Premium Only Content
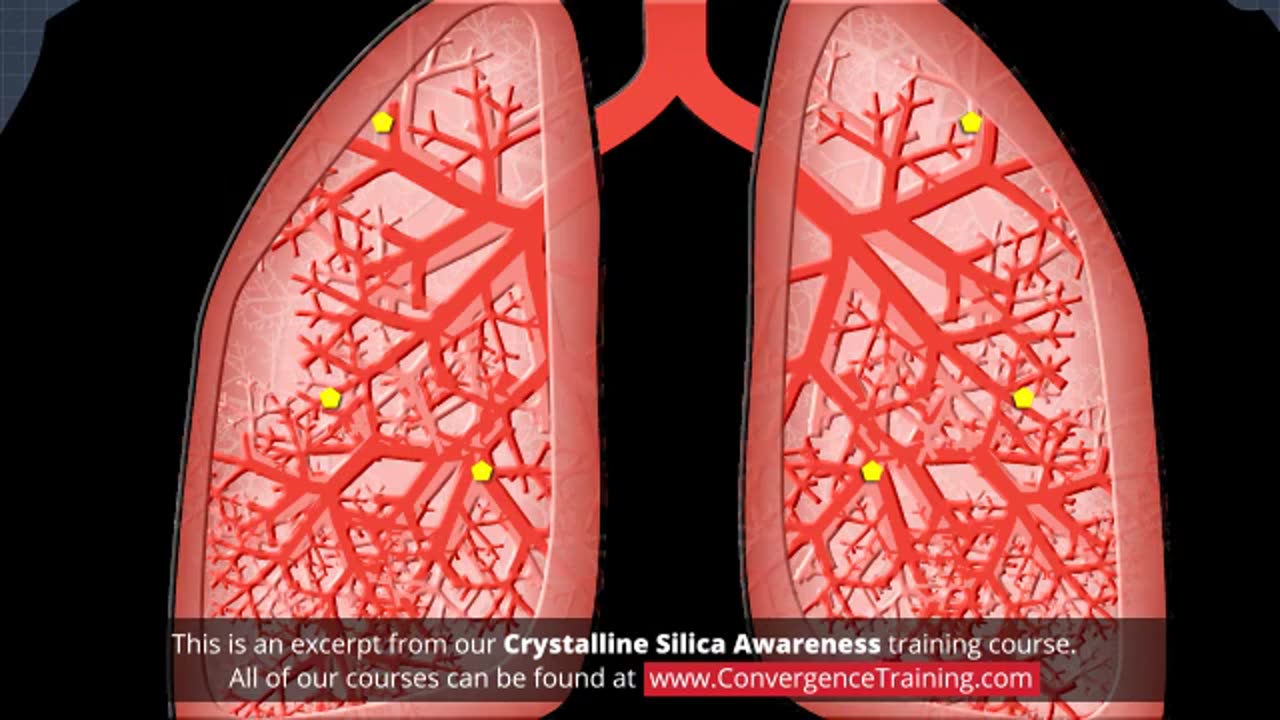
Crystalline Silica Awareness
### **Crystalline Silica Awareness Training**
Crystalline silica is a naturally occurring mineral found in materials like sand, concrete, and stone. Exposure to silica dust can pose significant health risks, including silicosis, lung cancer, and other respiratory diseases. Crystalline silica awareness training is critical for workers in industries like construction, mining, and manufacturing.
---
### **Training Objectives**
- Understand what crystalline silica is and its common sources.
- Recognize the hazards and health effects of silica exposure.
- Learn about workplace controls and personal protective measures.
- Familiarize with OSHA regulations and safety practices for crystalline silica.
---
### **Course Content**
#### **1. Introduction to Crystalline Silica**
- **What is Crystalline Silica?**
- A mineral found in quartz, granite, and other materials.
- Commonly released as fine dust during cutting, grinding, or drilling.
- **Common Work Activities that Produce Silica Dust:**
- Construction (concrete cutting, demolition, sanding).
- Mining and quarrying.
- Glass, ceramics, and foundry operations.
---
#### **2. Hazards of Crystalline Silica**
- **Health Effects:**
- **Silicosis:** An incurable lung disease caused by inhaling silica dust.
- **Lung Cancer:** Prolonged exposure increases the risk.
- **Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD).**
- Kidney disease and other systemic health issues.
- **Routes of Exposure:**
- Inhalation of airborne particles.
- Risk increases with prolonged exposure and lack of protective measures.
