Premium Only Content
Moving water in Space
In the microgravity environment of space, the behavior of fluids, including water, is quite different from what we experience on Earth due to the absence of gravity or the presence of extremely weak gravitational forces. Here's a description of moving water in space:
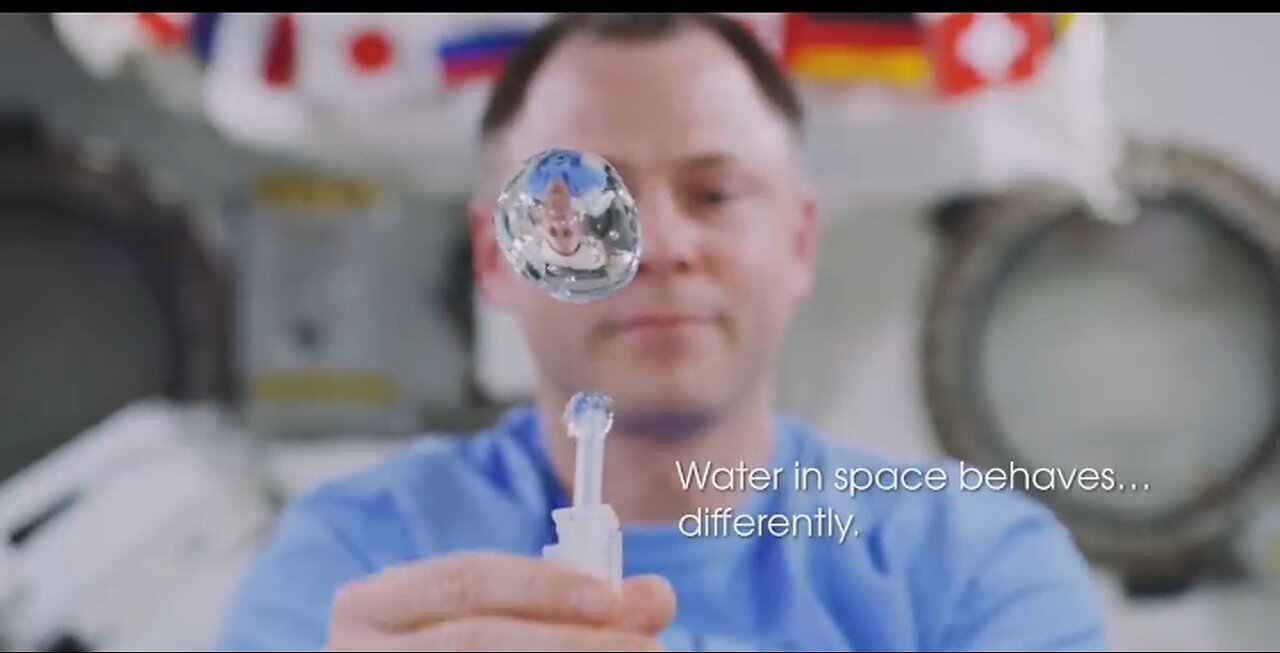
In the vacuum of space, water behaves in fascinating and unusual ways. Without the force of gravity pulling it downward, water doesn't naturally settle into a container or flow in the same manner as it does on Earth. Instead, water forms into spherical shapes due to the cohesive forces between its molecules. These spheres are referred to as "water droplets" or "water globules."
When water is set in motion in space, it doesn't flow like a traditional liquid but rather moves as discrete droplets that can collide, merge, and break apart. This behavior occurs due to the lack of buoyancy and the absence of a stable reference direction (such as "up" and "down"). As a result, water can be propelled using mechanical devices or by expelling it through a nozzle to create thrust.
In microgravity, surface tension becomes a dominant force. Water droplets tend to stick to surfaces and can form thin films, which can be counterintuitive when compared to the behavior of liquids on Earth. When water moves through the air inside a spacecraft, for example, it can form elongated shapes due to surface tension, resembling beads strung together.
Astronauts and researchers have studied the behavior of water in space extensively, as it has implications for various applications, including life support systems, propulsion mechanisms, and fundamental scientific research. By understanding how fluids behave in microgravity, scientists can develop innovative technologies and solutions for space exploration and utilization.
It's worth noting that water is a precious resource in space, and efficient management of water resources is crucial for sustaining human presence during long-duration missions. This includes carefully designed systems to capture, purify, and recycle water, minimizing waste and dependence on resupply from Earth.
In summary, moving water in space involves the manipulation of water droplets due to the absence of gravitational forces as we experience on Earth. This behavior has unique characteristics driven by surface tension, and understanding these behaviors is essential for various space applications.
#SpaceWater
#MicrogravityFluids
#ZeroGHydrodynamics
#AquaInSpace
#FluidBehavior
#GravityFreeWater
#SpaceDroplets
#WaterInMicrogravity
#SurfaceTensionSpace
#FluidsResearch
#SpaceScience
#AstronautExploration
#SpaceTech
#InnovationInSpace
#SustainableSpace
#WaterManagement
#FutureOfSpace
#SpaceExploration
#SpaceMissions
#BeyondEarth
#NASA
#SpaceResearch
#NASAExploration
#SpaceScience
#NASAInnovation
#Astronauts
#SpaceDiscovery
#NASAmissions
#NASAtech
#SpaceExploration
#NASAinsights
#NASAknowledge
#NASAcommunity
#SpaceInspiration
#NASAupdates
#NASAachievements
#NASAinsights
#NASAadvancements
-
 LIVE
LIVE
megimu32
4 hours agoON THE SUBJECT: Music fun, Marvel Madness, and HOTSEATTODD!
279 watching -
 7:24:37
7:24:37
Dr Disrespect
9 hours ago🔴LIVE - DR DISRESPECT - WARZONE - NEW SEASON 2 UPDATE
157K28 -
 58:55
58:55
Candace Show Podcast
5 hours agoBACKSTABBED: Justin Baldoni’s Leaked Voicemail, RFK Jr’s Betrayal | Candace Ep 140
114K187 -
 54:34
54:34
LFA TV
9 hours agoThe Deportation Mandate | TRUMPET DAILY 1.28.25 7pm
22.2K3 -
 1:31:36
1:31:36
The Big Mig™
12 hours agoFauci’s Fiction w/ Dr. Michael J Schwartz
37.6K6 -
 DVR
DVR
Edge of Wonder
4 hours agoChina’s DeepSeek AI Engineered to Censor, Control & Overpower USA
20.1K5 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Quite Frankly
6 hours ago"Small Town Charm, ICE ICE Baby, Open Lines" 1/28/25
1,722 watching -
 41:25
41:25
Chrissy Clark
3 hours agoJohn Fetterman TRIGGERS “The View,” Deportations Upset Selena Gomez, & MORE I Underreported Stories
11.3K9 -
 59:42
59:42
PMG
7 hours ago $0.34 earnedManhood in Crisis: What Ancient Rome Can Teach the 21st Century
13.5K2 -
 4:07:35
4:07:35
Akademiks
5 hours agoASAP Rocky Case has Begun . He's facing 24 years for SH**ting his friend!
75.9K8