Premium Only Content
Lead-Based Paint Training
Lead-Based Paint (LBP) Training focuses on educating workers about the hazards of lead in paint, safe practices for handling LBP, and compliance with regulations such as OSHA’s Lead Standard (**29 CFR 1926.62**) and the EPA's Renovation, Repair, and Painting (RRP) Rule. This training is crucial for construction, renovation, and maintenance professionals working in buildings constructed before 1978, when lead-based paint was commonly used.
---
### **Lead-Based Paint Training Outline**
#### **1. Introduction to Lead-Based Paint**
- **What is lead-based paint?**
- Paint containing lead to enhance durability and color vibrancy.
- Common in buildings constructed before 1978.
- **Why is LBP hazardous?**
- Lead exposure occurs when paint deteriorates, creating chips, dust, or fumes.
- Overview of regulatory requirements:
- OSHA Lead Standard (**29 CFR 1926.62**).
- EPA's Renovation, Repair, and Painting (RRP) Rule.
---
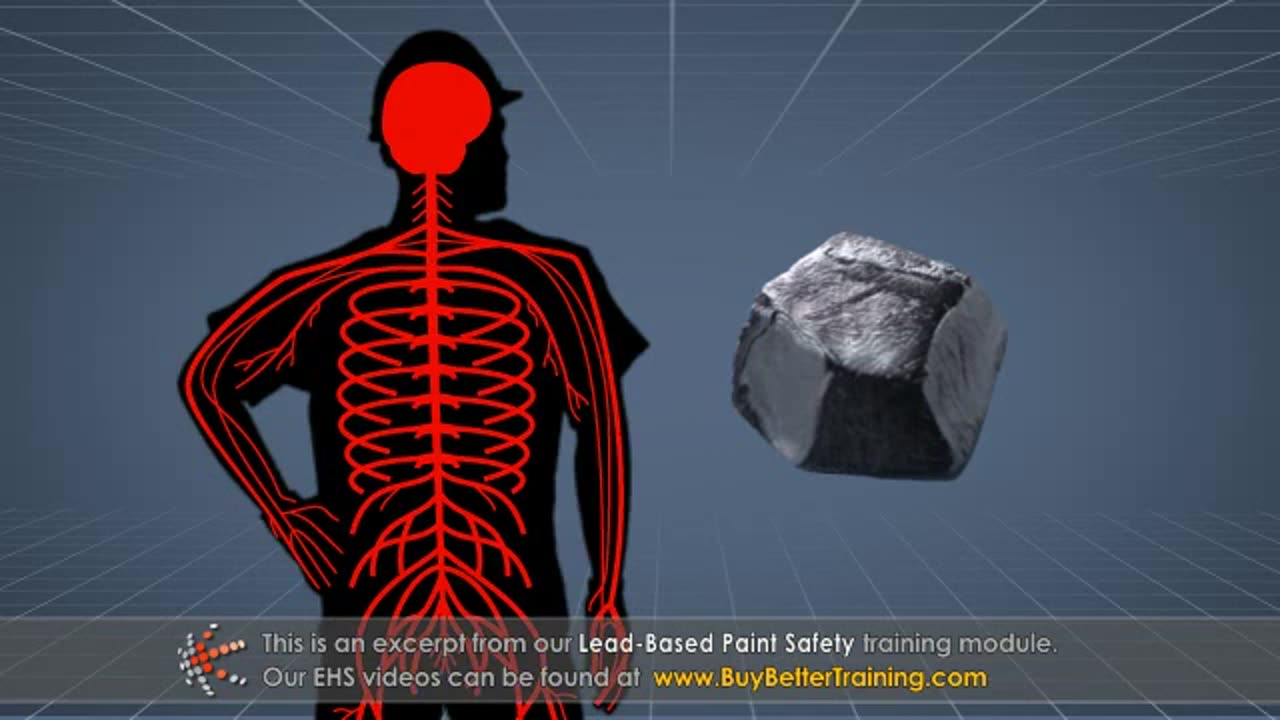
#### **2. Health Hazards of Lead Exposure**
- **How lead enters the body:**
- Inhalation of dust or fumes during sanding, cutting, or welding.
- Ingestion of lead-contaminated materials.
- **Health effects:**
- Short-term: Fatigue, headaches, and abdominal pain.
- Long-term: Damage to the nervous system, kidneys, and reproductive system.
- Increased risks for children and pregnant women exposed to lead dust.
