Premium Only Content
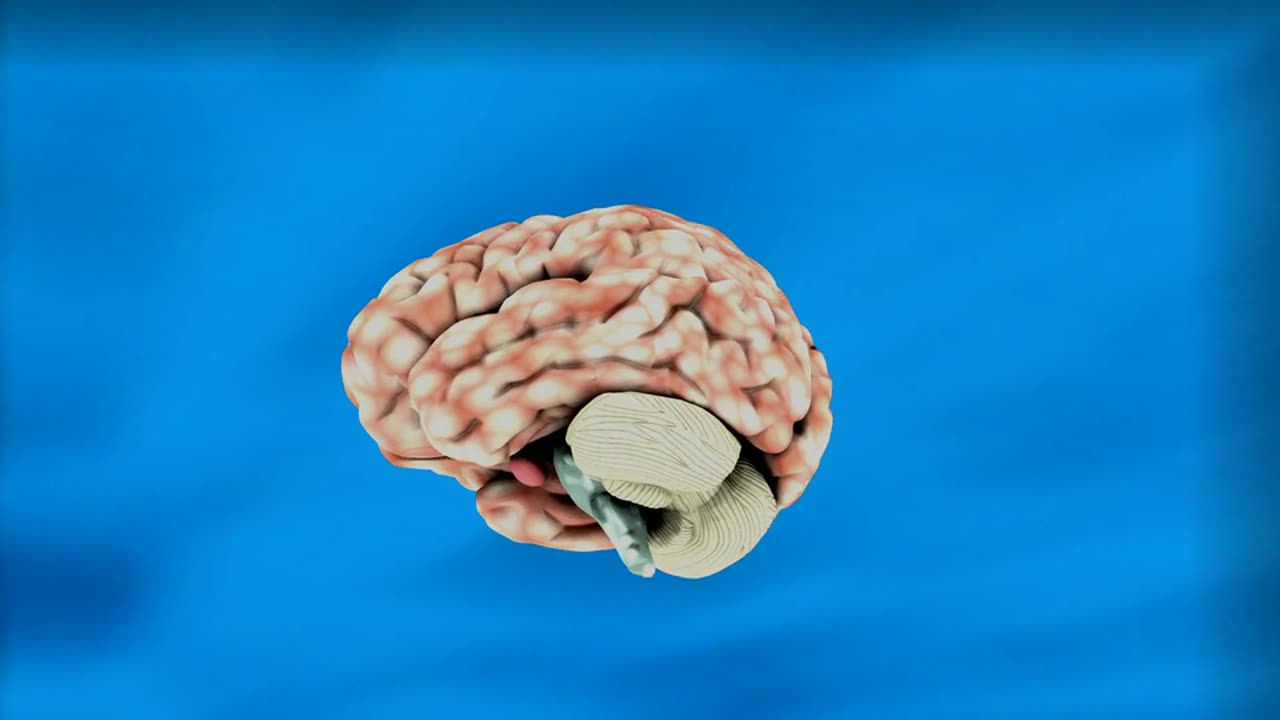
What is the brain?
The brain is a complex organ that controls thought, memory, emotion, touch, motor skills, vision, breathing, temperature, hunger and every process that regulates our body. Together, the brain and spinal cord that extends from it make up the central nervous system, or CNS.
What is the brain made of?
Weighing about 3 pounds in the average adult, the brain is about 60% fat. The remaining 40% is a combination of water, protein, carbohydrates and salts. The brain itself is a not a muscle. It contains blood vessels and nerves, including neurons and glial cells.
What is the gray matter and white matter?
Gray and white matter are two different regions of the central nervous system. In the brain, gray matter refers to the darker, outer portion, while white matter describes the lighter, inner section underneath. In the spinal cord, this order is reversed: The white matter is on the outside, and the gray matter sits within.
Gray matter is primarily composed of neuron somas (the round central cell bodies), and white matter is mostly made of axons (the long stems that connects neurons together) wrapped in myelin (a protective coating). The different composition of neuron parts is why the two appear as separate shades on certain scans.
How does the brain work?
The brain sends and receives chemical and electrical signals throughout the body. Different signals control different processes, and your brain interprets each. Some make you feel tired, for example, while others make you feel pain.
Some messages are kept within the brain, while others are relayed through the spine and across the body’s vast network of nerves to distant extremities. To do this, the central nervous system relies on billions of neurons (nerve cells).
Main Parts of the Brain and Their Functions
At a high level, the brain can be divided into the cerebrum, brainstem and cerebellum.
Brain Coverings: Meninges
Three layers of protective covering called meninges surround the brain and the spinal cord.
The outermost layer, the dura mater, is thick and tough. It includes two layers: The periosteal layer of the dura mater lines the inner dome of the skull (cranium) and the meningeal layer is below that. Spaces between the layers allow for the passage of veins and arteries that supply blood flow to the brain.
The arachnoid mater is a thin, weblike layer of connective tissue that does not contain nerves or blood vessels. Below the arachnoid mater is the cerebrospinal fluid, or CSF. This fluid cushions the entire central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and continually circulates around these structures to remove impurities.
The pia mater is a thin membrane that hugs the surface of the brain and follows its contours. The pia mater is rich with veins and arteries.
-
 LIVE
LIVE
2 MIKES LIVE
5 hours ago2 MIKES LIVE #205 with guest Nick Adams!
134 watching -
 54:38
54:38
LFA TV
8 hours agoThe Bread of Life | TRUMPET DAILY 4.14.25 7PM
7.2K6 -
 37:52
37:52
Kimberly Guilfoyle
4 hours agoThe Trump Effect, Plus More Scandals for Leticia James, Live with Roger Stone | Ep213
33.6K15 -
 1:13:45
1:13:45
Kim Iversen
4 hours agoWe're LOSING The Tariff War With China, How Our Elites Sold Us Out | Oct 7th Rape COVERUP
61.8K108 -
 1:23:13
1:23:13
Redacted News
4 hours agoTrump declaring MARTIAL LAW on April 20th according to fearmonger liberals, they want civil war
127K151 -
 2:21:58
2:21:58
vivafrei
12 hours agoEp. 259: Shapiro Home FIREBOMBED! Pavlovski Goes NUCLEAR on Dorsey Over AI! Elections Canada & MORE
117K63 -
 1:06:43
1:06:43
The Amber May Show
4 hours ago $0.57 earnedFinally, The Truth Comes Out In The News About What We Have Known For A While| Sam Anthony
14K2 -
 LIVE
LIVE
TwinGatz
5 hours ago🔴LIVE - Fighting Side By Side | ARMA Reforger
220 watching -
 1:58:54
1:58:54
Revenge of the Cis
6 hours agoEpisode 1474: Space Cadets
55.7K3 -
 1:11:57
1:11:57
The HotSeat
5 hours agoResurrection Week Kicks Off—And So Does the Democrat Freak Show: AOC and Bernie 2028
43.5K5