Premium Only Content
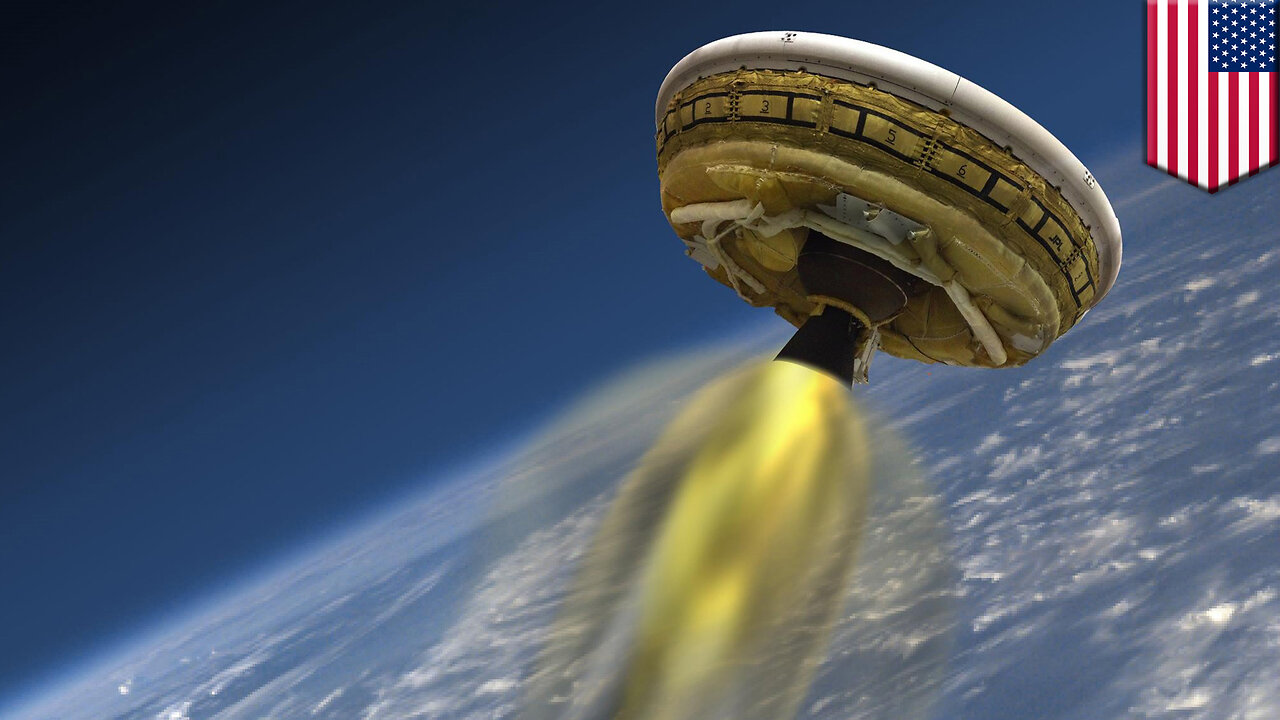

NASA's flying saucer, aka the Low-Density Supersonic Decelerator, paves the way for landing heavy sp - TomoNews
NASA was forced to cancel six attempted launches of a saucer-shaped Mars landing test vehicle in early June because of unusually strong winds at the Hawaiian test site. NASA has developed the Low-Density Supersonic Decelerator, a 3,048 kg flight vehicle, with a view to overcoming the obstacles of a Martian landing.The vehicle is launched by a helium balloon, which will ascend to 36,600 metres. "We cannot have very high winds near the ground so that the balloon is able to be launched and not be damaged by the winds," said Mark Adler, project manager of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, in an interview with Space.com. "We also have to have conditions where the higher level winds take the balloon away from populated areas." After reaching altitude, the balloon is detached from the craft, which will continue its ascent by igniting solid-fuel engines. When the vehicle reaches 54,800 metres, it will be travelling at a maximum speed of Mach 4. As it slows down from Mach 4 to Mach 3.8, it will deploy a device called a supersonic inflatable aerodynamic decelerator, which resembles an inflatable hula hoop, slowing the speed from Mach 3.8 to Mach 2.5. A 30.5-metre diameter parachute will then be deployed to further slow down the flight vehicle on its way back to Earth. If all things go well, the vehicle will be recovered in the Pacific Ocean off Hawaii. After the successful landing of Curiosity in 2012, NASA's next goal is to place heavier spacecraft and eventually astronauts on the red planet's surface. It presents a huge challenge as the atmosphere on Mars is about 100 times thinner than Earth, meaning that it cannot provide sufficient resistance to slow down a spacecraft for a safe landing.
-
 2:13:41
2:13:41
The Quartering
4 hours agoMillions Of Illegals Given Social Security Numbers, Wisconsin Supreme Court Race, Star Wars & More
162K53 -
 1:17:33
1:17:33
Awaken With JP
5 hours agoHitler Escaped to Argentina? (April Fools Special) - LIES Ep 85
37.6K24 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Revenge of the Cis
3 hours agoEpisode 1467: Mid-Wife
1,187 watching -
 23:55
23:55
The Brett Cooper Show
6 hours ago $4.13 earnedWhy Selling Your a$$ Online Is Not A Good Idea | Episode 16
16.9K21 -
 2:46:50
2:46:50
Right Side Broadcasting Network
5 hours agoLIVE REPLAY: Task Force on the Declassification of Federal Secrets: JFK Files - 4/1/25
39.2K7 -
 LIVE
LIVE
The HotSeat
1 hour agoPam Bondi seeks Death Penalty + Booker is still going and Hot Seat Calls LIVE!
646 watching -
 59:18
59:18
Jeff Ahern
1 hour agoTrending Tuesday with Jeff Ahern (1pm Pacific)
5.51K1 -
 21:10
21:10
Talk Nerdy Sports - The Ultimate Sports Betting Podcast
1 hour ago4/1/25 - No Jokes. Just Units.
3.57K -
![[Ep 640] Judicial Treason! | Trump Targets Ticketmaster | Guest Sam Anthony [your]NEWS](https://1a-1791.com/video/fww1/b8/s8/1/F/g/s/y/Fgsyy.0kob-small-Ep-640-Judicial-Treason-Tru.jpg) LIVE
LIVE
The Nunn Report - w/ Dan Nunn
2 hours ago[Ep 640] Judicial Treason! | Trump Targets Ticketmaster | Guest Sam Anthony [your]NEWS
162 watching -
 1:18:55
1:18:55
Russell Brand
5 hours agoTRUMP VS OBAMA 2028?! JD Vance Proven RIGHT On European DICTATORSHIP! – SF558
139K44