Premium Only Content
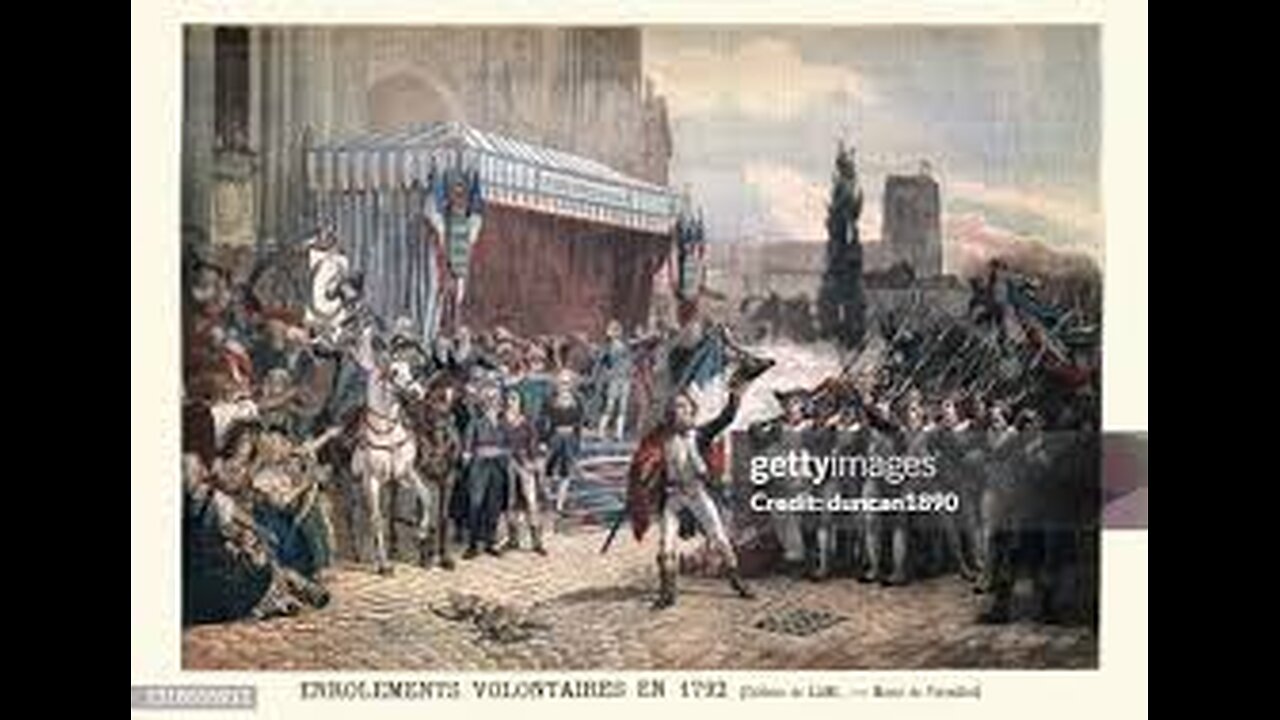

Civilization of France
The civilization of France is rich and diverse, marked by a history of cultural, artistic, and intellectual achievements. Here are some key aspects:
Historical Overview
Ancient and Medieval Era: The region now known as France was inhabited by various Celtic tribes before becoming part of the Roman Empire. After the fall of Rome, the Frankish kingdom emerged, laying the groundwork for modern France.
Feudalism: During the Middle Ages, France developed a feudal system, with powerful nobles, the rise of towns, and the influence of the Catholic Church.
Renaissance and Enlightenment: The Renaissance brought a flourishing of arts and sciences, with figures like François Rabelais and Leonardo da Vinci. The Enlightenment promoted ideas of liberty, reason, and secularism, contributing to revolutionary thought.
Cultural Contributions
Language: French is a Romance language that has influenced many languages worldwide. Literature in French includes works from renowned authors like Victor Hugo, Marcel Proust, and Simone de Beauvoir.
Art and Architecture: France has a profound artistic heritage, with contributions to painting, sculpture, and architecture. Iconic structures include the Gothic cathedrals, the Palace of Versailles, and modern works like the Pompidou Center. Artists such as Claude Monet, Edgar Degas, and Henri Matisse have left an indelible mark on global art.
Philosophy and Science
Philosophy: French philosophers, such as René Descartes, Voltaire, and Jean-Paul Sartre, have shaped Western thought on reason, ethics, and existence.
Scientific Achievements: France has contributed significantly to science and technology, with figures like Marie Curie in physics and chemistry, Louis Pasteur in microbiology, and Pierre-Simon Laplace in mathematics.
Political Landscape
Revolutions: France has experienced several revolutions, the most notable being the French Revolution (1789), which profoundly impacted democracy and human rights.
Republics and Empires: The nation has gone through multiple political regimes, including monarchies, empires, and republics, influencing the modern French state.
Contemporary Society
Multiculturalism: Modern France is characterized by a diverse population, with influences from former colonies in Africa, Asia, and the Caribbean.
Arts and Cinema: France is famous for its contributions to cinema, with celebrated filmmakers like François Truffaut and Jean-Luc Godard. The Cannes Film Festival is a prestigious global event.
Cuisine: French cuisine is renowned for its sophistication and regional diversity, including famed dishes, pastries, and wines. The culinary arts are an integral part of French culture.
Education and Intellectual Life
Education System: France has a strong emphasis on education, with a mix of public and private institutions. The education system is known for its rigor and focus on academic achievement.
Intellectualism: French intellectual life remains vibrant, with a tradition of philosophical inquiry and critical thinking.
Religion
Secularism: Although France is primarily a secular state, it has a rich religious history. The majority are Christian, but there is a significant Muslim population and various other faiths represented.
In summary, the civilization of France is characterized by its historical depth, cultural richness, and influence on global arts, philosophy, and politics. Its legacy continues to shape contemporary society both in France and beyond.
-
 LIVE
LIVE
The Quartering
2 hours agoAbsurd Epstein File Update, Trump Vs Supreme Court, Our Massive Giveaway, SodaGate & More!
47,162 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
Dr Disrespect
2 hours ago🔴LIVE - DR DISRESPECT - TARKOV - ZERO TO HERO RAIDS ONLY
3,170 watching -
 DVR
DVR
Sean Unpaved
2 hours agoMarch Madness Weekend Recap! Who Made It? Who Didn't?
6.77K1 -
 LIVE
LIVE
The White House
1 hour agoPresident Trump and the Governor of Louisiana Deliver Remarks
1,007 watching -
 15:39
15:39
T-SPLY
3 hours agoDemocrats Are Shocked to Find Out Americans Want Deportations
26 -
 1:02:58
1:02:58
Kyle Fortch
5 hours agoHeather Richardson: Proving Yourself As a Female On Tour, Netflix Secrets | THE ONE SHEET S1E9
91 -
 1:03:19
1:03:19
Timcast
2 hours agoMan DRIVES CAR Into Tesla Protesters, ARRESTED & Charged, DOJ THREATENS Arrestsc VIOLENCE Escalates
213K265 -

CryptoWendyO
48 minutes agoPREPARE FOR XRP’S NEXT BIG MOVE (3 HUGE ANNOUNCEMENTS)
1 -
 1:53:30
1:53:30
Steven Crowder
5 hours agoHow Rogue Judges Are Destroying MAGA & How Trump Can Stop Them
478K341 -
 1:30:41
1:30:41
Benny Johnson
3 hours ago🚨PANIC: DOJ Moves To LOCK-UP The Squad! Terrorism Charges For Libs | Snow White BOMBS, Trump Curse
82.8K102