Premium Only Content
DC Motor Operation
### **DC Motor Operation: Understanding How It Works**
A **DC motor** (Direct Current motor) is a type of electric motor that operates on direct current (DC) electricity. It converts electrical energy into mechanical energy through the interaction of magnetic fields. DC motors are commonly used in applications that require precise speed control and variable speed, such as in electric vehicles, tools, and robotics. Below is an overview of how a DC motor operates, its components, and key principles.
---
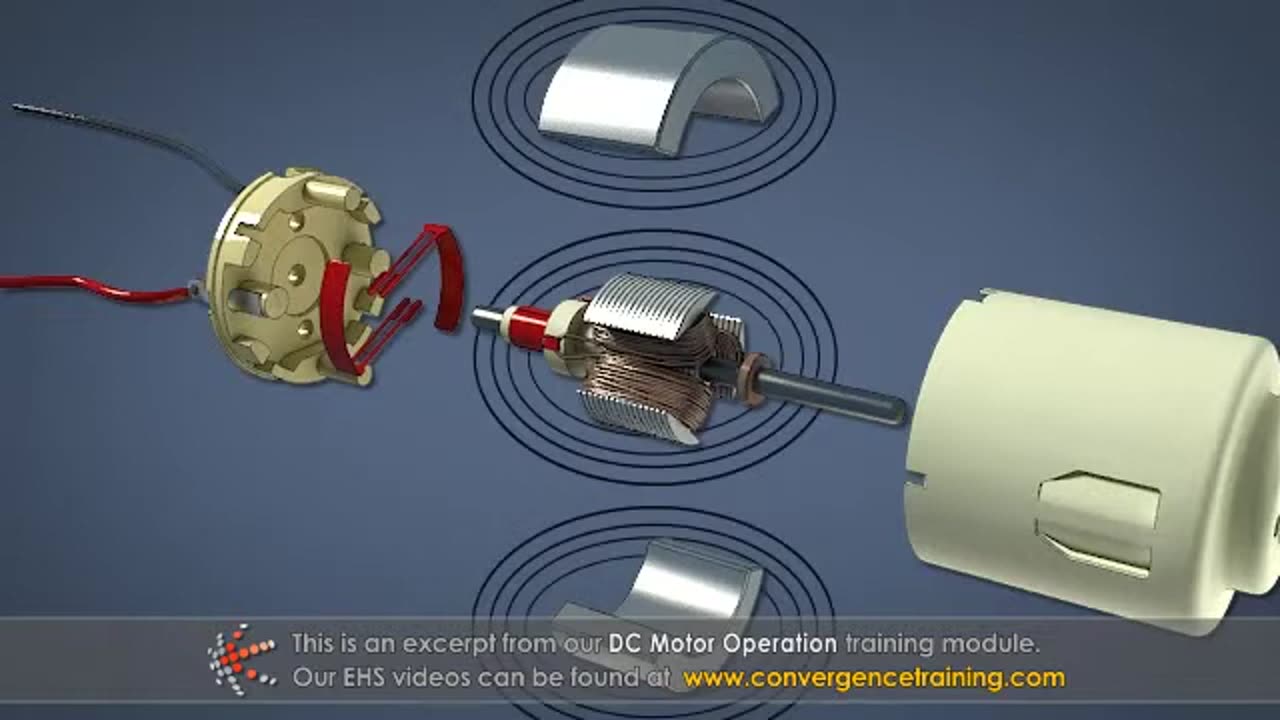
### **1. Basic Components of a DC Motor**
A DC motor consists of several key components that work together to produce rotational motion:
#### **A. Stator**
- **Function:** The stationary part of the motor that produces a magnetic field. In a simple DC motor, the stator can be either a permanent magnet or an electromagnet.
- **In the case of electromagnets:** It consists of field coils that are powered by a DC supply to create a magnetic field.
#### **B. Rotor (Armature)**
- **Function:** The rotating part of the motor that is attached to a shaft. The rotor is made of windings (usually copper) that carry the current and interact with the stator's magnetic field.
- **Structure:** The rotor is typically made up of laminated sheets to reduce energy loss due to eddy currents.
#### **C. Commutator**
- **Function:** A rotary switch that reverses the current direction in the rotor windings. This ensures that the rotor continues to rotate in the same direction.
- **Structure:** It is a split ring made of copper and mounted on the motor shaft. Brushes maintain contact with the commutator.
#### **D. Brushes**
- **Function:** Conduct electrical current between the rotating armature and the stationary commutator. They are made of carbon or graphite to ensure smooth current transfer with minimal wear.
- **Maintenance:** Brushes wear over time and need to be replaced periodically.
#### **E. Shaft**
- **Function:** The central rod that transmits mechanical motion from the rotor to the load (e.g., a fan, conveyor belt, or pump).
---
### **2. How a DC Motor Operates**
The operation of a DC motor is based on **electromagnetic induction** and the interaction between the magnetic fields of the stator and rotor. The steps are as follows:
#### **A. Magnetic Field Generation**
- When the motor is connected to a power source, current flows through the armature windings (rotor), creating a magnetic field around the rotor.
#### **B. Interaction of Magnetic Fields**
- The magnetic field of the rotor interacts with the magnetic field of the stator (created by either permanent magnets or electromagnets). This interaction produces a **force** on the rotor, causing it to rotate (according to **Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule**).
#### **C. Commutator Action**
- As the rotor turns, the commutator reverses the direction of current flow in the armature windings. This ensures that the magnetic field of the rotor continuously interacts with the stator's magnetic field in such a way that the rotor keeps rotating in the same direction. Without the commutator, the rotor would stop after half a turn due to the magnetic fields opposing each other.
