Premium Only Content
Understanding Metabolic Syndrome: Risk Factors and Implications
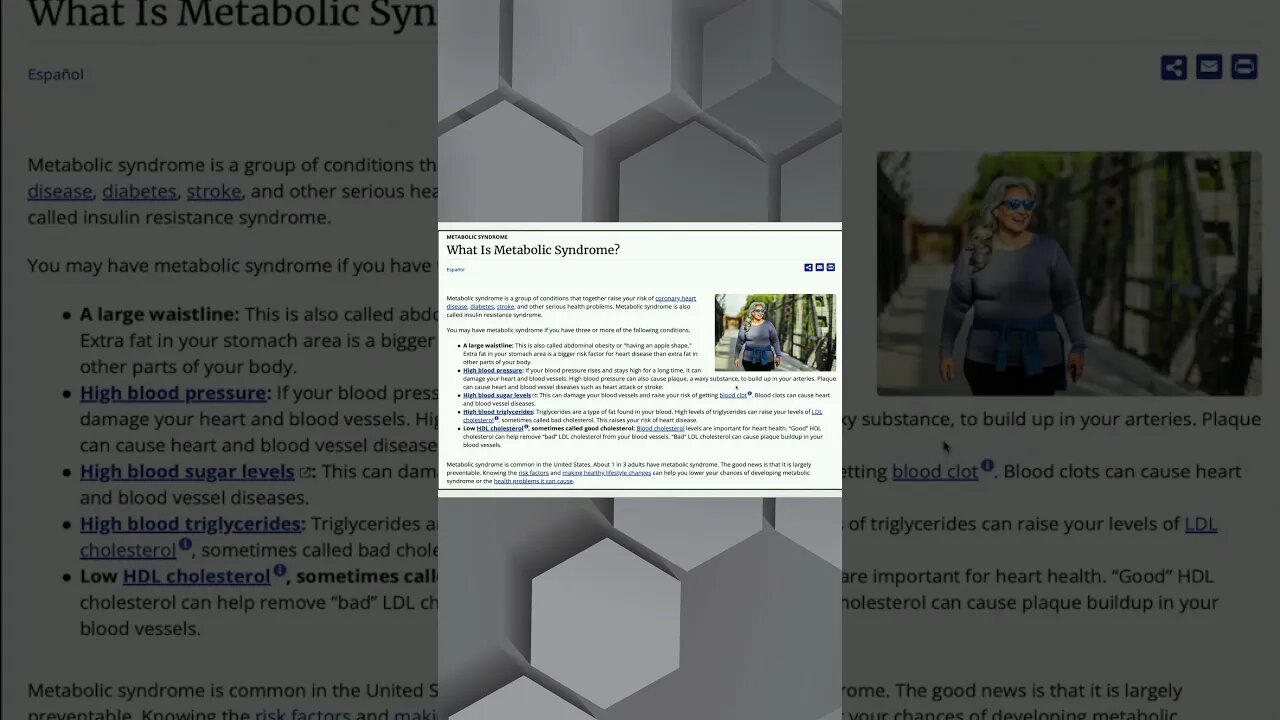
Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of health conditions that occur together, increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. To be diagnosed with metabolic syndrome, a person typically has at least three of the following five risk factors:
Elevated Blood Pressure: A blood pressure reading of 130/85 mm Hg or higher.
High Blood Sugar Levels: Fasting blood sugar (glucose) levels of 100 mg/dL or higher.
Abdominal Obesity: A waist circumference of 40 inches or more in men and 35 inches or more in women (measured at the level of the navel).
High Triglycerides: Triglyceride levels of 150 mg/dL or higher.
Low HDL Cholesterol: HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol levels of less than 40 mg/dL in men and less than 50 mg/dL in women.
Metabolic syndrome is often associated with other health issues, such as insulin resistance (a condition where the body's cells do not respond effectively to insulin), obesity, and an increased risk of blood clotting. The exact cause of metabolic syndrome is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to a combination of genetic factors, poor diet, lack of physical activity, and obesity.
Having metabolic syndrome significantly increases the risk of developing serious health problems, particularly cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes. Lifestyle changes, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and weight management, are often recommended as the first line of treatment for managing metabolic syndrome. In some cases, medications may be prescribed to control specific risk factors, such as high blood pressure or high cholesterol levels.
Early detection and proactive management of metabolic syndrome can help reduce the risk of associated health complications and improve overall well-being. Therefore, individuals with multiple risk factors should consult with a healthcare professional for evaluation and guidance on managing their metabolic health.
-
 49:29
49:29
A Different Perspective
9 months ago $0.03 earnedStress, Diets, and How to Lose Weight When it’s Hard | A Different Perspective | February 10, 2024
246 -
 3:01
3:01
MoneyMindsTrading
12 hours ago $3.99 earned#1 Day Trader on Rumble : NVIDIA EARNINGS 🚀
30.2K2 -
 3:13:12
3:13:12
Price of Reason
15 hours agoDisney CEO Bob Iger PANICS after Trump win? Is Landman any good? The Game Awards Announces Nominees!
59K11 -
 2:51:40
2:51:40
Jerry After Dark
15 hours ago3 Point Contest | Presented By Ghost Energy
127K6 -
 2:24:56
2:24:56
Kim Iversen
12 hours agoRussia Threatens To NUKE Ukraine | RFK Jr Called Science’s True Voice By Former CDC Chief
120K243 -
 1:16:12
1:16:12
Savanah Hernandez
10 hours agoCorrupt Democrats attempt to stop Trump’s plan to fix America
79.4K74 -
 53:12
53:12
Glenn Greenwald
12 hours agoImprisoned For Journalism: Jeremy Loffredo On His Detention In Israel, Censorship & More | SYSTEM UPDATE #368
111K115 -
 51:42
51:42
Man in America
14 hours agoTrump, Elon, CBDCs, Digital Prison & the Great Taking w/ James Patrick
85.9K42 -
 3:50:14
3:50:14
I_Came_With_Fire_Podcast
13 hours agoSPECIAL LIVE FIRE (w/ Aaron Praeger)
84.3K18 -
 49:18
49:18
PMG
1 day ago $5.71 earned"Biden Regime Trying to Trigger WW III Before Trump Term Begins, and Ballots Still Being Counted?"
52.3K3