Premium Only Content
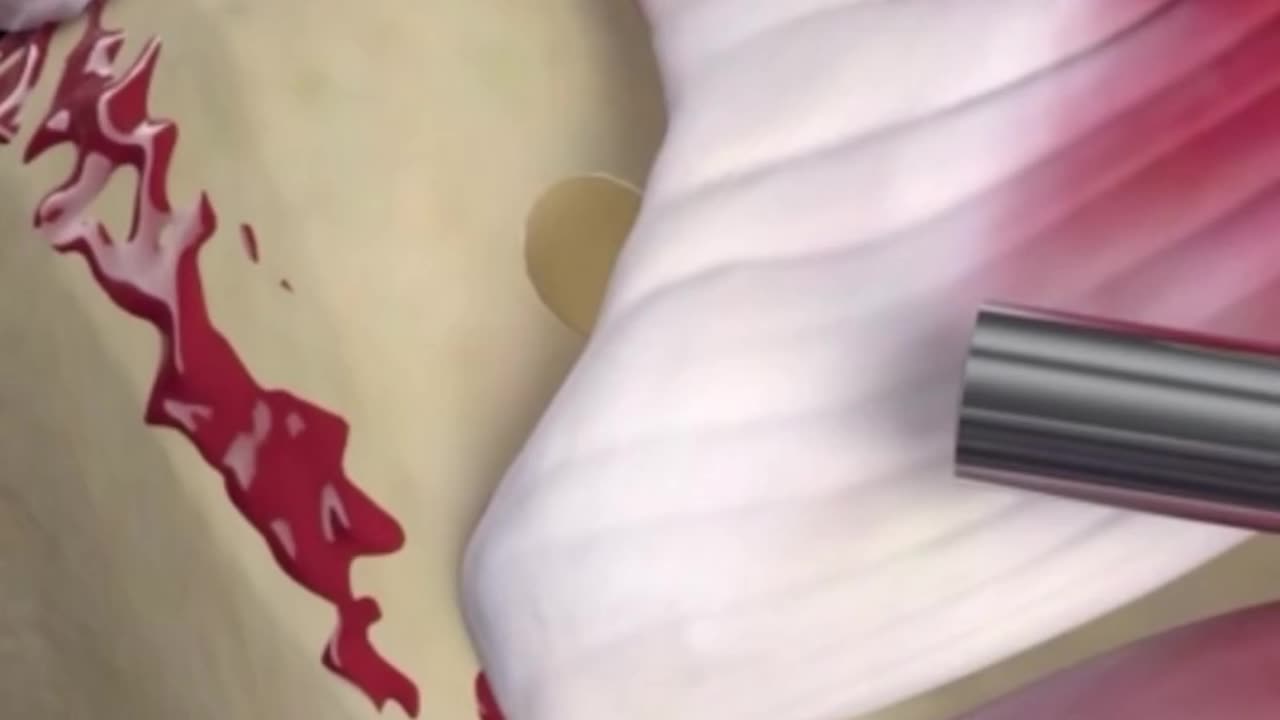
Rotator cuff surgery for the supraspinatus muscle
Rotator cuff surgery for the supraspinatus muscle.
Arthroscopic treatment of rotator cuff disease initially consisted of rotator cuff inspection and debridement and arthroscopic acromioplasty. If a repairable rotator cuff tear was discovered, an open or miniopen repair of the tendon was then performed. As surgeons’ skills improved and more specialised instrumentation was developed, it became possible to fix relatively small tears by using arthroscopic techniques to insert anchors, pass sutures, and tie knots. In current practice, surgeons can use these arthroscopic techniques in the shoulder to repair even large rotator cuff tears.
An overly aggressive acromioplasty must be avoided because excessive removal of the anterior acromion can result in the humeral head sliding forward, up, and out of the socket (anterosuperior subluxation).
The rotator cuff tear is then visualized through the lateral (side) portal from the “50-yard-line view.” The size and pattern of the tear are assessed. Any thin or fragmented portions are removed, and the area where the tendon will be reattached to the bone is lightly debrided to encourage new blood vessel ingrowth for healing.
The sutures are once again passed through the tendon and systematically tied. The sutures pull the tendon down to the prepared bone surface, closing the defect. This completes the repair.
-
 13:22
13:22
Stephen Gardner
4 hours ago🔥You'll NEVER Believe what Trump wants NOW!!
50K151 -
 54:56
54:56
Digital Social Hour
1 day ago $6.19 earnedDOGE, Deep State, Drones & Charlie Kirk | Donald Trump Jr.
22.6K -
 DVR
DVR
The Trish Regan Show
6 hours agoTrump‘s FCC Targets Disney CEO Bob Iger Over ABC News Alleged Misconduct
31.8K21 -
 1:48:19
1:48:19
The Quartering
6 hours agoElon Calls White People Dumb, Vivek Calls American's Lazy & Why Modern Christmas Movies Suck!
105K77 -
 2:08:42
2:08:42
The Dilley Show
7 hours ago $30.49 earnedH1B Visa Debate, Culture and More! w/Author Brenden Dilley 12/26/2024
96.9K24 -
 4:55:59
4:55:59
LumpyPotatoX2
10 hours agoThirsty Thursday on BOX Day - #RumbleGaming
96.4K5 -
 1:04:52
1:04:52
Geeks + Gamers
8 hours agoDisney RATIO'D on Christmas Day | Mufasa Embarrassed By Sonic 3
70.9K5 -
 8:27:46
8:27:46
Sm0k3m
12 hours agoPlaying games on Rumble
44.2K2 -
 10:37
10:37
Russell Brand
2 days agoHow is this even allowed?
193K872 -
 1:37:26
1:37:26
Real Coffee With Scott Adams
9 hours agoEpisode 2701 CWSA 12/26/24
106K95