Premium Only Content
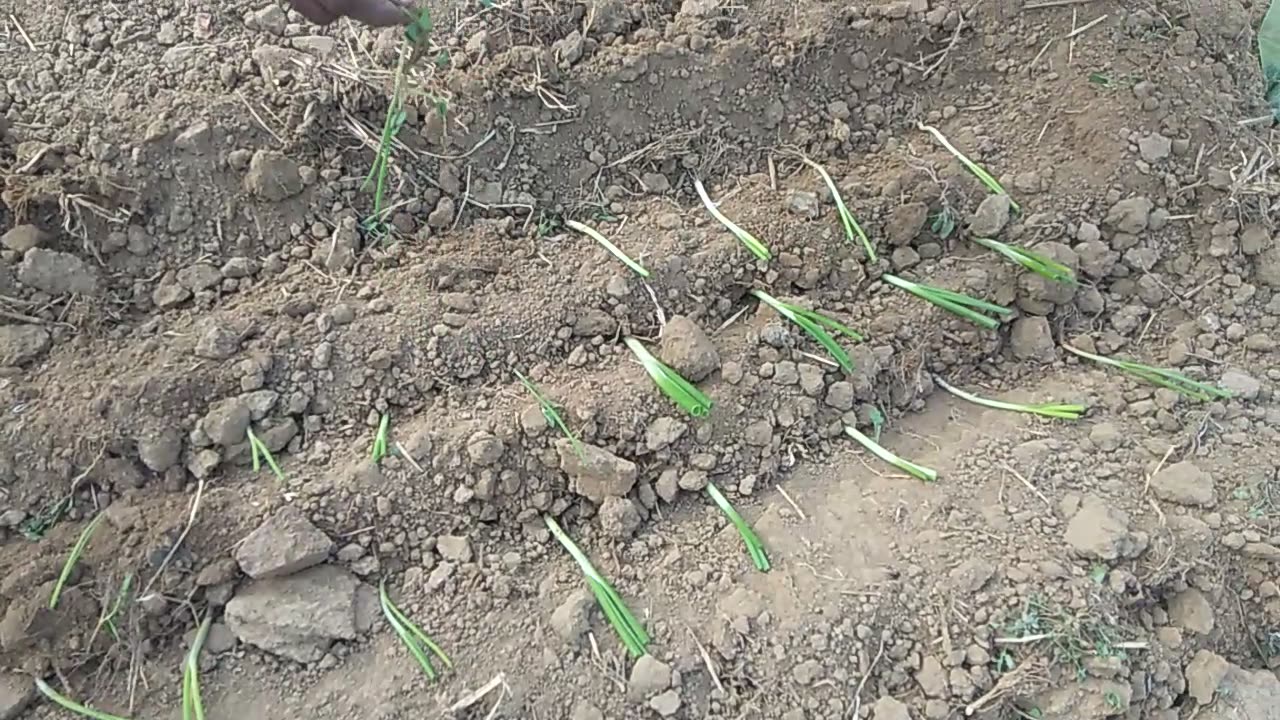

Onion farming in India
Onion farming in India is a significant agricultural activity, given the vegetable's widespread use in Indian cuisine. India is the second-largest producer of onions in the world, following China. Here's a detailed overview of onion farming in India:
---
### **Major Onion-Producing States**
1. **Maharashtra**: The largest producer, accounting for around 30-35% of India's total production.
2. **Karnataka**: Known for producing both kharif (monsoon) and rabi (winter) onions.
3. **Madhya Pradesh**: A key player in onion production, especially for domestic markets.
4. **Rajasthan**: Significant production due to its sandy soil and climatic conditions.
5. **Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar**: Other contributing states.
---
### **Varieties of Onions**
1. **Red Onions**: Dominant in India and used for domestic consumption.
2. **White Onions**: Primarily grown for export and industrial purposes.
3. **Pink Onions**: Grown in smaller quantities, especially in certain regions like Karnataka.
