Premium Only Content
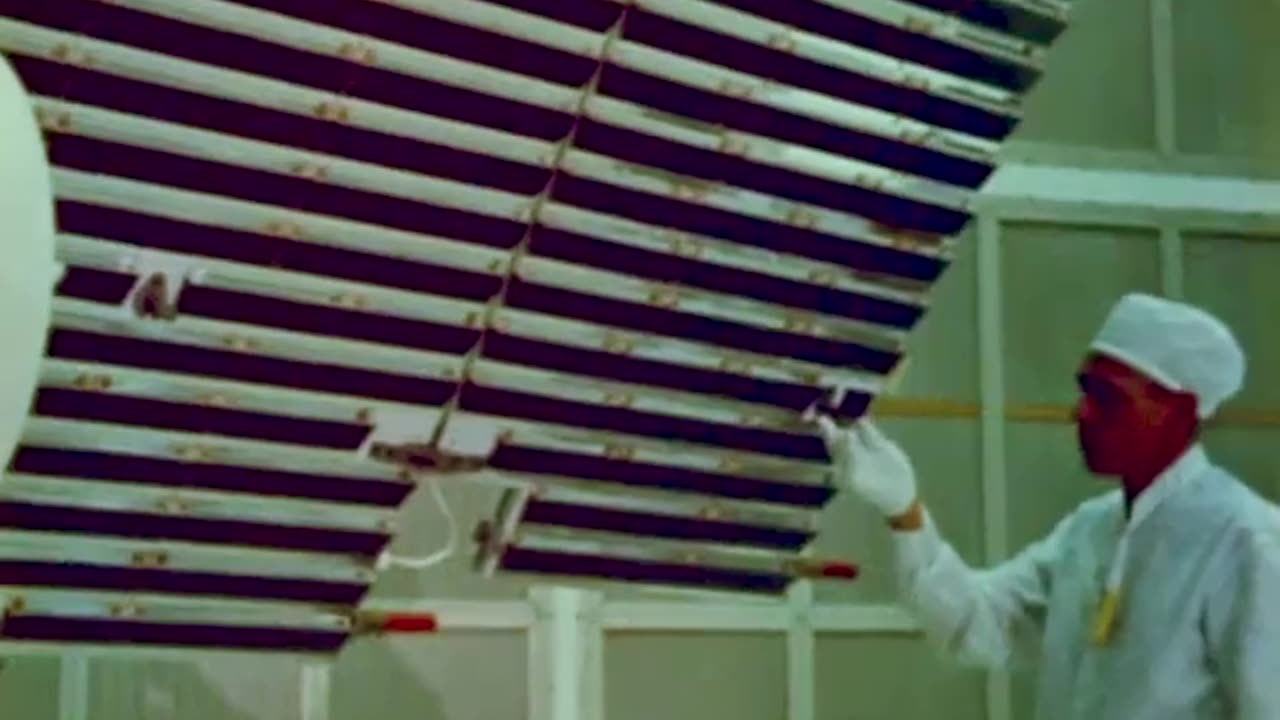
50th Anniversary of NASA's OAO 2 Mission
Hello!
Welcome To Asto Vista Rumble Channel...
On Dec. 7, 1968, an Atlas-Centaur rocket carrying NASA’s heaviest and most ambitious uncrewed satellite to date blasted into the sky from Launch Complex 36B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.
Formally known as Orbiting Astronomical Observatory (OAO) 2 and nicknamed Stargazer, it would become NASA’s first successful cosmic explorer and the direct ancestor of Hubble, Chandra, Swift, Kepler, FUSE, GALEX and many other astronomy satellites.
OAO 2 provided the first orbital stellar observations in ultraviolet light, shorter than wavelengths in the visible range spanning 3,800 (violet) to 7,500 (red) angstroms. Much of UV light is screened out by the atmosphere and unavailable to ground-based telescopes. Stargazer's experiments made nearly 23,000 measurements, showed that young, hot stars were hotter than theoretical models of the time indicated, confirmed that comets are surrounded by vast clouds of hydrogen and discovered a curious feature of the interstellar medium that would take scientists decades to understand.
One of the key problems scientists had to solve was how to direct a telescope to any point on the celestial sphere and hold it there for a half hour or so in order for instruments to record the data from faint sources. This makes OAO 2 the ancestor of all space telescopes that can point to a given spot on the sky and track it for an extended period.
Prior to OAO 2, ultraviolet observations of stars were acquired by suborbital sounding rockets which collect data for only five minutes each flight as they arc above much of the atmosphere. By 1968, it was estimated that sounding rockets had captured a total of three hours of stellar UV measurements in some 40 flights. OAO 2 could collect more data than this in a single day.
OAO 2 carried two experiments. Project Celescope (from "celestial telescope") was led by Fred Whipple, director of the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The Wisconsin Experiment Package was led by Arthur Code, a professor of astronomy at the University of Wisconsin-Madison. The experiments were mounted back-to-back within the 4,436-pound (2,012 kilogram) spacecraft and looked out opposite ends, taking turns viewing the universe.
#OAO2Mission
#NASAAnniversary
#SpaceHistory
#Astronomy
#SpaceScience
#SpaceExploration
#50YearsOAO2
#Astrophysics
#SpaceTechnology
#CelestialObservation
#AstronomicalResearch
#NASAHistory
#SpaceMilestones
#OAO2MissionAnniversary
#SpaceAchievements
#CosmicDiscovery
#SpaceInnovation
#AstroTech
#SpaceLegacy
#50thAnniversaryNASA
-
 LIVE
LIVE
LFA TV
13 hours agoLFA TV - ALL DAY LIVE STREAM 4/16/25
2,615 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
Bannons War Room
1 month agoWarRoom Live
17,069 watching -
![🔴[LIVE] Stocks Fall, Breaking Market News & Live Trading $1M || The MK Show](https://1a-1791.com/video/fww1/3e/s8/1/t/b/w/C/tbwCy.0kob-small-The-MK-Show-Apr.-16th.jpg)
Matt Kohrs
11 hours ago🔴[LIVE] Stocks Fall, Breaking Market News & Live Trading $1M || The MK Show
57.6K3 -
 LIVE
LIVE
The Big Mig™
4 hours agoIt’s Time To Pay The Piper Letitia James!
3,258 watching -
 33:37
33:37
Stephen Gardner
14 hours ago🔥Trump's LATEST legal NIGHTMARE explained by Alan Dershowitz!
10.4K48 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Badlands Media
7 hours agoBadlands Daily: April 16, 2025
4,835 watching -
 58:41
58:41
Randi Hipper
1 hour agoCRYPTO WINTER IS BACK? BITCOIN MAJOR LEVEL TO WATCH
1.57K -
 LIVE
LIVE
Wendy Bell Radio
6 hours agoDemocrats Are Making The Icing For Their Midterm Slaughter Cake
9,256 watching -
 1:06:43
1:06:43
Dear America
13 hours agoJoe Biden Emerges From Hibernation + Trump Fires 20,000 IRS Agents, Letitia James Get Karma?!
39.6K27 -
 1:26:12
1:26:12
JULIE GREEN MINISTRIES
4 hours agoLIVE WITH JULIE
147K167