Premium Only Content

Canada’s 2023 Wildfire Season: An Unprecedented Environmental Catastrophe
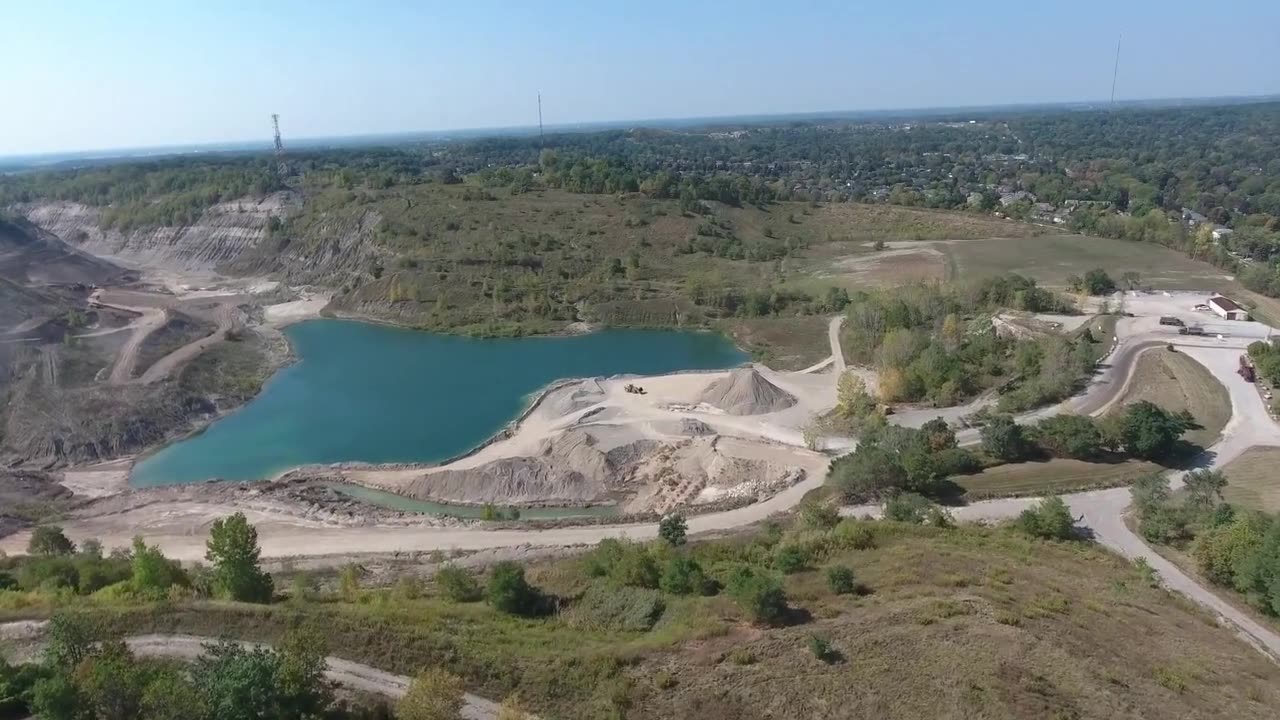
A study has found that contaminated mining sites increase the risks associated with fires.
The 2023 wildfire season in Canada was the most destructive ever recorded, and a new study suggests the impact was unprecedented. The research found that four wildfires in mine-impacted areas around Yellowknife, Northwest Territories, potentially contributed up to half of the global annual arsenic emissions from wildfires.
The work, led by researchers at the University of Waterloo and Nipissing University, is the first to calculate the amount of arsenic that was stored in areas at high risk of wildfires around Yellowknife. Looking at data from the past five decades, the team estimates the 2023 wildfires potentially released between 69 and 183 tonnes of arsenic.
Arsenic, a potent toxin, that the World Health Organization associates with diabetes, cardiovascular disease, various cancers, and infant mortality, can be transformed by wildfire and released into the environment from the soils that normally sequester it.
The Growing Risk of Wildfires
Given that the frequency and severity of wildfires are expected to increase because of climate change, the researchers caution that in any regions in the world where annual wildfires intersect with past or present mining and smelting operations, future fires could present a major risk for releasing stored toxins back into the environment.
“Yellowknife has a decades-long history of mining, which has led to an accumulation of arsenic in the surrounding landscape. However, Yellowknife is not unique in this regard, Canada has many industrially contaminated sites that are vulnerable to wildfire,” said Dr. Owen Sutton, a postdoctoral fellow in the Faculty of Environment at Waterloo.
-
 2:21:11
2:21:11
Nerdrotic
15 hours ago $31.95 earnedDown the Rabbit Hole with Kurt Metzger | Forbidden Frontier #090
145K25 -
 2:41:13
2:41:13
vivafrei
20 hours agoEp. 251: Bogus Social Security Payments? DOGE Lawsduit W's! Maddow Defamation! & MORE! Viva & Barnes
262K289 -
 1:19:23
1:19:23
Josh Pate's College Football Show
13 hours ago $4.78 earnedBig Ten Program Rankings | What Is College Football? | Clemson Rage| Stadiums I Haven’t Experienced
72.7K1 -
Vigilant News Network
18 hours agoBombshell Study Reveals Where the COVID Vaccine Deaths Are Hiding | Media Blackout
116K56 -
 1:17:59
1:17:59
Sarah Westall
14 hours agoDOGE: Crime & Hysteria bringing the Critics & the Fearful - Plus new CDC/Ukraine Crime w/ Dr Fleming
99.7K9 -
 45:39
45:39
Survive History
20 hours ago $10.98 earnedCould You Survive in the Shield Wall at the Battle of Hastings?
88.9K7 -
 1:50:28
1:50:28
TheDozenPodcast
19 hours agoViolence, Abuse, Jail, Reform: Michael Maisey
119K6 -
 23:01
23:01
Mrgunsngear
1 day ago $6.81 earnedWolfpack Armory AW15 MK5 AR-15 Review 🇺🇸
101K12 -
 25:59
25:59
TampaAerialMedia
1 day ago $4.58 earnedUpdate ANNA MARIA ISLAND 2025
65.4K4 -
 59:31
59:31
Squaring The Circle, A Randall Carlson Podcast
21 hours ago#039: How Politics & War, Art & Science Shape Our World; A Cultural Commentary From Randall Carlson
50K3