Premium Only Content
Flat Earth Astronomy: Revisiting Celestial Mechanics with Flat Earth South Pole Star Trails
In mainstream astronomy, the celestial sphere is an imaginary sphere of arbitrarily large radius, concentric with the Earth. All celestial objects are considered to be projected onto the inner surface of this sphere. Coordinates such as Right Ascension (RA) and Declination (DEC)are used to pinpoint the location of stars, much like longitude and latitude are used on Earth. This model is crucial for both the Globe and the Flat Earth perspectives as it provides a structured way to observe and categorize the movements of celestial bodies.
RA and DEC are celestial coordinates that allow astronomers to locate objects in the sky. In the Flat Earth model, these coordinates are interpreted as directions viewed from the Earth’s surface under a dome-like firmament. This ‘firmament’ concept aligns with the traditional celestial sphere used in spherical Earth astronomy,suggesting that the mechanism of locating celestial bodies using RA and DEC is fundamentally the same in both models.
Both models account for the observation that Polaris, the North Star,decreases in altitude above the horizon by approximately one degree for every 69 miles southward one travels, disappearing completely beyond the equator. Conversely, the southern celestial pole becomes visible only in the southern hemisphere, marked by a rotation of stars around a central point. This phenomenon is consistent across both models,attributed to Earth’s curvature in the Globe model and to the observer’s movement across a flat, circular Earth under a rotating dome in the Flat Earth model.
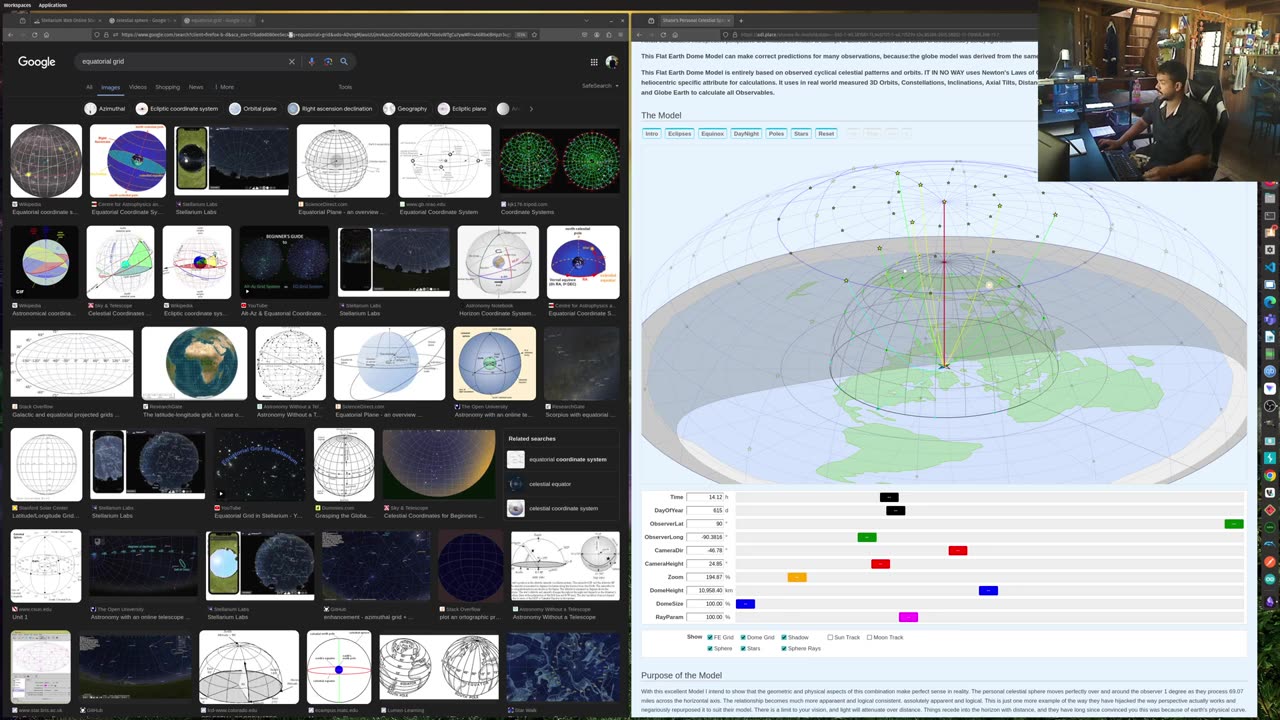
The appearance of star trails in the southern hemisphere provides significant point of discussion. In the Globe model, stars appear to rotate around the celestial poles due to Earth’s axial rotation. The Flat Earth model explains this with a dome on which stars are fixed,rotating around the observer. This dome’s behavior visually corresponds to the celestial sphere’s properties in conventional astronomy,demonstrating that the Flat Earth perspective can indeed replicate these observations through a different interpretative framework.
Fact check source journalofgeocentriccosmology.org/2024/05/04/revisiting-celestial-mechanics-a-comparative-analysis-of-flat-earth-and-spherical-earth-models/
Flat Earth Model Simulation: adl.place/shanes-fe-model
NASA JPL Horizons Geocentric Model: ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/horizons/
Stellarium Web: stellarium-web.org/
-
 4:24
4:24
Flat Earth University
1 month ago24hr Sun in Antarctica on the SVR model
1771 -
 3:03:35
3:03:35
TimcastIRL
10 hours agoTrump Just FIRED OVER 6,700 IRS Agents In PURGE, Democrats SOMEHOW Angry w/Chloe Cole | Timcast IRL
185K260 -
 1:39:48
1:39:48
Kim Iversen
13 hours agoThe Measles Fear Hoax: How They’re Using an Outbreak to Smear RFK Jr.
105K82 -
 1:18:19
1:18:19
Glenn Greenwald
12 hours agoRumble & Truth Social Sue Brazil’s Chief Censor Moraes in US Court; DC Establishment Melts Down Over Trump's Ukraine Policy | SYSTEM UPDATE #409
122K138 -
 1:33:39
1:33:39
Redacted News
14 hours agoBREAKING! Europe goes NUCLEAR against Trump over pushing for PEACE in Ukraine | Redacted
195K260 -
 1:00:43
1:00:43
The StoneZONE with Roger Stone
10 hours agoRoger Stone Destroys Mike Pence for Attacks on Trump | The StoneZONE
129K52 -
 1:05:43
1:05:43
Flyover Conservatives
1 day agoFederal Reserve on the Chopping Block—Trump’s Boldest Move Yet! - Floyd Brown, Western Journal | FOC Show
71.5K7 -
 2:50:40
2:50:40
Melonie Mac
15 hours agoGo Boom Live Ep 38!
72K4 -
 11:08
11:08
China Uncensored
14 hours agoXi Jinping's Greatest Fear
40.6K15 -
 2:11:20
2:11:20
I_Came_With_Fire_Podcast
19 hours agoFar Left TROJAN HORSE | SPECIAL Forces in MEXICO | GERMANY under FIRE
32.3K13