Premium Only Content
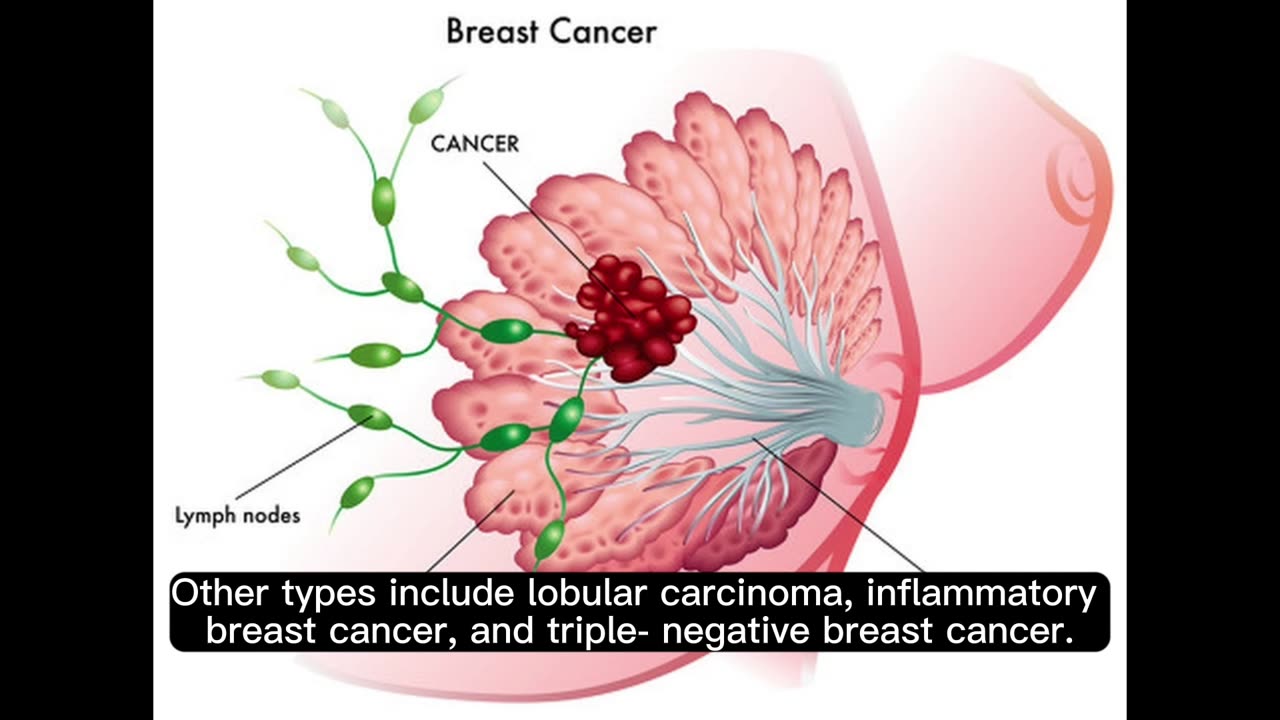
breast cancer, its causes, symptoms, and treatment #breastcancer #care #health #awareness #foryou
Breast cancer is a complex and pervasive disease that affects millions of individuals worldwide. It is the most common cancer among women, making it a significant public health concern. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of breast cancer, covering its causes, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
Understanding Breast Cancer:
Breast cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the cells of the breast. It can occur in both men and women, but it is much more common in women. The disease typically starts when cells in the breast tissue divide and grow uncontrollably. Over time, these abnormal cells can form a lump or mass known as a tumor.
Causes and Risk Factors:
The exact cause of breast cancer is not fully understood, but several risk factors have been identified. Some of the common risk factors include:
Gender: Women are at a significantly higher risk of developing breast cancer compared to men.
Age: The risk of breast cancer increases with age, with most cases diagnosed in women over 50.
Family History: Individuals with a family history of breast cancer, especially in close relatives like a mother, sister, or daughter, have an increased risk.
Inherited Gene Mutations: Certain gene mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, can significantly increase the risk of breast cancer.
