Premium Only Content
How Your Childhood Affects Your Life
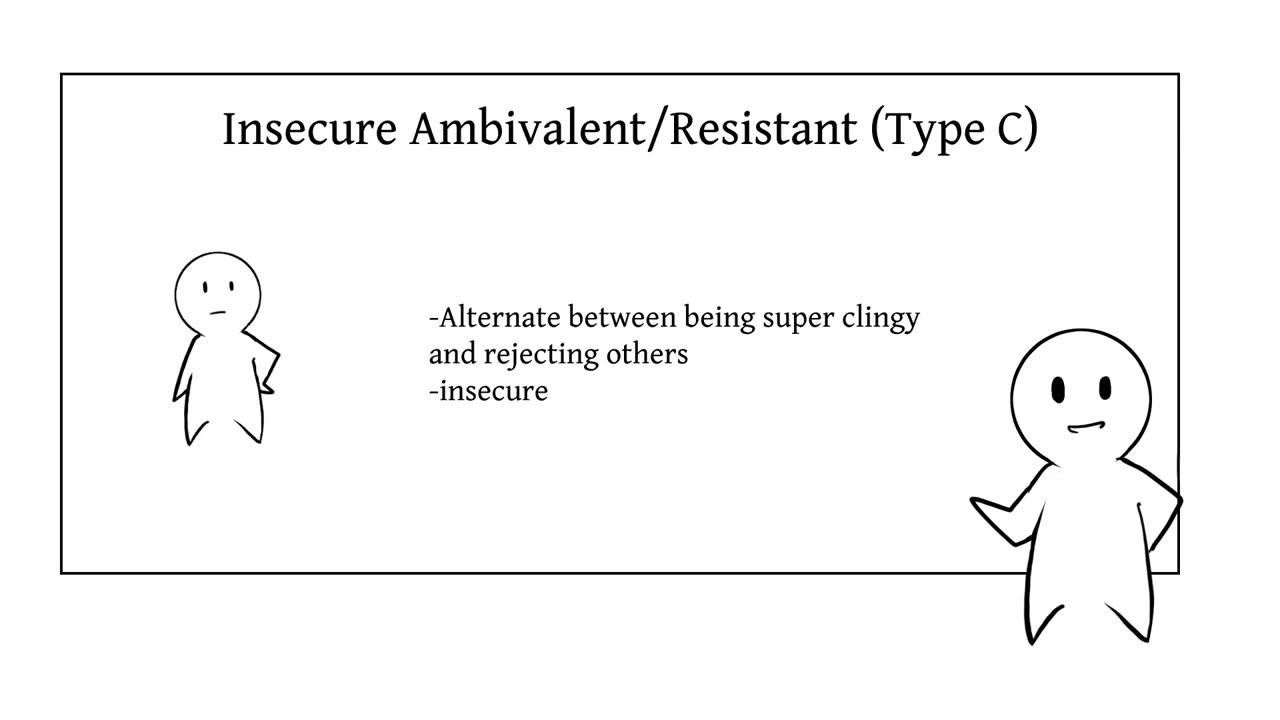
In the previous video, we briefly discussed attachment styles and how each type responds to parenting, relationships, friendships, and outlook on life. In this video, Psych2Go aims to explore each of the four attachment styles: Secure (type B), Avoidant Insecure (type A), Ambivalent/Resistant Insecure (Type C), and Disorganized. And how each type functions at work or school, relationships, and crises.
Hope it is useful. Thank You
Credit
Screenwriter: Amy
Script Editor: Kelly Soong
VOICE OVER: Amanda Silvera
Animation creator: Gabriella
YouTube Manager: Cindy Cheong
Reference:
Levy, K.N., Ellison, W.D., Scott, L.N., & Bernecker, S.L. (2011). Attachment style. Journal of clinical psychology, 67(2), 193-203.
Solomon, J., & George, C. (Eds.). (2011). Disorganized attachment and parenting. Guilford Press.
Feeney, J. A., & Noller, P. (1990). Attachment style as a predictor of adult romantic relationships. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 58(2), 281.
Bartholomew, K., Henderson, A., & Dutton, D. (2012). Insecure attachments and violent intimate relationships. In Adult attachment and couples psychotherapy (pp. 67-85). Routledge.
Davila, J., Burge, D., & Hammen, C. (1997). Why do attachment styles change? Journal of personality and social psychology, 73(4), 826.
Vicedo, Marga (14 February 2017). "Putting attachments in their place: Disciplinary and cultural contexts". European Journal of Developmental Psychology.14(6): 684–699. doi:1080/17405629.2017.1289838.
Mikulincer, M. (1995). Attachment styles and mental representations of the self. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 69(6), 1203.
-
 2:24:10
2:24:10
Price of Reason
11 hours agoCan Hollywood Recover After Years of WOKE Activism? Will 2025 See B.O. Reversal? Wukong vs Microsoft
15.2K5 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Jerry After Dark
14 hours agoHole In One Challenge | Presented by TGL
4,802 watching -
 3:56:39
3:56:39
Alex Zedra
6 hours agoLIVE! New Game | The Escape: Together
47.5K7 -
 5:01:11
5:01:11
FreshandFit
7 hours agoJoe Budden Arrested For Being A Perv! Tesla Cybertruck Explosion
80.1K12 -
 2:08:45
2:08:45
Kim Iversen
10 hours agoNew Year, New PSYOP?: The Fort Bragg Connection In The New Years Terror Attacks
67.3K119 -
 1:41:18
1:41:18
Glenn Greenwald
9 hours agoTerror Attacks Exploited To Push Unrelated Narratives; Facing Imminent Firing Squad, Liz Cheney Awarded Presidential Medal | SYSTEM UPDATE #381
97K175 -
 1:00:32
1:00:32
Man in America
11 hours ago🔴 LIVE: Terror Attacks or False Flags? IT DOESN'T ADD UP!!!
59K19 -
 1:02:38
1:02:38
Donald Trump Jr.
13 hours agoNew Year’s Terror, Latest Breaking News with Sebastian Gorka | TRIGGERED Ep.204
194K398 -
 59:59
59:59
The StoneZONE with Roger Stone
8 hours agoAfter Years of Targeting Trump, FBI and DOJ are Unprepared to Stop Terror Attacks | The StoneZONE
60.7K19 -
 1:26:42
1:26:42
Leonardaisfunny
6 hours ago $4.26 earnedH-1b Visas: Infinity Indians
39.1K18