Premium Only Content
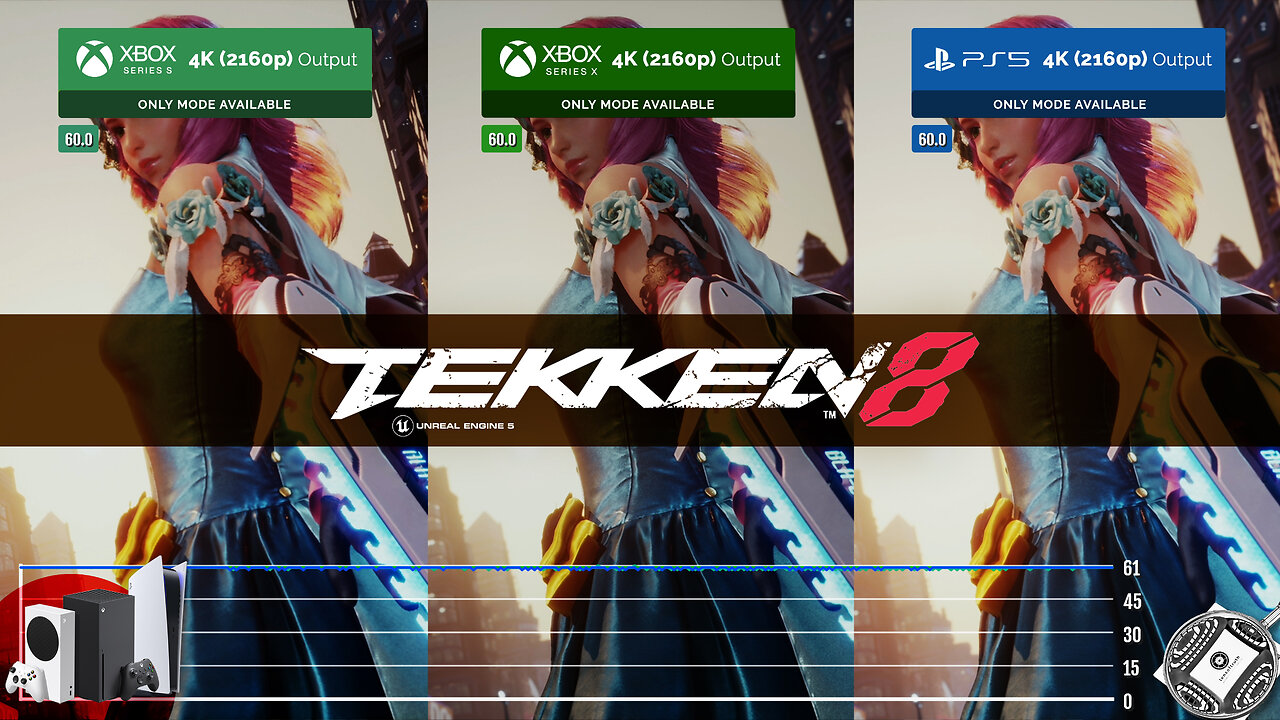
Tekken 8 - Tech Analysis on Xbox SS, SX and PS5 (Unreal 5)
Analysis of performance and image quality of Tekken 8 on Xbox Series S/X and PS5.
Index:
Intro 00:00
Frame Rate – Xbox Series S 00:09
Resolution 01:43
Frame Rate – Xbox Series X 03:23
Reflections 04:57
Frame Rate – Playstation 5 06:05
Shadows 07:39
Frame Rate – Face-off 08:39
Environment Geometry 10:13
Textures 11:13
Loading 12:13
Conclusions 13:00
Xbox Series S Tech Specs 17:05
Xbox Series X Tech Specs 17:15
PS5 Tech Specs 17:25
Technical dictionary:
- Draw Distance:
In computer graphics, draw distance (render distance or view distance) is the maximum distance of objects in a three-dimensional scene that are drawn by the rendering engine. Polygons that lie beyond the draw distance will not be drawn to the screen.
- AMD FidelityFX™ Super Resolution (FSR):
FidelityFX Super Resolution (FSR) is used to upsample an input image into a higher resolution. There are two versions of FSR with distinctive upscaling technique and image quality.
FSR 1 is a spatial upscaler based on the Lanczos algorithm* requiring an anti aliased lower resolution image.
FSR 2 and 2.1 is a temporal upscaler based on a modified Lanczos* requiring an aliased lower resolution image and utilising the temporal data (such as motion vectors and frame history) and then applies its own anti aliasing pass which replaces the game's temporal anti-aliasing solution.
