Premium Only Content
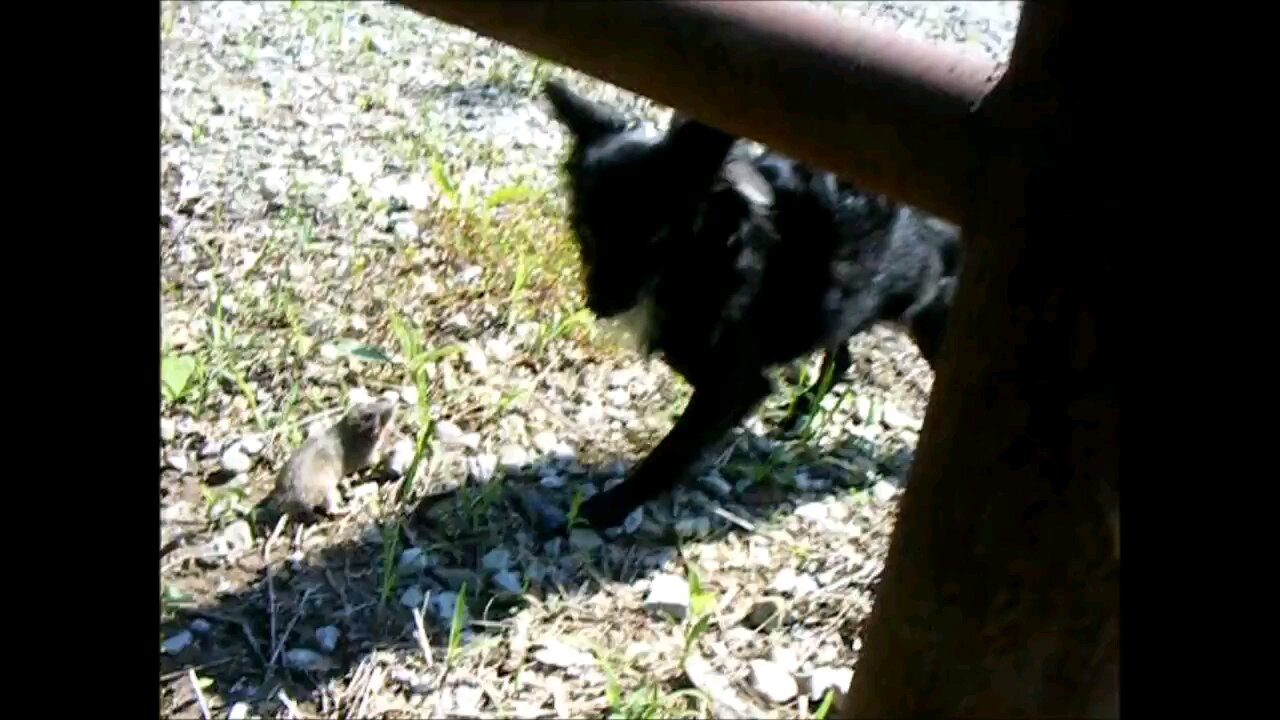

Max and I turn a Pocket Gopher loose...
Pocket gophers, scientifically known as Thomomys spp., are small burrowing rodents belonging to the Geomyidae family. They are native to North and Central America, where they inhabit a variety of environments, including grasslands, agricultural fields, and forests.
These rodents are well-adapted to their subterranean lifestyle, spending most of their time underground in a network of tunnels and burrows. They have stout bodies, small eyes, and powerful forelimbs equipped with large claws for digging. One of their distinctive features is their fur-lined external cheek pouches, or "pockets," which they use to carry food and nesting materials.
Pocket gophers primarily feed on underground plant parts, such as roots, tubers, and bulbs. They are herbivores, and their diet includes a wide range of plant species, including grasses, shrubs, and trees. They use their sharp incisors to gnaw through plant material, and they are capable of consuming large quantities of vegetation.
Their burrowing behavior has a significant impact on the ecosystem. Pocket gophers play a crucial role in soil aeration and nutrient cycling. Their burrows can extend for several hundred feet and include nesting chambers, food storage areas, and multiple entrances. These burrows help to mix and aerate the soil, improve water infiltration, and create habitat for other species.
Despite their small size, pocket gophers can be considered pests in agricultural areas, as they can damage crops and garden plants by feeding on their roots and tubers. However, they are an essential part of the ecosystem, and their burrowing activity helps to maintain soil health and biodiversity in many natural environments.
-
 LIVE
LIVE
The Jimmy Dore Show
2 hours agoElon Musk’s DOGE Exposes INSANE USAID Waste! Trump Says U.S. Should Take Over Gaza! w/ Iyah May
18,758 watching -
 27:28
27:28
Glenn Greenwald
5 hours agoGlenn Reacts to Trump's Gaza Take Over: System Update Special
100K184 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Melonie Mac
1 hour agoGo Boom Live Ep 36!
473 watching -
 1:02:11
1:02:11
Sarah Westall
2 hours agoFreezing USAID & its Operations in Ukraine: A Massive Money Laundering Organization? w/ Sam Anthony
18.9K1 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Space Ice
5 hours agoSpace Ice & Redeye: Neil Breen's Pass Thru
45 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
The StoneZONE with Roger Stone
1 hour agoRoger Stone Talks Trump’s Electric First 100 Day Agenda | The StoneZone w/ Roger Stone
558 watching -
 DVR
DVR
Redacted News
5 hours agoBREAKING! EPSTEIN LIST INCOMING UNDER AG PAM BONDI? DEMOCRATS FREAKING OUT, PRINCE ANDREW NERVOUS
145K170 -
 52:02
52:02
Candace Show Podcast
7 hours agoBecoming Brigitte: An Inaccessible Past | Ep 2
128K144 -
 LIVE
LIVE
2 MIKES LIVE
5 hours ago2 MIKES LIVE #176 News Breakdown Wednesday!
181 watching -

I_Came_With_Fire_Podcast
6 hours agoGAZA TAKEOVER | USAID EXPLAINED | TARIFF TAKEDOWN
32.9K2