Premium Only Content

NASA | X-ray Nova Reveals a New Black Hole in Our Galaxy
407,591 views Oct 5, 2012
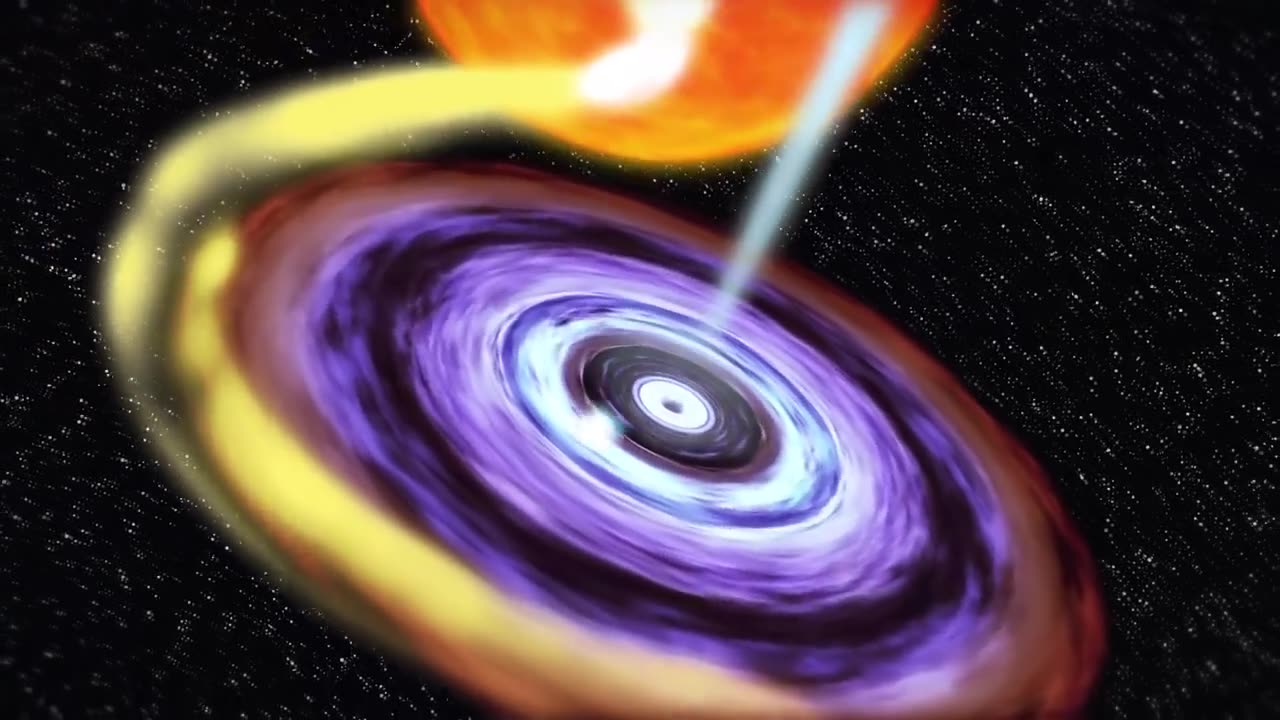
On Sept. 16, NASA's Swift satellite detected a rising tide of high-energy X-rays from a source toward the center of our Milky Way galaxy. The outburst, produced by a rare X-ray nova, announced the presence of a previously unknown stellar-mass black hole.
An X-ray nova is a short-lived X-ray source that appears suddenly, reaches its emission peak in a few days and then fades out over a period of months. The outburst arises when a torrent of stored gas suddenly rushes toward one of the most compact objects known, either a neutron star or a black hole.
Named Swift J1745-26 after the coordinates of its sky position, the nova is located a few degrees from the center of our galaxy toward the constellation Sagittarius. While astronomers do not know its precise distance, they think the object resides about 20,000 to 30,000 light-years away in the galaxy's inner region. The pattern of X-rays from the nova signals that the central object is a black hole.
Ground-based observatories detected infrared and radio emissions, but thick clouds of obscuring dust have prevented astronomers from catching Swift J1745-26 in visible light.
The black hole must be a member of a low-mass X-ray binary (LMXB) system, which includes a normal, sun-like star. A stream of gas flows from the normal star and enters into a storage disk around the black hole. In most LMXBs, the gas in the disk spirals inward, heats up as it heads toward the black hole, and produces a steady stream of X-rays.
But under certain conditions, stable flow within the disk depends on the rate of matter flowing into it from the companion star. At certain rates, the disk fails to maintain a steady internal flow and instead flips between two dramatically different conditions -- a cooler, less ionized state where gas simply collects in the outer portion of the disk like water behind a dam, and a hotter, more ionized state that sends a tidal wave of gas surging toward the center.
This phenomenon, called the thermal-viscous limit cycle, helps astronomers explain transient outbursts across a wide range of systems, from protoplanetary disks around young stars, to dwarf novae - where the central object is a white dwarf star - and even bright emission from supermassive black holes in the hearts of distant galaxies.
-
 59:59
59:59
The StoneZONE with Roger Stone
10 hours agoAfter Years of Targeting Trump, FBI and DOJ are Unprepared to Stop Terror Attacks | The StoneZONE
70.2K28 -
 1:26:42
1:26:42
Leonardaisfunny
8 hours ago $5.18 earnedH-1b Visas: Infinity Indians
46.5K27 -
 1:08:33
1:08:33
Josh Pate's College Football Show
13 hours ago $2.95 earnedPlayoff Reaction Special: Ohio State Owns Oregon | Texas Survives | UGA vs Notre Dame Takeaways
42K6 -
 58:04
58:04
Kimberly Guilfoyle
13 hours agoFBI's Terror Response Failures, Live with Steve Friend & Kyle Seraphin | Ep. 185
115K46 -
 2:15:01
2:15:01
WeAreChange
13 hours agoMassive Developments In Vegas Investigation! UNREAL DETONATION, Shocking Details Emerge!
120K89 -
 54:02
54:02
LFA TV
20 hours ago2025 Is Off to a Violent Start | TRUMPET DAILY 1.2.25 7pm
53.2K12 -
 59:27
59:27
theDaily302
19 hours agoThe Daily 302- JJ Carrell
45.2K5 -
 2:57
2:57
EvenOut
2 days ago $2.13 earnedTHE TELEPORTING PORTA POTTY TWIN RPANK!
41.8K3 -
 1:02:55
1:02:55
In The Litter Box w/ Jewels & Catturd
1 day agoAmerica Is Under Attack! | In the Litter Box w/ Jewels & Catturd – Ep. 711 – 1/02/2025
106K163 -
 1:45:25
1:45:25
The Quartering
16 hours agoHuge Update In Cybertruck Attack & Dark New Details From New Orleans Attacker & More!
136K69