Premium Only Content
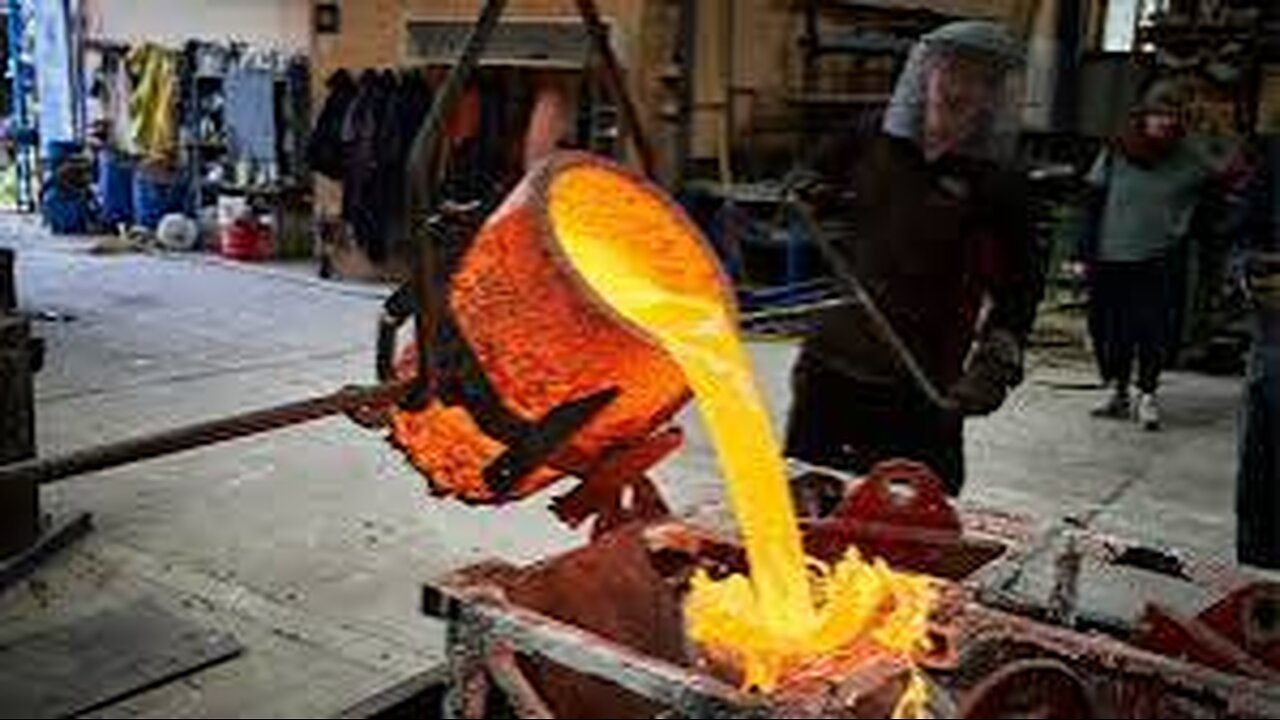

How Does a Foundry Work?
How Does a Foundry Work?
A foundry is a factory that produces metal castings. Metals are cast into shapes by melting them into a liquid, pouring the metal into a mold, and removing the mold material after the metal has solidified as it cools. The most common metals processed are aluminum and cast iron. However, other metals, such as bronze, brass, steel, magnesium, and zinc, are also used to produce castings in foundries. In this process, parts of desired shapes and sizes can be formed.
Foundries are one of the largest contributors to the manufacturing recycling movement, melting and recasting millions of tons of scrap metal every year to create new durable goods. Moreover, many foundries use sand in their molding process. These foundries often use, recondition, and reuse sand, which is another form of recycling.
In metalworking, casting involves pouring liquid metal into a mold, which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape, and then allowing it to cool and solidify. The solidified part is also known as a casting, which is ejected or broken out of the mold to complete the process. Casting is most often used for making complex shapes that would be difficult or uneconomical to make by other methods
What are the foundry types?
Sand casting utilises sand moulds to create metal castings, which form integral parts of vital machinery that is relied upon by over 80% of manufactured goods. In the foundries themselves, the fundamental difference that sets foundries apart is whether they are ferrous or non-ferrous; i.e whether they work using iron or iron-based metals such as steel, or other types of metals like aluminium, brass, or bronze.
Chemically bonded sand casting
Our equipment is tailor-made for use in chemically bonded or “no-bake” mould production, where sand is mixed with a binder to create a uniform and durable mould, ready to be used in the casting process. This is also known as “air set” mould production.
Who and what is this suitable for?
Our ranges of specialised foundry machinery designed for the no-bake foundry sector can be used in a variety of situations and industries, such as:
Jobbing foundries
Prototype castings
Heavy engineering
Specialised automotive castings
Casting for mining solutions
Construction equipment castings
Petrochemical industry castings
-

Josh Pate's College Football Show
3 hours ago $0.86 earnedBig Ten Program Rankings | What Is College Football? | Clemson Rage| Stadiums I Haven’t Experienced
17.1K -
 LIVE
LIVE
Vigilant News Network
8 hours agoBombshell Study Reveals Where the COVID Vaccine Deaths Are Hiding | Media Blackout
2,275 watching -
 1:17:59
1:17:59
Sarah Westall
4 hours agoDOGE: Crime & Hysteria bringing the Critics & the Fearful - Plus new CDC/Ukraine Crime w/ Dr Fleming
15.7K2 -
 45:39
45:39
Survive History
10 hours ago $2.10 earnedCould You Survive in the Shield Wall at the Battle of Hastings?
14.6K5 -
 1:50:28
1:50:28
TheDozenPodcast
8 hours agoViolence, Abuse, Jail, Reform: Michael Maisey
34K1 -
 23:01
23:01
Mrgunsngear
1 day ago $3.53 earnedWolfpack Armory AW15 MK5 AR-15 Review 🇺🇸
42.2K12 -
 25:59
25:59
TampaAerialMedia
1 day ago $1.19 earnedUpdate ANNA MARIA ISLAND 2025
22.3K1 -
 59:31
59:31
Squaring The Circle, A Randall Carlson Podcast
10 hours ago#039: How Politics & War, Art & Science Shape Our World; A Cultural Commentary From Randall Carlson
17.4K2 -
 13:21
13:21
Misha Petrov
10 hours agoThe CRINGIEST Thing I Have Ever Seen…
14.5K36 -
 11:45
11:45
BIG NEM
6 hours agoWe Blind Taste Tested the Best Jollof in Toronto 🇳🇬🇬🇭
9.1K