Premium Only Content
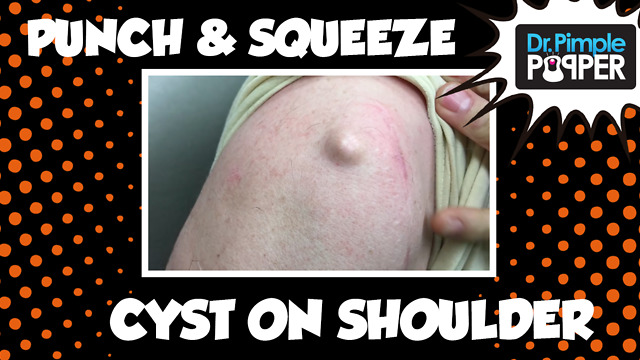
Epidermoid Cyst on the Shoulder Excised - The Size of a Marble
This patient came in to see more for this bump on his shoulder that was growing larger. He wanted to have it removed, and was so nice to allow us to film it so you all could see it removed as well. I suspected that this one would come out easily since it had never been inflamed or even had been squeezed.
Thank you for watching!!
An epidermoid cyst (Epidermal Inclusion cyst, Infundibular cyst), is a benign growth commonly found in the skin and typically appears on the face, neck or trunk, but can occur anywhere on the body. Another name used is “sebacous cyst” but this is actually an antiquated misnomer, and is not a term used by dermatologists. They are also the most common type of cutaneous cysts. Epidermoid cysts result from the reproduction of epidermal cells within a confined space of the dermis. The pasty contents are mostly composed of macerated keratin (wet skin cells), which creates this “cheesy” consistency, and there can be a pungent odor. An epidermoid cyst may have no symptoms and are typically harmless. Usually people seek removal but they don’t like the appearance of these bumps, or the cyst has ruptured or been inflamed or “infected” in the past. Rupture is associated with sudden redness, pan, swelling, and local heat, and can lead to abscess formation. Also, a history of inflammation, often increases scar tissue in the area, makes the cyst more firmly adherent to surrounding skin, and makes it more difficult to remove. Surgical excision is curative, but the complete cyst removal including the entire cyst sac and contents need to be removed to ensure that the cyst won’t reoccur.
For more content, exclusive content, and of course to get your Dr. Pimple Popper schwag, visit us at www.drpimplepopper.com!
Instagram:
@DrPimplePopper for 24/7 pops
@DrSandraLee for my work, my life, my pops
Facebook: Dr Sandra Lee
Twitter: @SandraLeeMD
Snapchat: drpimplepopper
Periscope: Dr. Sandra Lee
This video may contain dermatologic surgical and/or procedural content. The content seen in this video is provided only for medical education purposes and is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
-
 0:14
0:14
Torric714
3 years agoShoulder cat
28 -
 1:58
1:58
CortlandStoneDesign
3 years agoMarble Clouds
24 -
 17:47
17:47
Home Décor
3 years agoDIY Marble Table- Elegant Marble Table
19 -
 0:17
0:17
danielTTT
3 years agoinjured shoulder
63 -
 0:06
0:06
alfonsosnap
4 years agoA big marble
51 -
 1:15
1:15
Marat23
3 years agoShoulder tri set
46 -
 0:35
0:35
punchfoster
4 years agoMarble fun
1991 -
 1:44
1:44
STLNutritionDoc
3 years agoDB shoulder press
49 -
 1:03
1:03
STLNutritionDoc
3 years agoMachine shoulder press
26 -
 4:16
4:16
8FooToad
3 years agoMarble Elimination
79