Premium Only Content
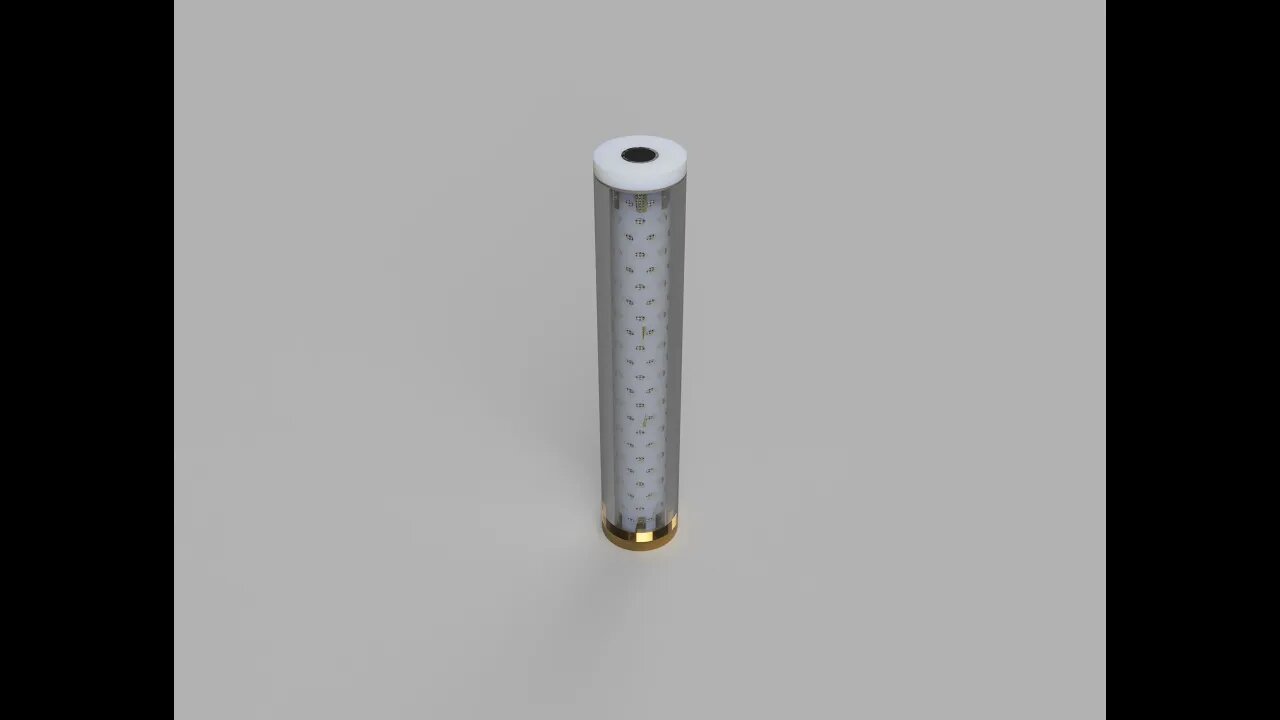

Finger Fuel Cell
Plastic cylinder with reloadable metal pipe electrode, separator, carbon felt and graphite rod core, metal pipe touches the bottom metal plate and graphite rod is the top contact, with some carbon felt to let the fuel cell exchange air, and add the electrolyte. Designed to be used upright but can be possibly used in any orientation, because electrolyte liquid does not escape from the separator and carbon felt, but is infused in the salt bridge. Majority of the fuel cell weight is the metal pipe, from 80% up, other materials are plastic and carbon felt/graphite, which are many times lighter than the metal in same volume, especially iron. Specific energy rating is 80-95% close to the metal energy density, from 1.3kWh/kg of zinc to 9.0kWh/kg of silicon. Fast swap of the metal-pipe electrode after full consumption, swap out the powder dust metal oxide and insert a new metal pipe, such as zinc, iron, tin, aluminium, magnesium, silicon pipe, even copper metal electrode provides some electricity in pure ethanol-koh electrolyte, aluminium is not compatible with aluminium metal electrode in water-koh electrolyte for hydrogen evolution. Ethanol/water-KOH electrolyte is recommended, as NaOH in water will not etch metal oxides enough, also sulfates like magnesium sulfate, iron sulfate or zinc sulfate in water are possible electrolytes. In ethanol-KOH/NaOH electrolyte mixes, potassium/sodium ethoxide in solution will enhance etching-removal of the metal oxides from the electrodes, also providing low temperature compatibility-operation of the aqueous/ethanol fuel cells.
-
 0:12
0:12
Jkauppafi
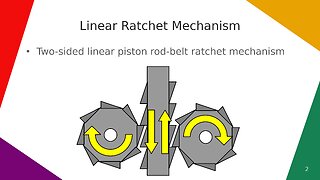
21 days agoLinear Ratchet Mechanism
-
 40:25
40:25
BonginoReport
4 hours agoTrump Cancels Zelensky’s 'Gravy Train' (Ep.144) - 02/20/2025
58.8K84 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Wendy Bell Radio
5 hours agoLONG LIVE THE KING
12,594 watching -
 1:27:55
1:27:55
Game On!
17 hours ago $4.36 earnedThe BIGGEST Hockey Match of the Century: USA vs Canada!
47.1K3 -
 17:20
17:20
Bearing
1 hour agoElon Musk's Baby Mama Drama 😧 Did he Stick it in CRAZY??
6.73K4 -
 LIVE
LIVE
2 MIKES LIVE
2 hours agoTHE MIKE SCHWARTZ SHOW with DR. MICHAEL J SCHWARTZ 02-20-2025
197 watching -
 10:33
10:33
ThinkStory
19 hours agoCOMPANION Ending Explained!
62.9K3 -
 19:59
19:59
Neil McCoy-Ward
19 hours ago🇺🇸 $5,128.21 DOGE Stimulus Check Refund?! Here’s What You Need to Know!
46.6K25 -
 29:22
29:22
Degenerate Jay
22 hours ago $3.94 earnedIs Captain America: Brave New World That Bad? - Movie Review
41.3K5 -
 2:35
2:35
Mrgunsngear
21 hours ago $4.74 earnedFrying Pan As Improvised Body Armor?
63.2K26