---
#### **3. Recognizing Lead-Based Paint Hazards**
- Identifying potential LBP areas:
- Peeling, chipping, or cracking paint.
- Painted surfaces subject to friction (e.g., windows, doors).
- Testing for lead-based paint:
- Using EPA-approved test kits or certified inspectors.
- Reviewing Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for paint and coatings.
---
#### **4. Regulatory Compliance**
- Overview of the **EPA RRP Rule**:
- Certification requirements for contractors working with LBP.
- Worksite containment and cleaning standards.
- OSHA requirements for lead-safe practices:
- Monitoring and controlling exposure levels.
- Providing training, PPE, and medical surveillance.
---
#### **5. Controlling Lead-Based Paint Hazards**
- **Engineering controls:**
- Using wet methods to minimize dust.
- Employing HEPA-filtered vacuums for cleanup.
- **Work practice controls:**
- Avoiding dry scraping, sanding, or blasting.
- Using barriers to contain work areas and prevent dust spread.
- **Personal protective equipment (PPE):**
- Respirators, gloves, coveralls, and shoe covers.
- Ensuring proper fit and maintenance of PPE.
---
#### **6. Safe Work Practices**
- Preparing the worksite:
- Setting up containment barriers.
- Removing or covering furniture and belongings.
- Performing lead-safe work:
- Keeping surfaces damp during removal or repairs.
- Properly disposing of lead-contaminated debris and materials.
- Post-worksite cleanup:
- Thorough cleaning with HEPA vacuums and wet wipes.
- Verifying cleanliness with lead dust clearance testing.
---
#### **7. Housekeeping and Hygiene Practices**
- Preventing contamination:
- Separating work clothes from personal items.
- Avoiding eating, drinking, or smoking in work areas.
- Decontaminating after work:
- Washing hands and face thoroughly.
- Showering and changing clothes before leaving the site.
---
#### **8. Emergency Response and Exposure Procedures**
- How to respond to accidental exposure:
- Immediate decontamination of affected skin or eyes.
- Reporting incidents to supervisors and seeking medical attention.
- Managing unexpected lead hazards:
- Stopping work and notifying trained personnel.
---
#### **9. Roles and Responsibilities**
- **Employer responsibilities:**
- Provide proper training, equipment, and medical surveillance.
- Ensure compliance with OSHA and EPA regulations.
- **Employee responsibilities:**
- Follow lead-safe work practices and use PPE correctly.
- Report unsafe conditions or potential hazards.
---
#### **10. Practical Exercises and Demonstrations**
- Setting up a lead-safe worksite:
- Containment barriers, proper signage, and restricted zones.
- Hands-on practice:
- Using PPE, HEPA vacuums, and wet methods.
- Simulating safe removal or repair of LBP surfaces.
- Role-playing emergency response procedures.
---
#### **11. Quiz and Certification**
- Knowledge assessment to test comprehension.
- Issuance of certificates for participants who complete the training successfully.
---
Would you like to customize this training for your specific team, create materials, or explore certification options?
-
 7:58
7:58
HSESafetyInformation
7 days agoAuthentic Peshawari Rosh _ Namkeen Gosht Recipe __ Traditional KPK and Baluchistan
441 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Wendy Bell Radio
6 hours agoThe Party's Over
12,754 watching -
 45:46
45:46
Randi Hipper
1 hour agoBitcoin CRASHES to 3 month low! Crypto investors BEWARE
6.48K1 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Conspiracy Pilled
12 hours agoAvowed
89 watching -
 5:31
5:31
Adam Does Movies
23 hours ago $3.00 earnedThe Monkey Movie Review - This Is From The Longlegs Director?
32.9K3 -
 14:47
14:47
Tactical Considerations
16 hours ago $3.99 earnedClassic Precision Woox Furiosa Bergara Premier 6.5 CREED
36.4K1 -
 40:44
40:44
Rethinking the Dollar
1 day agoDonald & Elon Head to Fort Knox—What Are They Planning?
25.6K24 -
 1:10:15
1:10:15
MTNTOUGH Fitness Lab
1 day ago"My Baseball Career Wasn't Enough": Adam LaRoche's Life-Changing Anti-Trafficking M
20.8K4 -
 1:00:12
1:00:12
The Tom Renz Show
20 hours agoComing to America & Coming to Christ
48.8K7 -
 1:12:21
1:12:21
TheRyanMcMillanShow
1 day ago $0.58 earnedDebbie Lee: Mother of First Navy Seal Killed In Iraq, Marc Lee - RMS 019
22.2K1