Premium Only Content
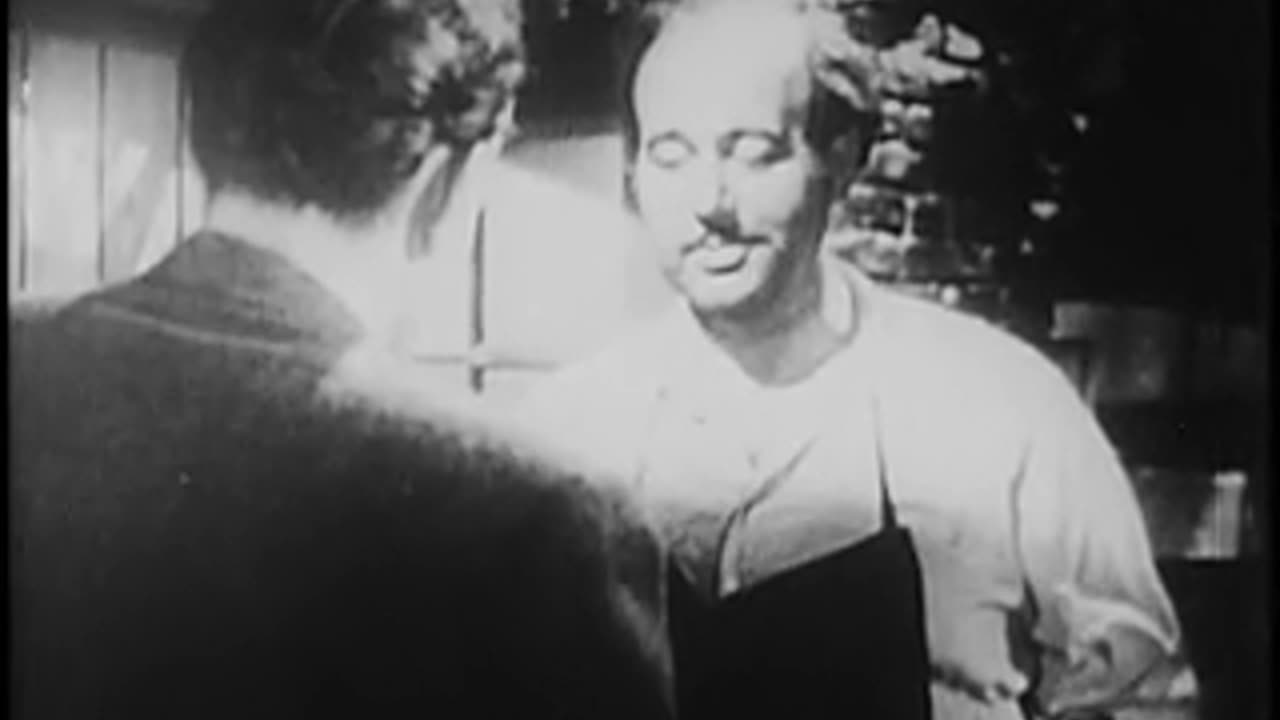

CIA Archives: Cutout Devices - Espionage (1953)
The dark side of history: https://thememoryhole.substack.com/
In espionage parlance, a cutout is a mutually trusted intermediary, method or channel of communication that facilitates the exchange of information between agents. Cutouts usually know only the source and destination of the information to be transmitted, not the identities of any other persons involved in the espionage process (need to know basis). Thus, a captured cutout cannot be used to identify members of an espionage cell. The cutout also isolates the source from the destination, so neither necessarily knows the other.
Outside espionage
Some computer protocols, like Tor, use the equivalent of cutout nodes in their communications networks. The use of multiple layers of encryption usually stops nodes on such networks from knowing the ultimate sender or receiver of the data.
In computer networking, darknets have some cutout functionality. Darknets are distinct from other distributed peer-to-peer (P2P) networks, as sharing is anonymous, i.e., IP addresses are not publicly shared and nodes often forward traffic to other nodes. Thus, with a darknet, users can communicate with little fear of governmental or corporate interference.[1] Darknets are thus often associated with dissident political communications as well as various illegal activities.
A dead drop or dead letter box is a method of espionage tradecraft used to pass items or information between two individuals (e.g., a case officer and an agent, or two agents) using a secret location. By avoiding direct meetings, individuals can maintain operational security. This method stands in contrast to the live drop, so-called because two persons meet to exchange items or information.
Spies and their handlers have been known to perform dead drops using various techniques to hide items (such as money, secrets or instructions) and to signal that the drop has been made. Although the signal and location by necessity must be agreed upon in advance, the signal may or may not be located close to the dead drop itself. The operatives may not necessarily know one another or ever meet.[1][2]
Considerations
The location and nature of the dead drop must enable retrieval of the hidden item without the operatives being spotted by a member of the public, the police, or other security forces—therefore, common everyday items and behavior are used to avoid arousing suspicion. Any hidden location could serve, although often a cut-out device is used, such as a loose brick in a wall, a (cut-out) library book, or a hole in a tree.