Quality Preset Scale Factor Render Scale
Performance 2.0x 50.0% (e.g. for 4k: 1080p upscale to 2160p with FSR)
Balanced 1.7x 58.8% (e.g. for 4k: 1270p upscale to 2160p with FSR)
Quality 1.5x 66.6% (e.g. for 4k: 1440p upscale to 2160p with FSR)
* The Lanczos algorithm is an iterative algorithm invented by Cornelius Lanczos that is an adaptation of power methods to find eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a square matrix or the singular value decomposition of a rectangular matrix. It is particularly useful for finding decompositions of very large sparse matrices.
- Cube Mapping Reflections:
A Cubemap is a collection of six square textures that represent the reflections on an environment. The six squares form the faces of an imaginary cube that surrounds an object; each face represents the view along the directions of the world axes (up, down, left, right, forward and back). Cubemaps are often used to capture reflections or “surroundings” of objects; for example skyboxes and environment reflections often use cubemaps.
- Screen Space Reflections (SSR):
Screen space reflections (SSR): a more expensive technique that traces reflection rays in screen space (as opposed to world space in e.g. ray tracing). This is done for each rendered pixel of the reflected surface, using the surface normal and scene depth.
The disadvantage is that objects not captured in the rendered frame cannot appear in the reflections, which results in unresolved intersections and incomplete reflection image.
- Ray-Traced Reflections
Ray-Traced Reflections is a more accurate ray-traced solution to Screen Space Reflection technique (that traces reflection rays in screen space), ray tracing traces reflection rays in world space.
The disadvantage of the technique using ray tracing is the need for a dedicated hardware for accelerating the calculations needed to perform the feature.
- Shadow Mapping
Shadow mapping or shadowing projection is a process by which shadows are added to 3D computer graphics. This concept was introduced by Lance Williams in 1978, in a paper entitled "Casting curved shadows on curved surfaces."[1] Since then, it has been used both in pre-rendered and realtime scenes in many console and PC games. Shadows are created by testing whether a pixel is visible from the light source, by comparing the pixel to a z-buffer or depth image of the light source's view, stored in the form of a texture.
- Simple Shadow Mapping
Simplest possible implementation of Shadow Mapping, without any smoothing or additional features.
- Soft Shadows Mapping
Soft shadows are typically rendered in games by using shadow mapping and Percentage Closer Filtering with a uniform kernel size. The Percentage-Closer Soft Shadows (PCSS) algorithm computes a variable kernel size based on the distance between the relative position of the receiver point, an approximation of the blocker, and the area light.
- Ray-traced Shadows
Ray-traced shadows are generated by tracing the path of rays sampled from a light source. Ray-traced shadows are more accurate than shadow-mapped shadows. All ray-traced shadows are world space shadows.
-
 9:46
9:46
Mrgunsngear
6 hours ago $8.73 earnedHow To Turn Your Glock Into A PCC
56K11 -
 16:12
16:12
T-SPLY
14 hours agoJeff Bezos Is Now Enemy #1 For The Trump Administration
114K84 -
 12:24
12:24
Tundra Tactical
6 hours ago $4.27 earnedThe SIG Roast to ND Them All
63.2K8 -
 1:02:31
1:02:31
BonginoReport
10 hours agoDeportations Keep “Frightened” Michelle Obama Awake at Night (Ep. 37) - Nightly Scroll with Hayley
150K190 -
 1:54:29
1:54:29
Adam Does Movies
2 days ago $3.28 earnedTalking Movie News & Just Chatting About Films - LIVE!
46.3K3 -
 1:02:51
1:02:51
Anthony Rogers
1 day agoEpisode 364 - JFK FILES
24.7K1 -
 1:41:02
1:41:02
megimu32
6 hours agoON THE SUBJECT: 1 Million Views Party! Diddy Drama, Marvel Weirdness, and Total Prom Chaos
35.5K16 -
 1:18:44
1:18:44
Kim Iversen
9 hours agoMagnetic Pole Shift: Europe’s Blackout Is Just the Beginning | 90° Earth Flip Coming
118K289 -
 2:44:58
2:44:58
Laura Loomer
8 hours agoEP118: LIVE COVERAGE: Trump Celebrates 100 Days In Office At Michigan Rally
77.6K38 -
 3:40:42
3:40:42
Barry Cunningham
15 hours agoWATCH TRUMP RALLY LIVE: PRESIDENT TRUMP MARKS 100 DAYS IN OFFICE WITH A RALLY IN MICHIGAN
56.7K23