of f(a).
Applications of the remainder theorem
The remainder theorem has several important applications in algebra and other areas of mathematics, such as:
1. _Calculation of residues_: The residue theorem is used to calculate residues in polynomial division.
2. _Factoring polynomials_: The remainder theorem is used to factorize polynomials.
3. _Solving equations_: The remainder theorem is used to solve polynomial equations.
4. _Analysis of functions_: The remainder theorem is used to analyze the properties of polynomial functions.
Example
Suppose we want to calculate the remainder of f(x) = x^2 + 3x + 2 divided by (x - 1).
According to the remainder theorem, the remainder is equal to f(1).
f(1) = 1^2 + 3(1) + 2
f(1) = 6
Therefore, the remainder is 6.
-
 55:18
55:18
LFA TV
1 day agoEurope’s Sudden Turn Against America | TRUMPET DAILY 3.6.25 7PM
32.2K3 -
 4:21
4:21
Tundra Tactical
4 hours ago $2.12 earnedPam Bondi MUST Enforce Due Process NOW!
23.7K1 -
 56:42
56:42
VSiNLive
5 hours agoFollow the Money with Mitch Moss & Pauly Howard | Hour 1
48K1 -
 1:05:32
1:05:32
In The Litter Box w/ Jewels & Catturd
1 day agoShalom Hamas | In the Litter Box w/ Jewels & Catturd – Ep. 756 – 3/6/2025
103K37 -
 1:23:00
1:23:00
Sean Unpaved
7 hours ago $3.19 earnedNFL Free Agency
53.4K4 -
 18:25
18:25
Stephen Gardner
6 hours ago🔥The REAL REASON the Epstein Files are being HIDDEN | I CONFRONT Alan Dershowitz for details!
66.2K145 -
 1:58:44
1:58:44
The Quartering
10 hours agoTrump To Charge USAID Staff, Campus RIOT Erupts, Theo Von & Candace Owens, Ukraine Gets Worse!
117K72 -
 1:08:42
1:08:42
Winston Marshall
10 hours ago“This Is a Ticking Timebomb!” Trump’s Unlikely Coalition & The Woke Right w/James Lindsay
65.3K11 -
 24:32
24:32
Rethinking the Dollar
10 hours agoWhy Washington Will NEVER Fix the Debt Crisis w/ Paul Stone
36.5K2 -
 4:40:22
4:40:22
Viss
11 hours ago🔴LIVE - PUBG New Extraction Shooter Coming Soon? - PUBG
52.2K2