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): Long-term use of hormone replacement therapy, particularly estrogen and progestin, has been associated with an increased risk.
Reproductive Factors: Factors like early menstruation, late menopause, and never giving birth or having the first child after age 30 may increase the risk.
Symptoms:
Breast cancer symptoms can vary widely, but some common signs to watch for include:
A lump or thickening in the breast or underarm.
Changes in breast size or shape.
Unexplained pain in the breast or nipple.
Nipple discharge, other than breast milk.
Skin changes on the breast, such as redness, dimpling, or puckering.
It's important to note that these symptoms may not always indicate breast cancer, but they should be promptly evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Diagnosis:
The diagnosis of breast cancer typically involves several steps, including:
Clinical Breast Exam: A physical examination by a healthcare provider to check for lumps or abnormalities.
Mammography: X-ray images of the breast tissue to detect tumors that may not be felt during a clinical exam.
Biopsy: Removal of a small tissue sample from the suspicious area for laboratory analysis to determine if it is cancerous.
Treatment Options:
Treatment for breast cancer depends on various factors, including the stage of the cancer, its type, and the individual's overall health. Common treatment options include:
Surgery: The removal of the tumor or the entire breast (mastectomy).
Radiation Therapy: The use of high-energy rays to target and destroy cancer cells.
Chemotherapy: The use of drugs to kill cancer cells or stop their growth.
Hormone Therapy: Medications that block the effects of hormones on breast cancer cells.
Targeted Therapy: Drugs that specifically target certain proteins involved in cancer growth.
Immunotherapy: Boosting the body's immune system to fight cancer.
Prevention:
While breast cancer cannot always be prevented, there are steps individuals can take to reduce their risk:
Maintain a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise and a balanced diet.
Limit alcohol consumption.
Avoid long-term use of hormone replacement therapy.
Know your family history and discuss it with your healthcare provider.
Consider genetic testing if you have a strong family history of breast cancer.
In conclusion, breast cancer is a formidable adversary, but advances in early detection and treatment have improved the prognosis for many patients. Regular screenings and awareness of risk factors are crucial for early detection, which can significantly improve the chances of successful treatment and survival. If you have concerns about breast cancer, consult with a healthcare professional for guidance and support.
-
 10:17
10:17
Dermatologist Dr. Dustin Portela
1 day ago $7.81 earnedOlay Cleansing Melts: Dermatologist's Honest Review
53.6K -
 1:02:20
1:02:20
Trumpet Daily
2 days ago $26.68 earnedObama’s Fake World Comes Crashing Down - Trumpet Daily | Dec. 20, 2024
35.1K34 -
 6:29
6:29
BIG NEM
22 hours agoCultivating God Mode: Ancient Taoist NoFap Practices
30.5K6 -
 30:53
30:53
Uncommon Sense In Current Times
1 day ago $7.99 earned"Pardon or Peril? How Biden’s Clemency Actions Could Backfire"
50.6K3 -
 40:01
40:01
CarlCrusher
20 hours agoSkinwalker Encounters in the Haunted Canyons of Magic Mesa - ep 4
47K2 -
 59:44
59:44
PMG
1 day ago $5.74 earned"BETRAYAL - Johnson's New Spending Bill EXPANDS COVID Plandemic Powers"
54.9K21 -
 6:48:50
6:48:50
Akademiks
18 hours agoKendrick Lamar and SZA disses Drake and BIG AK? HOLD UP! Diddy, Durk, JayZ update. Travis Hunter RUN
176K30 -
 11:45:14
11:45:14
Right Side Broadcasting Network
9 days agoLIVE REPLAY: TPUSA's America Fest Conference: Day Three - 12/21/24
360K28 -
 12:19
12:19
Tundra Tactical
18 hours ago $13.18 earnedDaniel Penny Beats Charges in NYC Subway Killing
74.5K14 -
 29:53
29:53
MYLUNCHBREAK CHANNEL PAGE
1 day agoUnder The Necropolis - Pt 1
163K67