#### **D. Rotor Rotation**
- The continuous reversal of current in the rotor windings, facilitated by the commutator, allows the rotor to keep rotating. The force produced by the interaction of the magnetic fields between the rotor and stator causes the rotor to rotate continuously.
#### **E. Output Motion**
- The mechanical energy produced by the rotor’s rotation is transmitted through the shaft to the load (e.g., turning a fan blade or driving a conveyor belt).
---
### **3. Types of DC Motors**
There are several types of DC motors, each with unique features and applications:
#### **A. Brushed DC Motors**
- **Description:** These motors use brushes to make contact with the commutator to deliver current to the armature.
- **Applications:** Used in toys, household appliances, and small power tools.
#### **B. Brushless DC Motors (BLDC)**
- **Description:** These motors use a permanent magnet rotor and an electronically controlled commutator (via a controller) instead of brushes and mechanical commutators. They are more efficient and require less maintenance.
- **Applications:** Found in computer hard drives, electric vehicles, drones, and precision machinery.
#### **C. Permanent Magnet DC Motors (PMDC)**
- **Description:** The stator of these motors consists of permanent magnets instead of electromagnets. They offer better efficiency and compact design.
- **Applications:** Used in automotive applications, fans, and small machinery.
#### **D. Series DC Motors**
- **Description:** In a series DC motor, the armature and field windings are connected in series. The current through both is the same.
- **Applications:** These are used in applications requiring high starting torque, such as electric trains and cranes.
#### **E. Shunt DC Motors**
- **Description:** In a shunt DC motor, the field windings are connected in parallel (shunt) to the armature. This configuration provides a more consistent speed under varying load conditions.
- **Applications:** Often used in industrial applications where constant speed is needed.
#### **F. Compound DC Motors**
- **Description:** A compound motor combines the features of both series and shunt motors. It provides both high starting torque and constant speed.
- **Applications:** Used in elevators, conveyor belts, and other industrial machinery.
---
### **4. Control of DC Motor Speed**
The speed of a DC motor can be controlled by adjusting several parameters:
#### **A. Voltage Control**
- Increasing or decreasing the voltage supplied to the motor changes the speed. Higher voltage results in a higher speed, and lower voltage results in a slower speed.
#### **B. Field Control**
- The speed of a DC motor can also be controlled by varying the current in the field windings (stator). Reducing the current in the field windings will increase the speed of the motor.
#### **C. Armature Control**
- By controlling the current in the armature windings (rotor), the speed can be adjusted. This method is more commonly used in industrial applications where precise speed control is required.
#### **D. Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)**
- PWM is a modern technique used for controlling the speed of DC motors in a more efficient way. It involves adjusting the duration of the voltage applied to the motor, controlling the motor’s average power and, therefore, its speed.
---
### **5. Advantages and Disadvantages of DC Motors**
#### **Advantages:**
- **Precise Speed Control:** DC motors are known for their ability to provide precise control over speed and direction, making them ideal for applications where accuracy is essential.
- **Simple Construction:** Their simple design makes them cost-effective for many applications.
- **High Starting Torque:** DC motors offer high starting torque, which is useful in many applications requiring quick starts.
#### **Disadvantages:**
- **Brush Maintenance:** Brushed DC motors require regular maintenance, as brushes wear out over time and need to be replaced.
- **Less Efficiency (Brushed Motors):** Brushed DC motors are less efficient due to friction and heat generation from the brushes.
- **Noise and Wear:** The commutator and brushes can create electrical noise and mechanical wear, which reduces the motor's lifespan.
---
### **Conclusion**
A **DC motor** is a versatile and widely used motor that provides reliable and efficient mechanical power in various applications. Whether you're using a brushed or brushless DC motor, understanding the motor's operation, components, and control methods will help you select the right motor for your application and optimize performance. With their ability to provide precise control over speed and torque, DC motors are invaluable in many industries, including automotive, robotics, and consumer electronics.
-
 7:58
7:58
HSESafetyInformation
1 month agoAuthentic Peshawari Rosh _ Namkeen Gosht Recipe __ Traditional KPK and Baluchistan
581 -
 59:50
59:50
Motherland Casino
4 hours agoMel x Zofie
24.3K4 -
 44:54
44:54
Ami's House
2 days agoThe Dave Smith Debate is Broken. Here's a Better Way In | Dave's Rogan Appearance
48.4K7 -
 3:47:20
3:47:20
SlingerGames
5 hours agoDiving (get it?) Back Into Subnautica!
27.4K1 -
 58:35
58:35
BonginoReport
10 hours agoFormer Trans Athlete Accepts Biological Reality - Nightly Scroll w/Hayley Caronia (Ep.24) - 04/10/25
153K93 -
 2:48:38
2:48:38
The Sufari Hub
5 hours ago🔴NOT ENDING STREAM TILL I WIN - ROAD TO #1 GAMER ON RUMBLE - #RumbleGaming
12.6K1 -
 1:49:21
1:49:21
Joker Effect
5 hours ago250$$ Giveaway! MOTHERLAND TAKEOVER!
26.1K -
![🔴 MAFIA III [first look]](https://1a-1791.com/video/fww1/21/s8/1/V/_/U/A/V_UAy.0kob-small--MAFIA-III-first-look.jpg) 3:01:30
3:01:30
Fragniac
1 day ago🔴 MAFIA III [first look]
15.8K2 -
 2:06:26
2:06:26
megimu32
8 hours agoON THE SUBJECT: Movies We Had Zero Business Watching.. But Totally Did!
29.2K2 -
 2:02:59
2:02:59
Precision Rifle Network
2 days agoS4E12 Guns & Grub Live - Guns, Politics, & Training
13.5K