Premium Only Content
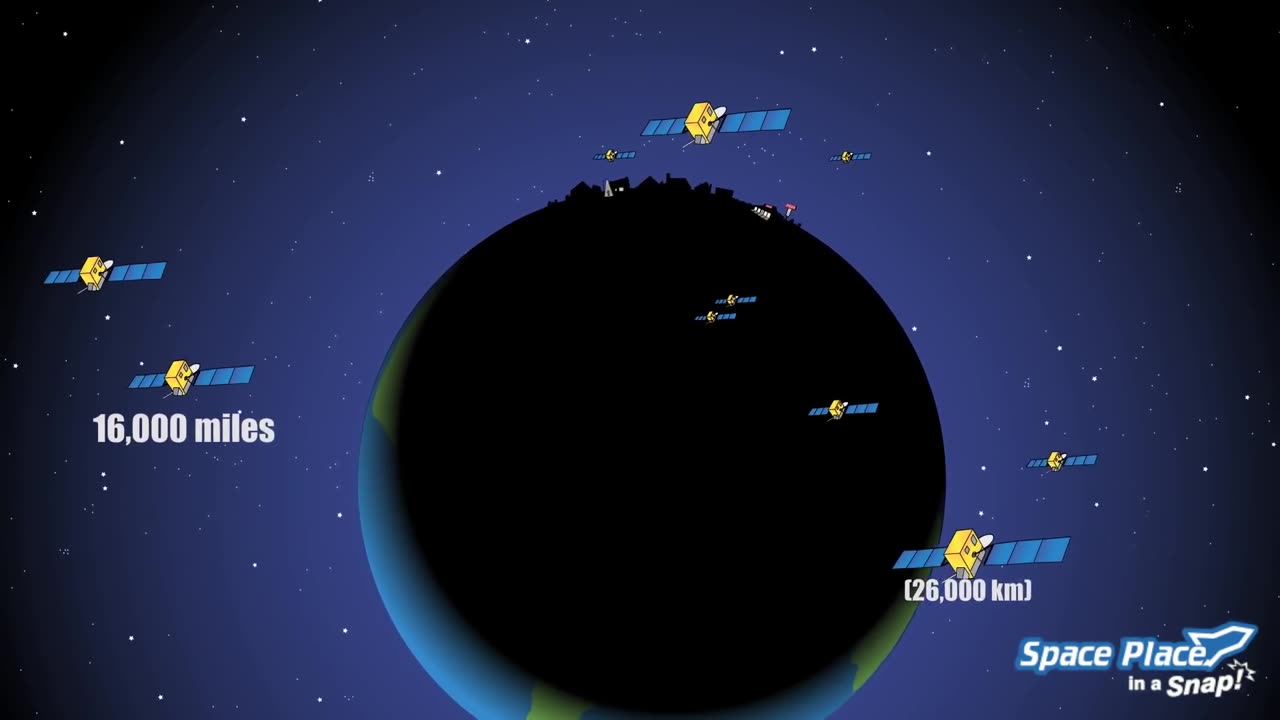
How Does GPS Work?
GPS, or Global Positioning System, works by using a network of satellites orbiting the Earth. Here's a simplified explanation of how it works:
Satellite Constellation: There are approximately 24 to 32 GPS satellites in orbit around the Earth. These satellites are spread out in such a way that at least four of them are visible from almost any point on Earth at any given time.
Triangulation: Each GPS satellite continuously broadcasts its position and a precise timestamp signal. A GPS receiver on the ground (such as in your smartphone or GPS device) picks up signals from multiple satellites. By measuring the time it took for the signals to travel from each satellite to the receiver, the receiver can calculate its distance from each satellite.
Trilateration: With distance measurements from at least four satellites, the GPS receiver can determine its precise location on Earth's surface using a mathematical process called trilateration. Trilateration involves intersecting spheres (representing the distances from each satellite) to pinpoint the receiver's location.
Calculating Position: Once the receiver knows its distance from each satellite and their precise locations in space, it can calculate its latitude, longitude, altitude, and the exact time.
User Display: The GPS receiver then displays your location and can provide navigation instructions, track movement, and more.
In summary, GPS works by measuring the time it takes for signals from multiple satellites to reach a receiver and using that information to calculate the receiver's precise location on Earth. This technology has a wide range of applications, from navigation to tracking and surveying
-
 6:15
6:15
SKAP ATTACK
1 day ago $1.76 earnedGiannis Goes Full FREAK MODE in Historic Game
12.4K2 -
 19:35
19:35
DeVory Darkins
1 day ago $32.66 earnedMedia suffers failure after Elon Musk hit piece gets DEBUNKED
76.1K144 -
 12:38
12:38
Talk Nerdy Sports - The Ultimate Sports Betting Podcast
5 hours ago4/5/25 - Talk Nerdy Sports – Madness. Money. Mayhem.
36.7K4 -
 3:18:37
3:18:37
I_Came_With_Fire_Podcast
13 hours agoTHE HUNDREDTH EPISODE!!!
52.2K7 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Gatoroz
6 hours agoTake Me Back To Verdansk
133 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
STGKAMZZ
8 hours ago"🔥Blunt & Battle: Chill Vibes Only in COD Ranked! 🌼💨 Spring Saturdays Just Got Epic!"
77 watching -
 34:00
34:00
Tactical Advisor
6 hours agoRetiring This Rifle | Vault Room LIve Stream 019
43.4K10 -
 16:29
16:29
Sideserf Cake Studio
8 hours ago $3.21 earnedThis Cruise Ship Is A CAKE!
52.7K9 -
 14:49
14:49
Clownfish TV
23 hours agoNintendo Switch 2 BACKLASH! Gamers BOYCOTT Over Pricing?!
41.1K10 -
 24:17
24:17
JasminLaine
22 hours agoCTV Reporter DESTROYS Carney By Quoting His BOOK—His INSANE Answer STUNS Host
48.7K33