---
### **Seasonal Classification**
1. **Kharif (Monsoon)**: Sown in July-August and harvested in October-December.
2. **Late Kharif**: Sown in September-October and harvested in January-February.
3. **Rabi (Winter)**: Sown in October-November and harvested in March-May.
---
### **Climate and Soil Requirements**
- **Climate**: Onions require moderate temperatures (13°C to 24°C) during growth and dry conditions during bulb maturity.
- **Soil**: Well-drained sandy loam to clay loam soils with a pH of 6.0–7.5 is ideal.
---
### **Farming Practices**
1. **Land Preparation**: Deep plowing and leveling of land to ensure proper drainage.
2. **Seed Selection**: High-yield varieties like N-53, Agrifound Light Red, and Arka Kalyan are commonly used.
3. **Irrigation**: Regular watering is required, but over-irrigation can cause fungal diseases.
4. **Fertilizers**: Balanced application of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium is critical for growth.
---
### **Challenges in Onion Farming**
1. **Price Fluctuations**: Seasonal supply-demand imbalances often lead to volatility in onion prices.
2. **Storage Issues**: Onions are prone to sprouting and rotting if not stored in proper ventilated facilities.
3. **Pests and Diseases**:
- Pests: Thrips and onion flies.
- Diseases: Purple blotch, downy mildew, and stemphylium blight.
4. **Weather Dependence**: Unseasonal rains or drought can severely affect production.
---
### **Government Support and Policies**
1. **Market Intervention**: The government sometimes procures onions to stabilize prices.
2. **Export Policies**: India regulates onion exports based on domestic market conditions to prevent shortages.
3. **Subsidies**: Farmers receive subsidies for improved storage infrastructure and quality seeds.
4. **National Horticulture Mission (NHM)**: Provides support for onion production and post-harvest management.
---
### **Opportunities in Onion Farming**
1. **Value Addition**: Processing onions into powder, flakes, or paste for extended shelf life and better marketability.
2. **Export Market**: India exports onions to Gulf countries, Bangladesh, Malaysia, and Sri Lanka.
3. **Organic Onions**: Increasing demand for organic produce offers premium pricing.
---
Let me know if you'd like details about a specific aspect, such as disease control, marketing strategies, or storage solutions.
-
 LIVE
LIVE
Tucker Carlson
1 hour agoThe Pentagon Didn’t Fire Dan Caldwell Over Leaks. They Fired Him for Opposing War With Iran.
8,843 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
The Jimmy Dore Show
2 hours agoHillary Calls for Imprisoning Hillary! Rogan MOCKS Douglas Murray! w/ Kari Simpson & Katie Pasitney
13,493 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
JustPearlyThings
1 hour agoHigh Value Men Are Happy With Wives That Are Mid (Call-in Show) | Pearl Daily
492 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
megimu32
1 hour agoON THE SUBJECT: Mixtapes, Mosh Pits & Mistakes: How 90s Rock Raised Us
195 watching -
 58:57
58:57
Donald Trump Jr.
4 hours agoAmerica First, Always. Interviews with Ned Ryun & Kenny Cody | TRIGGERED Ep.235
72K59 -
 52:11
52:11
BonginoReport
4 hours agoDHS Sec Noem ROBBED By Masked Man on Easter - Nightly Scroll w/ Hayley Caronia (Ep.31)
65.7K57 -
 1:13:46
1:13:46
Kim Iversen
4 hours agoKlaus Schwab Steps Down—But the WEF Agenda Marches On
53.9K76 -
 1:24:34
1:24:34
vivafrei
6 hours agoVan Hollen's Tax-Payer Funded Vacay! Canada Liberals are Absolutely INSANE! Hegseth Hit Piece & MORE
80.7K26 -
 55:55
55:55
LFA TV
1 day agoEurope’s Religious Revival | TRUMPET DAILY 4.21.25 7PM
21.2K -
 LIVE
LIVE
Quite Frankly
6 hours ago"Death of Pope Francis, Klaus Retires, Easter Review" 4/21/25
1,039 watching