Premium Only Content
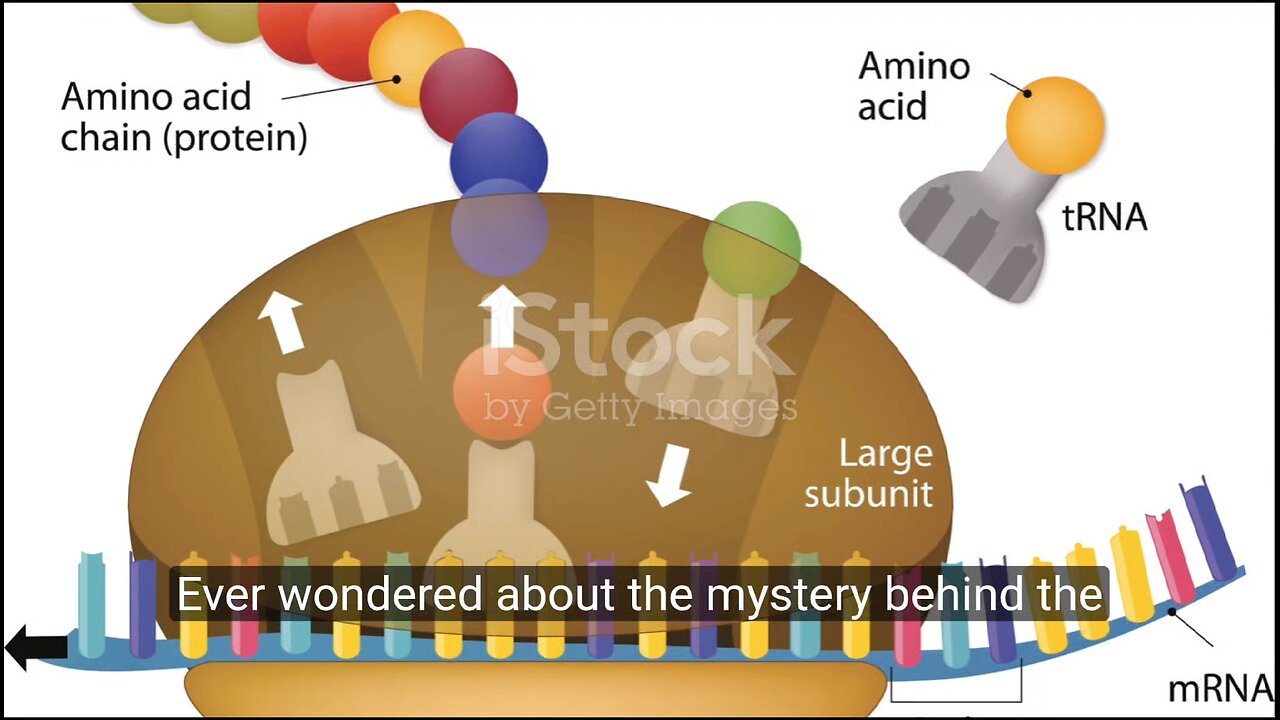
The function of tRNA and its significance.
tRNA, or Transfer RNA, plays a crucial role in protein synthesis by facilitating the transfer of amino acids to the ribosome during the process of translation. Its significance lies in ensuring the accurate and specific incorporation of amino acids into the growing polypeptide chain.
Here's a breakdown of the role and significance of tRNA:
Amino Acid Transport: tRNA binds to specific amino acids in the cytoplasm and transports them to the ribosome. Each tRNA molecule is associated with a particular amino acid, and the amino acid carried by the tRNA corresponds to the anticodon sequence on the tRNA molecule.
Recognition of Codons: The anticodon region of tRNA base-pairs with the complementary codon on the mRNA during translation. This ensures that the correct amino acid is added to the growing protein chain according to the sequence encoded in the mRNA.
Facilitating Protein Synthesis: As the ribosome moves along the mRNA, tRNA molecules bring in the appropriate amino acids one by one, allowing the ribosome to link them together in the order specified by the mRNA code.
Accuracy in Translation: The specificity of tRNA for both amino acids and codons ensures the fidelity of translation. This accuracy is crucial for the proper functioning of proteins and, by extension, cellular processes.
In essence, tRNA serves as an adaptor molecule, linking the genetic information encoded in mRNA with the sequence of amino acids in a protein. Its precise role is vital for the accurate translation of the genetic code into functional proteins, influencing various aspects of cellular structure and function.
-
 1:14:36
1:14:36
The Heidi St. John Podcast
1 day agoLoving God Means Loving People
181 -
 38:05
38:05
The Bryce Eddy Show
18 hours agoMichael A. Letts: Why Cops Are Quitting
271 -
 27:34
27:34
Economic War Room
1 day agoIs Wall Street Sleeping with the Enemy? | Guest: Justin Bernier | Ep 340
9191 -
 18:17
18:17
John Fredericks Media Network
21 hours ago $0.01 earnedFredericks & John Anthony: Trump Clowns Wall Street - 10% Tariffs A Thing of Beauty
96 -
 46:14
46:14
CutJibNewsletter
1 day agoCJN Speaks: the Tariffs & Goniffs & Momzers Oh MYEpisode
11 -
 3:21:57
3:21:57
I_Came_With_Fire_Podcast
22 hours agoCHINA CENSORED AMERICANS | NO PRAYER DOWN UNDER | SAVE ACT
89.2K20 -
 1:26:01
1:26:01
Roseanne Barr
18 hours ago $29.39 earnedAbsolutely Fabulous W/ Shannon Hughey #94
121K32 -
 8:00:05
8:00:05
SpartakusLIVE
16 hours agoDuos w/ Nicky || Friday Night HYPE
24.6K -
 2:06:42
2:06:42
TimcastIRL
14 hours agoPolice ARREST "MR SATAN" For Threatening To ASSASSINATE Trump, KILL ICE Agents | Timcast IRL
265K300 -
 8:12:48
8:12:48
XxXAztecwarrior
13 hours agoKilling Little Timmy's On Verdansk
87.9K3