Premium Only Content
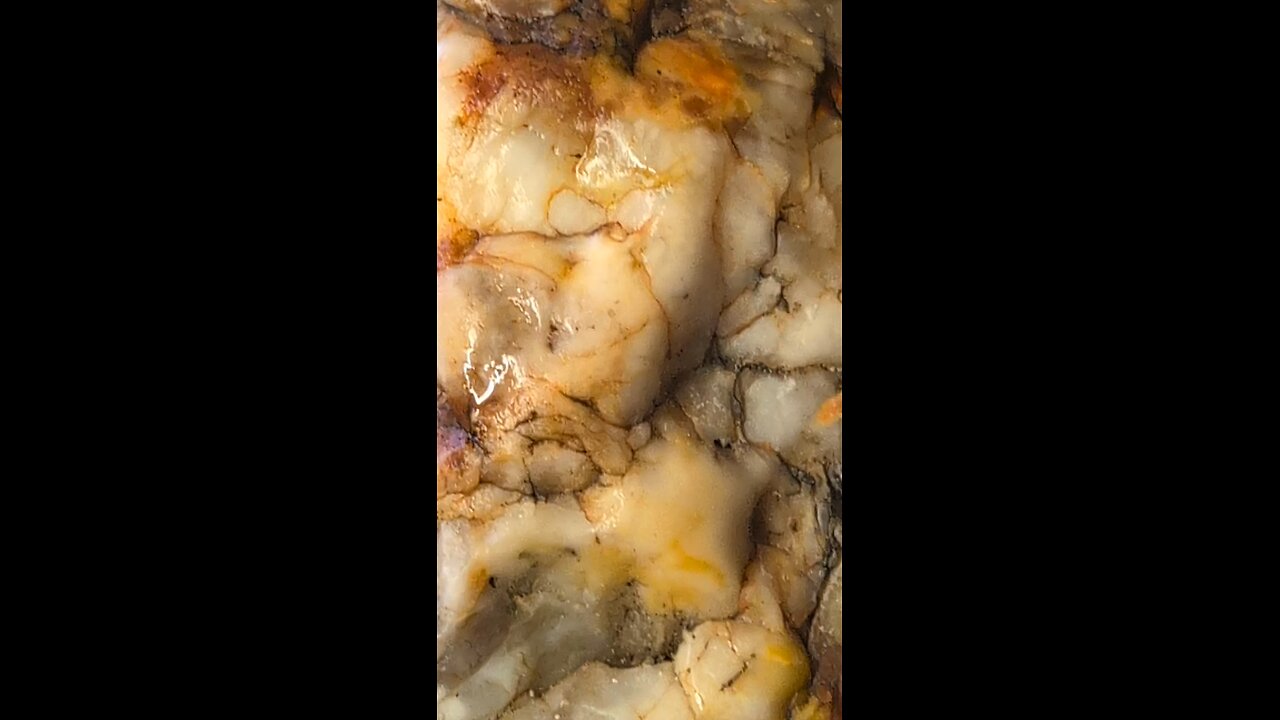
Agate chunk!
Agate is a microcrystalline variety of quartz, specifically a form of chalcedony, known for its fine grain and bright color patterns. Here are some key points about agate:
Formation: Agate forms in volcanic and sedimentary rocks. It often begins as a cavity in the rock, which then gets filled with layers of silica-rich water. Over time, this solution deposits minerals in layers, creating the characteristic banding of agate. This process can take millions of years.
Appearance: Agate is famous for its beautiful, often banded patterns of color, which can range from translucent to opaque. Colors include white, blue, red, black, yellow, and brown among others, with the patterns formed by the successive layers of chalcedony being deposited. Sometimes, agates can be found with inclusions like moss (moss agate) or even fossils.
Types of Agate:
Banded Agate: Shows clear, concentric bands of color.
Moss Agate: Contains mineral inclusions that look like moss or foliage.
Dendritic Agate: Similar to moss agate but with tree-like or branch-like patterns.
Fire Agate: Contains iridescent layers that appear to glow with fiery colors.
Lace Agate: Features lace-like patterns, most notably in Blue Lace Agate from Namibia.
Crazy Lace Agate: Known for its wild, chaotic patterns of colors.
Locations: Agates are found worldwide, but some of the most famous locations include Brazil, Uruguay, Mexico, Germany, Madagascar, and the United States (particularly in Oregon, Washington, and Idaho).
Uses:
Jewelry: Due to its beauty when polished, agate is widely used in jewelry like rings, pendants, and beads.
Decorative Items: Larger pieces or slices are used for decorative objects, bookends, or as display pieces.
Metaphysical: In metaphysical practices, agate is believed to have various healing properties, like balancing physical, emotional, and intellectual energy, and promoting strength and courage.
Cultural Significance: Agate has been used since ancient times; it was prized in Ancient Egypt for amulets and seals, in Greece and Rome for intaglios and cameos, and by many other cultures for its beauty and supposed protective qualities.
Cutting and Polishing: When cutting agate for jewelry or display, lapidaries look for the most visually appealing patterns. The process involves sawing, grinding, and polishing to bring out the internal beauty of the stone.
Agate's diversity in color and pattern, combined with its durability, makes it one of the most sought-after stones in the world of gemology and mineral collecting.
-
 59:11
59:11
The Rubin Report
2 hours agoWatch the Moment Charlamagne tha God Realizes Dems Have Been Lying the Whole Time
39.3K34 -
 3:32:27
3:32:27
Right Side Broadcasting Network
23 hours agoLIVE REPLAY: RSBN Post-Inauguration Coverage - 1/22/25
113K12 -
 LIVE
LIVE
LFA TV
17 hours ago$3 TRILLION IN 3 DAYS! | LIVE FROM AMERICA 1.22.25 11am
6,116 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
Grant Stinchfield
1 hour agoD.C. Judge Defies Trump! J6ers Still Being Held Hostage Despite Pardon!
366 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
The Shannon Joy Show
2 hours ago🔥🔥WARP SPEED 2.0 On Steroids! Trump Announces STARGATE ‘The LARGEST AI Infrastructure Project In History’ To Expand mRNA Tech & Surveillance🔥🔥
433 watching -
 33:41
33:41
Tudor Dixon
2 hours agoDementia: A Growing Concern for America | The Tudor Dixon Podcast
3.16K -
 12:50
12:50
Dr David Jockers
2 hours ago $0.67 earnedThe Truth About Seed Oils! Very Simple HACKS You Need To Know
9.99K -
 1:16:59
1:16:59
Caleb Hammer
2 hours agoMail-Order Bride Hates Her New Husband | Financial Audit
19.7K1 -
 LIVE
LIVE
MYLUNCHBREAK CHANNEL PAGE
18 hours agoThe Old World Marathon #1
1,017 watching -
 1:15:47
1:15:47
Graham Allen
4 hours agoNBC ATTACKS Pete Hegseth Just Before his Confirmation!! + Woke Bishop LECTURES Trump!
108K88