Dead drop spike
A dead drop spike is a concealment device similar to a microcache. It has been used since the late 1960s to hide money, maps, documents, microfilm, and other items. The spike is water- and mildew-proof and can be pushed into the ground or placed in a shallow stream to be retrieved at a later time.
Signaling devices can include a chalk mark on a wall, a piece of chewing gum on a lamppost, or a newspaper left on a park bench. Alternatively, the signal can be made from inside the agent's own home, by, for example, hanging a distinctively-colored towel from a balcony, or placing a potted plant on a window sill where it is visible to anyone on the street.
Drawbacks
While the dead drop method is useful in preventing the instantaneous capture of either an operative/handler pair or an entire espionage network, it is not without disadvantages. If one of the operatives is compromised, they may reveal the location and signal for that specific dead drop. Counterintelligence can then use the dead drop as a double agent for a variety of purposes, such as to feed misinformation to the enemy or to identify other operatives using it or ultimately to booby trap it.[3] There is also the risk that a third party may find the material deposited.
Modern techniques
See also: Short-range agent communications
On January 23, 2006, the Russian FSB accused Britain of using wireless dead drops concealed inside hollowed-out rocks ("spy rock") to collect espionage information from agents in Russia. According to the Russian authorities, the agent delivering information would approach the rock and transmit data wirelessly into it from a hand-held device, and later, his British handlers would pick up the stored data by similar means.[4]
SecureDrop, initially called DeadDrop, is a software suite for teams that allows them to create a digital dead drop location to receive tips from whistleblowers through the Internet. The team members and whistleblowers never communicate directly and never know each other's identity, therefore allowing whistleblowers to dead-drop information despite the mass surveillance and privacy violations which had become commonplace in the beginning of the twenty-first century.
See also
Espionage
Foldering
PirateBox
USB dead drop
References
Robert Wallace and H. Keith Melton, with Henry R. Schlesinger, Spycraft: The Secret History of the CIA's Spytechs, from Communism to al-Qaeda, New York, Dutton, 2008. ISBN 0-525-94980-1. Pp. 43-44, 63, and 74-76.
Jack Barth, International Spy Museum Handbook of Practical Spying, Washington DC, National Geographic, 2004. ISBN 978-0-7922-6795-9. Pp. 119-125.
Wettering, Frederick L. (2001-07-01). "The Internet and the Spy Business". International Journal of Intelligence and CounterIntelligence. 14 (3): 342–365. doi:10.1080/08850600152386846. ISSN 0885-0607. S2CID 153870872.
Nick Paton Walsh, The Guardian (23 January 2006). "Moscow names British 'spies' in NGO row". TheGuardian.com. Archived from the original on 29 August 2013. Retrieved 8 April 2012.
Bibliography
"Russians accuse 4 Britons of spying".International Herald Tribune. January 24, 2006. News report on Russian discovery of British "wireless dead drop".
"Old spying lives on in new ways". BBC. 23 January 2006.
Madrid suspects tied to e-mail ruse. International Herald Tribune. April 28, 2006.
Military secrets missing on Ministry of Defence computer files
Robert Burnson, "Accused Chinese spy pleads guilty in U.S. 'dead-drop' sting", Bloomberg, 25 novembre 2019[1].
Robert Wallace and H. Keith Melton, with Henry R. Schlesinger, Spycraft: The Secret History of the CIA's Spytechs, from Communism to al-Qaeda, New York, Dutton, 2008. ISBN 0-525-94980-1.
-
 54:05
54:05
The Memory Hole
22 days agoThe CIA Exposed: How the World Is Run - John Stockwell (1987)
7144 -
 LIVE
LIVE
FRENCHY4185
5 hours agoFRENCHY'S BIRTHDAY BASH !!! THE BIG 40 !!!
401 watching -
 1:23:33
1:23:33
Michael Franzese
14 hours agoThings to look forward to in 2025
67.7K34 -
 3:23:02
3:23:02
I_Came_With_Fire_Podcast
15 hours agoDefeating VICTIMHOOD: Advocacy, Resiliency, and Overcoming Abuse
81.8K15 -
 2:00:56
2:00:56
Game On!
21 hours ago $9.89 earnedNFL Experts debate if Joe Burrow will make HISTORY in Week 18!
103K12 -
 2:07:57
2:07:57
InfiniteWaters(DivingDeep)
4 days agoHOW TO ENTER 2025 LIKE A BOSS!
35.4K1 -
 15:43
15:43
Tactical Advisor
7 hours agoBEST and WORST Guns Of 2024
26.3K7 -
 9:14
9:14
Dermatologist Dr. Dustin Portela
7 hours ago $0.90 earnedProducts a Dermatologist Actually Uses
24.2K10 -
 20:54
20:54
inspirePlay
9 hours ago $3.88 earned🏌️♀️ Extreme Knockout Golf Challenge Part 2 – Do the GIRLS beat the BOYS? 🏌️
46.5K2 -
 24:09
24:09
Squaring The Circle, A Randall Carlson Podcast
8 hours ago#033 At The Crossroads - Squaring the Circle: A Randall Carlson Podcast
30.9K12