Premium Only Content
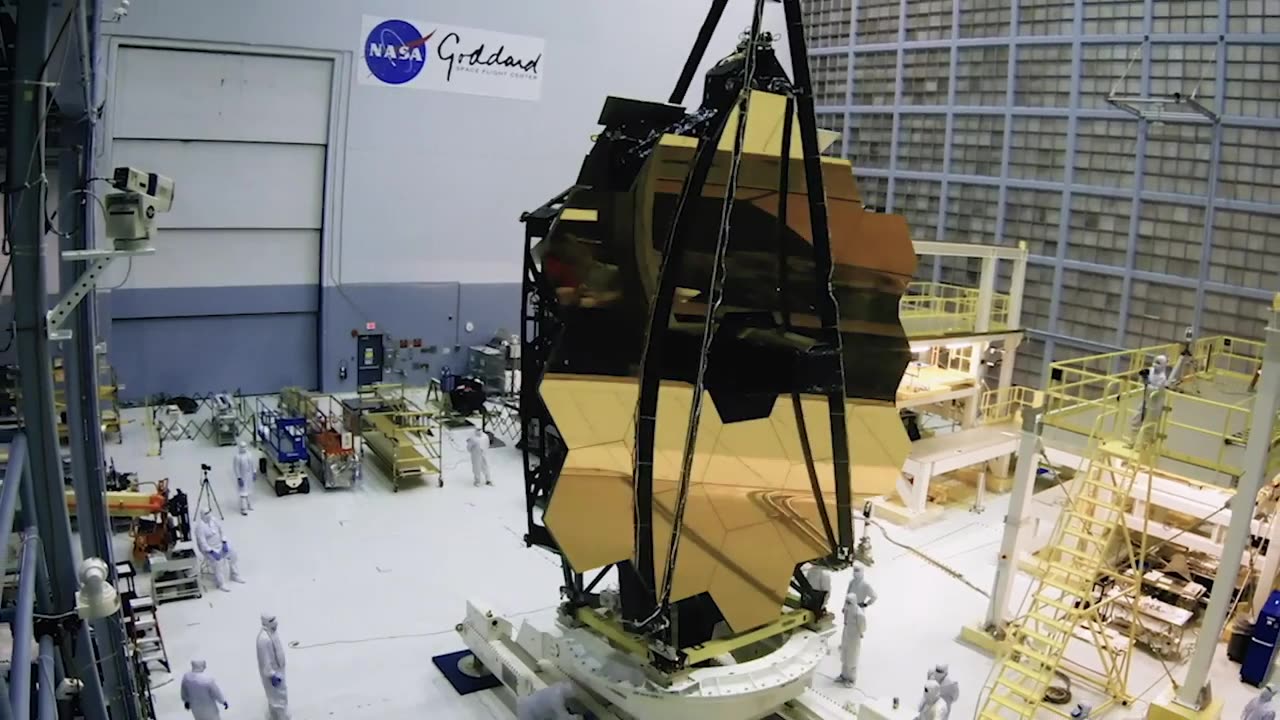
Introduction to the James Webb Space Telescope Mission
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a large, infrared-optimized space telescope that is a collaborative project between NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA). It is named after James E. Webb, who served as the second administrator of NASA and played a crucial role in the Apollo program.
The main objectives of the James Webb Space Telescope mission are:
Infrared Observations: JWST is designed to observe the universe in the infrared wavelength range, which allows it to see through dust and gas that often obscure visible light observations. This enables JWST to study a wide range of astronomical phenomena, from the formation of stars and galaxies to the detection of exoplanets and the study of distant galaxies.
Cosmic Origins: JWST aims to study the origins of the universe by observing the first galaxies that formed after the Big Bang, helping astronomers better understand the early universe and the processes that led to the formation of galaxies, stars, and planets.
Exoplanet Characterization: One of JWST's key goals is to study exoplanets (planets outside our solar system) in detail. It can analyze the atmospheres of exoplanets, which can provide insights into their composition, temperature, and potential habitability.
Stellar Evolution: JWST will study the life cycles of stars, from their formation in dense interstellar clouds to their evolution into various types of stars and ultimately their deaths as supernovae or other stellar remnants.
Formation of Solar Systems: The telescope will observe protoplanetary disks around young stars, helping scientists understand how planets form within these disks and how our own solar system might have formed.
Galactic Evolution: By observing distant galaxies, JWST will shed light on how galaxies have evolved over cosmic time, allowing astronomers to better understand the processes that drive their growth and transformation.
Key Science Programs: JWST has been designed with several specific science programs in mind, including the study of the early universe, the assembly of galaxies, the birth of stars and planetary systems, and the characterization of exoplanet atmospheres.
-
 2:11:20
2:11:20
I_Came_With_Fire_Podcast
16 hours agoFar Left TROJAN HORSE | SPECIAL Forces in MEXICO | GERMANY under FIRE
23K13 -
 1:41:00
1:41:00
Darkhorse Podcast
13 hours agoIf Only We’d Known: The 265th Evolutionary Lens with Bret Weinstein and Heather Heying
153K38 -
 1:58:29
1:58:29
Conspiracy Pilled
3 days agoThe Vaccine Conversation (S5 - Ep17)
65K2 -
 11:22
11:22
Tundra Tactical
10 hours ago $4.23 earnedUSA vs Canada HOCKEY Fight: The Real PRIDE Fighting.
66.5K8 -
 54:43
54:43
LFA TV
1 day agoWhy Exposing Waste and Fraud Terrifies the Beltway | TRUMPET DAILY 2.19.25 7PM
61.2K10 -
 1:01:13
1:01:13
Candace Show Podcast
11 hours agoBlake Lively's BOMBSHELL Legal Filing | Candace Ep 149
131K153 -
 1:11:22
1:11:22
Vigilant News Network
14 hours agoElon Musk Shuts Down RFK Jr. Critics With One Powerful Statement | The Daily Dose
85.8K29 -
 1:12:23
1:12:23
Dad Dojo Podcast
1 day ago $2.49 earnedEP20: The Super Bowl and Solving The Economy
49.8K -
 4:49
4:49
Tactical Advisor
3 days agoBest Small Handgun Optics | CH PWS Shot Show 2025
34.8K2 -
 1:01:21
1:01:21
In The Litter Box w/ Jewels & Catturd
1 day agoI've Got Your Proof - Right Here! | In the Litter Box w/ Jewels & Catturd – Ep. 745 – 2/19/2025
114K34