Premium Only Content
what is Mitochondria ,structure and function of Mitochondria #viral #2023 #education#learning
Asalamualaikum EveryOne......!
Welcome to our education channel! Here, we strive to provide a comprehensive platform for learning and sharing knowledge on a wide range of subjects. Whether you're a student, educator, or simply someone with a thirst for knowledge, our channel is designed to cater to your intellectual curiosity.
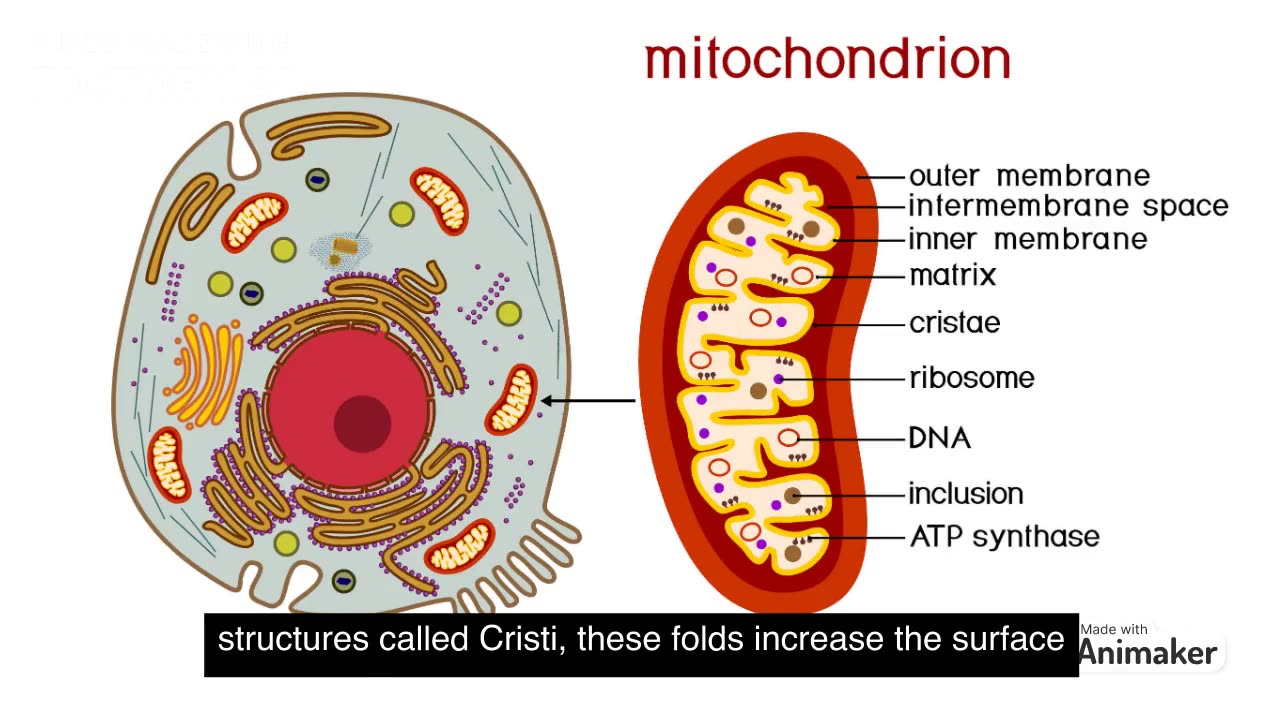
WHAT IS MITOCHONDRIA?
Mitochondria are organelles found in the cells of most eukaryotic organisms. Often referred to as the "powerhouses" of the cell, mitochondria play a crucial role in cellular respiration and energy production. They are often described as the cell's energy generators or factories.
Here are some key features and functions of mitochondria:
Structure: Mitochondria have a distinct double-membrane structure. The outer membrane acts as a protective barrier, while the inner membrane is highly folded, forming structures called cristae. These folds increase the surface area available for chemical reactions. The innermost space within the inner membrane is called the mitochondrial matrix.
ATP Production: Mitochondria are responsible for generating adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is the primary energy currency of cells. The process of ATP production occurs through aerobic respiration in the presence of oxygen, specifically in a series of reactions called the electron transport chain (ETC) and oxidative phosphorylation. This process takes place on the inner mitochondrial membrane and within the mitochondrial matrix.
Metabolic Functions: In addition to ATP production, mitochondria are involved in other metabolic processes. They are essential for the breakdown of carbohydrates, fats, and amino acids, which are used as fuel sources for energy production. These organelles are also involved in the synthesis of certain molecules, such as heme (a component of hemoglobin) and some amino acids.
Calcium Regulation: Mitochondria play a role in regulating calcium ion concentrations within the cell. They can store and release calcium ions, which are crucial for various cellular processes, including muscle contraction, cell signaling, and apoptosis (programmed cell death).
Cell Signaling: Mitochondria are involved in cell signaling pathways. They produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) as byproducts of ATP production, which can act as signaling molecules. ROS can participate in cellular signaling pathways involved in processes like apoptosis, inflammation, and the regulation of gene expression.
It is important to note that mitochondria have their own DNA, known as mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). This unique feature suggests that mitochondria have their own evolutionary origin and are believed to have originated from a symbiotic relationship between early eukaryotic cells and ancestral bacteria.
-
 4:27:46
4:27:46
Nerdrotic
11 hours ago $51.32 earnedDaredevil Born Again REVIEW, Harry Potter Show DOA, DC HACKED! | Friday Night Tights 344 Paul Chato
143K39 -
 1:15:15
1:15:15
Glenn Greenwald
8 hours agoWeek in Review: Lee Fang and Leighton Woodhouse on Ukraine War and NYT Piece Revealing Tensions within Trump Admin; PLUS: Lee Fang Takes Audience Questions on DOGE and Big Tech | SYSTEM UPDATE #420
85.6K44 -
 1:03:30
1:03:30
Sarah Westall
10 hours agoMassive Government Overhaul: FBI, CIA, IRS and more to be Gutted w/ Sam Anthony
94.5K28 -
 1:07:40
1:07:40
IsaacButterfield
10 hours ago $4.77 earnedAustralia Under Attack | Trump's State of the Union | All LGBTQ Cast (W Guest Frenchy)
48.8K9 -
 1:23:37
1:23:37
Edge of Wonder
10 hours agoIs Your Car Collecting Your Biodata? Whistleblower Exposes Dark Agenda
45.3K9 -
 2:08:50
2:08:50
Quite Frankly
13 hours ago"A Rat at HHS, Gene Hackman, Musical Extras" ft. J Gulinello 3/7/25
47.4K15 -
 55:49
55:49
LFA TV
1 day agoGermany Started Two World Wars and Now Wants Nuclear Weapons | TRUMPET DAILY 3.7.25 7PM
40.6K46 -
 1:34:38
1:34:38
2 MIKES LIVE
9 hours ago2 MIKES LIVE #189 Open Mike Friday (Sort Of)
30K -
 1:48:14
1:48:14
Right Side Broadcasting Network
17 hours agoLIVE REPLAY: President Trump Delivers Remarks at The White House Digital Assets Summit - 3/7/25
152K42 -
 2:07:17
2:07:17
The Quartering
14 hours agoTrump Goes Ballistic On Russia & Ukraine Gets Results, Democrat Cringe, FBI Arrests Military Men
148K83