Premium Only Content
Prof. Nektarios Tavernarakis Plenary FLOGEN SIPS 2022 Yoshikawa Intl. Symposium on Oxidative Stress
FLOGEN SIPS 2022: Yoshikawa International Symposium on Oxidative Stress for Sustainable Development of Human Beings (2nd international Symposium)
Presenter:
Prof. Nektarios Tavernarakis, University of Crete, Heraklion, Greece
Title:
The Molecular Links Between Ageing And Neurodegeneration
Abstract
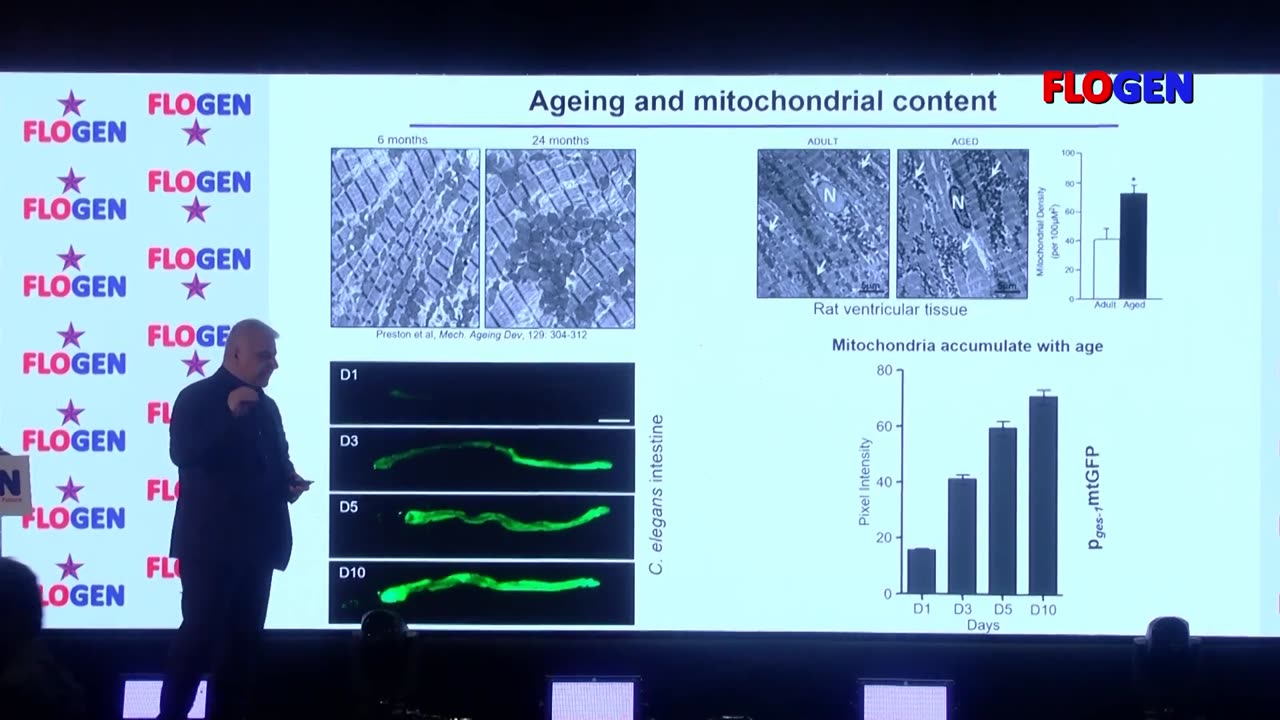
Numerous gene mutations and treatments have been shown to extend the lifespan of diverse organisms ranging from the unicellular yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae to primates. It is becoming increasingly apparent that most such interventions ultimately interface with cellular stress response mechanisms, suggesting that longevity is intimately related to the ability of the organism to effectively cope with both intrinsic and extrinsic stress. Key determinants of this capacity are the molecular mechanisms that link ageing to main stress response pathways. How each pathway contributes to modulate the ageing process is not fully elucidated. Mitochondrial impairment is a major hallmark of several age-related neurodegenerative pathologies, including Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Accumulation of damaged mitochondria has been observed in post-mortem brains of Alzheimer’s disease patients. Mitophagy is a selective type of autophagy mediating elimination of damaged mitochondria, and the major degradation pathway, by which cells regulate mitochondrial number in response to their metabolic state. Little is known about the role of mitophagy in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. We find that neuronal mitophagy is impaired in animal models of Alzheimer’s disease. Indeed, mitophagy stimulation restores learning and memory capacity, in these animals. Moreover, age-dependent decline of mitophagy both inhibits removal of dysfunctional or superfluous mitochondria and impairs mitochondrial biogenesis resulting in progressive mitochondrial accretion and, consequently, deterioration of cell function. Our observations indicate that defective removal of damaged mitochondria is a pivotal event in neurodegeneration. These findings highlight mitophagy as a potential target for the development of innovative, effective therapeutic interventions towards battling human neurodegenerative disorders.
-
 1:09:53
1:09:53
Slightly Offensive
9 hours ago $7.59 earnedIs the US Headed for MORE WAR Under TRUMP? | Guest: Scott Horton
51.3K13 -
 58:29
58:29
The StoneZONE with Roger Stone
9 hours agoRoger Stone Hails Confirmation of Kash Patel, Trashes Schiff for Attacks On Patel | The StoneZONE
57.7K21 -
 48:44
48:44
Man in America
14 hours agoA MASSIVE Global Financial Reset Is Coming—Are You Ready?
45.3K22 -
 1:15:42
1:15:42
Precision Rifle Network
1 day agoS4E5 Guns & Grub - The Best Rifle Under $2000
77.9K8 -
 1:02:54
1:02:54
Glenn Greenwald
1 day agoSouth Korean Economist Ha-Joon Chang on the Economic World Order, Trump's Tariffs, China & More | SYSTEM UPDATE #410
94.3K52 -
 1:02:27
1:02:27
Donald Trump Jr.
14 hours agoBye Mitch, plus Kash confirmed, Interview with AJ Rice | Triggered Ep.218
138K77 -
 1:12:27
1:12:27
The Amber May Show
16 hours ago $3.52 earnedWomen Of Rumble 02-20-25
40.8K8 -
 41:18
41:18
Kimberly Guilfoyle
14 hours agoToday, We Kash in on Equal Justice, Live with Ryan Walters & Daniel Turner | Ep.198
102K23 -
 1:36:50
1:36:50
Redacted News
13 hours agoThe TRUTH in Ukraine has been EXPOSED by Trump and they are melting down | Redacted w Clayton Morris
143K236 -
 2:05:35
2:05:35
The White House
15 hours agoPresident Trump Hosts a Reception Honoring Black History Month
90.1K47