---
#### **3. OSHA Regulations**
- **Permissible Exposure Limits (PELs):**
- OSHA's standard for crystalline silica exposure (50 µg/m³ as an 8-hour time-weighted average).
- **Medical Surveillance:**
- Employers must provide health screenings for workers exposed above action levels.
- **Written Exposure Control Plan:**
- Requirement for employers to identify and mitigate silica hazards.
---
#### **4. Identifying Silica Hazards**
- Recognizing tasks and environments with high silica exposure.
- Using monitoring equipment to measure airborne silica levels.
- Reviewing Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for materials containing silica.
---
#### **5. Engineering Controls**
- **Dust Suppression Methods:**
- Use water or wet cutting methods to reduce dust.
- **Ventilation Systems:**
- Local exhaust ventilation (LEV) to capture dust at the source.
- **Enclosures:**
- Using barriers or isolation methods to limit worker exposure.
---
#### **6. Safe Work Practices**
- Minimizing dust generation during tasks.
- Avoiding dry sweeping or using compressed air for cleanup.
- Maintaining equipment to prevent dust release.
- Limiting time spent in high-exposure areas.
---
#### **7. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)**
- **Respiratory Protection:**
- Use NIOSH-approved respirators (e.g., N95 masks) when engineering controls are insufficient.
- **Eye and Skin Protection:**
- Goggles and protective clothing to prevent silica dust contact.
---
#### **8. Housekeeping and Maintenance**
- Proper cleaning methods:
- HEPA-filtered vacuum systems.
- Wet cleaning techniques.
- Regular maintenance of dust control systems and PPE.
---
#### **9. Emergency Response and Reporting**
- Recognizing signs of silica overexposure:
- Shortness of breath, coughing, chest pain.
- Reporting unsafe conditions or equipment failures immediately.
- First aid and medical attention for acute exposure incidents.
---
### **Practical Component**
- **Demonstration:**
- Proper use of water suppression and vacuum systems.
- Correct fitting and usage of respirators.
- **Interactive Scenarios:**
- Identifying silica hazards in workplace simulations.
- Practicing safe work practices in mock setups.
---
### **Employee Responsibilities**
- Attend regular training and refreshers.
- Follow workplace safety protocols.
- Use and maintain PPE correctly.
- Report unsafe practices or equipment malfunctions.
---
### **Employer Responsibilities**
- Conduct regular exposure monitoring and risk assessments.
- Provide necessary engineering controls and PPE.
- Offer medical surveillance and maintain training records.
- Develop and implement an exposure control plan.
---
### **Certification**
Participants typically complete a short quiz and practical exercise to earn a certificate of awareness.
Would you like help designing a detailed training program, creating visual materials, or preparing a written exposure control plan for silica?
-
 1:01:26
1:01:26
PMG
8 hours ago $4.61 earnedLibs In FULL PANIC Since Trump Took Office! Creating a Faith to Fit their Agenda
39.4K9 -
 7:09:22
7:09:22
Dr Disrespect
16 hours ago🔴LIVE - DR DISRESPECT - TRIPLE THREAT CHALLENGE - EXTREME EDITION
266K33 -
 55:00
55:00
LFA TV
16 hours agoThe End of the January 6 Hoax | TRUMPET DAILY 1.22.25 7pm
54K12 -
 1:13:37
1:13:37
Battleground with Sean Parnell
14 hours agoPresident Trump Is On FIRE w/ Savage Rich Baris
191K33 -
 1:59:59
1:59:59
Melonie Mac
10 hours agoGo Boom Live Ep 34!
83.2K14 -
 49:27
49:27
Sarah Westall
9 hours agoTrillion Dollar 5G Lawsuit, Project Archimedes, Mind Control & DEW Weapons w/Attorney Todd Callender
83.3K39 -
 53:11
53:11
Standpoint with Gabe Groisman
1 day agoTrump Is Crucial For Hostage Agreement Says Israeli Colonel
59.1K5 -
 1:01:22
1:01:22
Anthony Pompliano
1 day ago $1.68 earnedTrump Inauguration Sends Bitcoin Flying
41.3K4 -
 15:21
15:21
LFA TV
17 hours agoWHY GOLD WILL CONTINUE TO SKYROCKET
28.8K4 -
 1:31:40
1:31:40
MTNTOUGH Fitness Lab
11 hours agoThe Power of Brotherhood: How Vulnerability and Grit Shape Resilient Men with Thosh Collins
43.9K2