Premium Only Content
Deriving Ceva's theorem from Menelaus's theorem | plane geometry | intermediate level
Episode 84.
Deriving Ceva's theorem from Menelaus's theorem | plane geometry | intermediate level.
Branch of mathematics: plane geometry.
Difficulty level: intermediate.
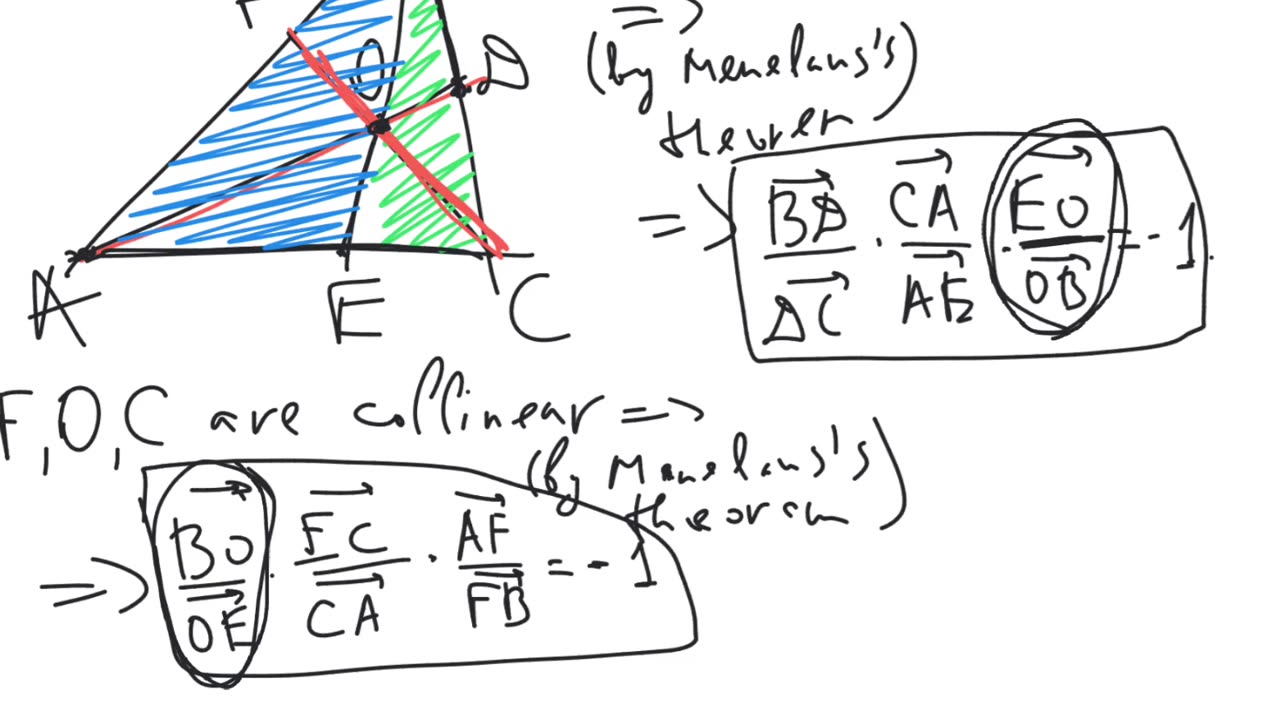
Ceva's theorem. Let $ABC$ be a triangle. Let $D$, $E$, $F$ be points on the lines $BC$, $CA$, $AB$ respectively. Then the lines $AD$, $BE$, $CF$ intersect at a single point or all 3 are parallel to each other if and only if $\frac{\overrightarrow{BD}}{\overrightarrow{DC}} \cdot \frac{\overrightarrow{CE}}{\overrightarrow{EA}} \cdot \frac{\overrightarrow{AF}}{\overrightarrow{FB}} = 1$.
Menelaus's theorem. Let $ABC$ be a triangle. Let $D$, $E$, $F$ be points on the lines $BC$, $CA$, $AB$ respectively. Then the points $D$, $E$, $F$ are collinear if and only if $\frac{\overrightarrow{BD}}{\overrightarrow{DC}} \cdot \frac{\overrightarrow{CE}}{\overrightarrow{EA}} \cdot \frac{\overrightarrow{AF}}{\overrightarrow{FB}} = -1$.
This video contains the proof of Ceva's theorem using Menelaus's theorem.
Mathematics. Geometry. Plane geometry.
#Mathematics #Geometry #PlaneGeometry
The same video on YouTube:
https://youtu.be/KyZlev9j--w
The same video on Telegram:
https://t.me/mathematical_bunker/108
-
 4:13:39
4:13:39
Nobodies Gaming
14 hours ago $35.68 earnedNobodies : Rumble Gaming MARVEL RIVALS
201K11 -
 24:08
24:08
MYLUNCHBREAK CHANNEL PAGE
1 day agoUnder The Necropolis - Pt 4
184K31 -
 19:52
19:52
Adam Does Movies
11 hours ago $5.44 earnedEmilia Pérez Movie Review - It's Uniquely Awful
53.2K3 -
 20:07
20:07
BlackDiamondGunsandGear
17 hours agoSPRINGFIELD ECHELON COMPACT / NOT GOOD
51.7K3 -
 1:05:06
1:05:06
Man in America
18 hours agoThe Terrifying Truth Behind Chemical Fog, Wildfire Smoke & Chemtrails w/ Dr. Robert Young
52.7K74 -
 2:54:47
2:54:47
Tundra Tactical
11 hours ago $16.83 earnedSHOT Show 2025 Wrap Up!! On The Worlds Okayest Gun Live Stream
87.2K5 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Right Side Broadcasting Network
1 day agoLIVE REPLAY: President Donald J. Trump Holds His First Rally After Inauguration in Las Vegas - 1/25/25
3,496 watching -
 2:55:24
2:55:24
Jewels Jones Live ®
1 day agoWEEK ONE IN REVIEW | A Political Rendezvous - Ep. 107
141K45 -
 1:33:29
1:33:29
Michael Franzese
1 day agoTrump Wastes No Time: Breaking Down Trump’s First Week Executive Orders | LIVE
148K124 -
 1:26:44
1:26:44
Tactical Advisor
20 hours agoTrump Starting Strong/Shot Show Recap | Vault Room Live Stream 015
105K9