Premium Only Content
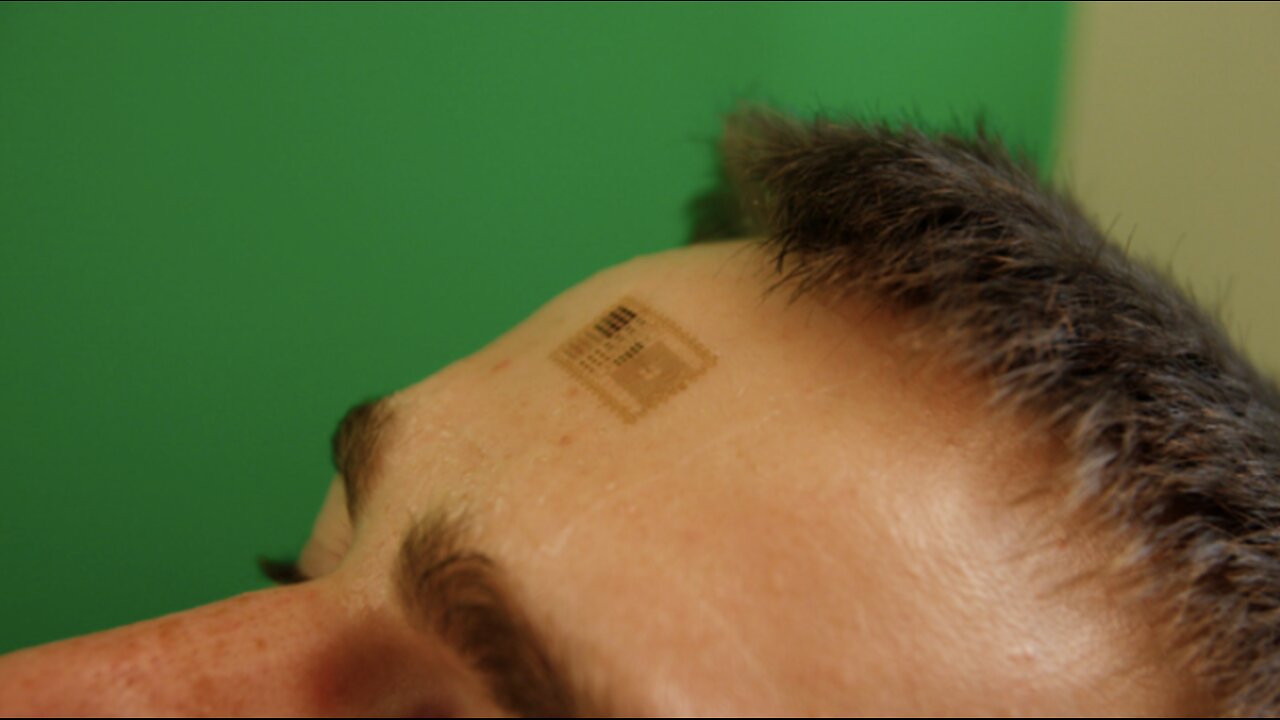
Electronic tattoos
E-tattoos
1)Ultra-thin and conformal: E-tattoos are often less than 100 micrometers thick, allowing them to seamlessly adhere to the skin without causing discomfort or irritation. 2)Biocompatibility: The materials used in e-tattoos are carefully selected to ensure compatibility with the skin and minimize any adverse reactions. 3)Physiological monitoring: E-tattoos are primarily used for continuous, non-invasive monitoring of vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, temperature, and respiration. 4)Transdermal drug delivery: Some e-tattoos are designed to deliver medications through the skin,
https://www.nanowerk.com/nanotechnology-glossary/electronic-tattoo.php
Associate Professor of Bioengineering at the University of California, Todd Coleman, the brain-reading genius behind this project: 'Brain Machine Interface'.
https://www.techradar.com/news/world-of-tech/future-tech/would-you-want-an-electronic-tattoo-that-could-read-your-mind-1148670
Electronic Tattoos are getting traction in Healthcare
https://digitalhealthcentral.com/electronic-tattoos-are-getting-traction-in-healthcare/
E-Tattoos: The cyborg transformation of society. Digital tattoos are on their way to cyborg us and give us superpowers. By monitoring vital signs continuously and discreetly, electronic tattoos are still in their infancy, but their healthcare potential is limitless.
https://digitalhealthcentral.com/what-are-digital-tattoos/
The conductive layers of electronic tattoos can be made using pure conductive materials, like gold or carbon. To attain the flexibility required for these applications, gold is stretched into thin, s-shaped ribbons and carbon is arranged in a two-dimensional hexagonal lattice (carbon arranged in this way is commonly referred to as graphene).
https://builtin.com/hardware/electronic-tattoo
-
 59:57
59:57
The StoneZONE with Roger Stone
11 hours agoJ6 Martyr Enrique Tarrio Describes Inhumane Prison Conditions Ordered by Biden | The StoneZONE
47.4K4 -
 16:48
16:48
Tundra Tactical
11 hours ago $9.65 earnedAffordable Medical Gear From ACETAC SHOT Show 2025
84.8K4 -
 1:46:16
1:46:16
Redacted News
14 hours agoRFK CONFIRMATION: Kennedy goes to WAR with Big Pharma Democrats in Fiery Hearing | Redacted Live
264K431 -
 57:31
57:31
Candace Show Podcast
14 hours agoBREAKING! Taylor Swift Turns Against Blake Lively & Ryan Reynolds | Candace Ep 141
241K178 -
 1:04:59
1:04:59
Sarah Westall
11 hours agoRFK Jr Report, Constitution Suspended, War Time Procedures in Place, WHO Exit, DOD w/ Sasha Latypova
81K34 -
 1:56:37
1:56:37
Melonie Mac
15 hours agoGo Boom Live Ep 35!
69.6K15 -
 1:01:13
1:01:13
LFA TV
18 hours agoPRESIDENT TRUMP SIGNS LAKEN RILEY ACT | BASED AMERICA 1.29.25 6pm
74.5K8 -
 1:43:07
1:43:07
2 MIKES LIVE
12 hours ago2 MIKES LIVE #172 News Breakdown Wednesday!
40.4K2 -
 1:26:16
1:26:16
The Big Mig™
13 hours agoJ6’r Ryan Samsel Free At Last The BOP & DOJ Exposed
39K4 -
 31:34
31:34
The Based Mother
13 hours ago $2.41 earnedEXECUTIVE ORDER MUTILATES GENDER IDEOLOGY! Trump’s pulling out all the stops.
26.8K10