Premium Only Content
133 Days on the Sun - Solar System
Solar System
The solar system is a vast and intricate cosmic structure consisting of a star, planets, moons, asteroids, comets, and other celestial objects bound together by gravity. Our solar system is located within the Milky Way galaxy, specifically in one of its spiral arms known as the Orion Arm.
Here are some key facts and a brief description of the major components of the solar system:
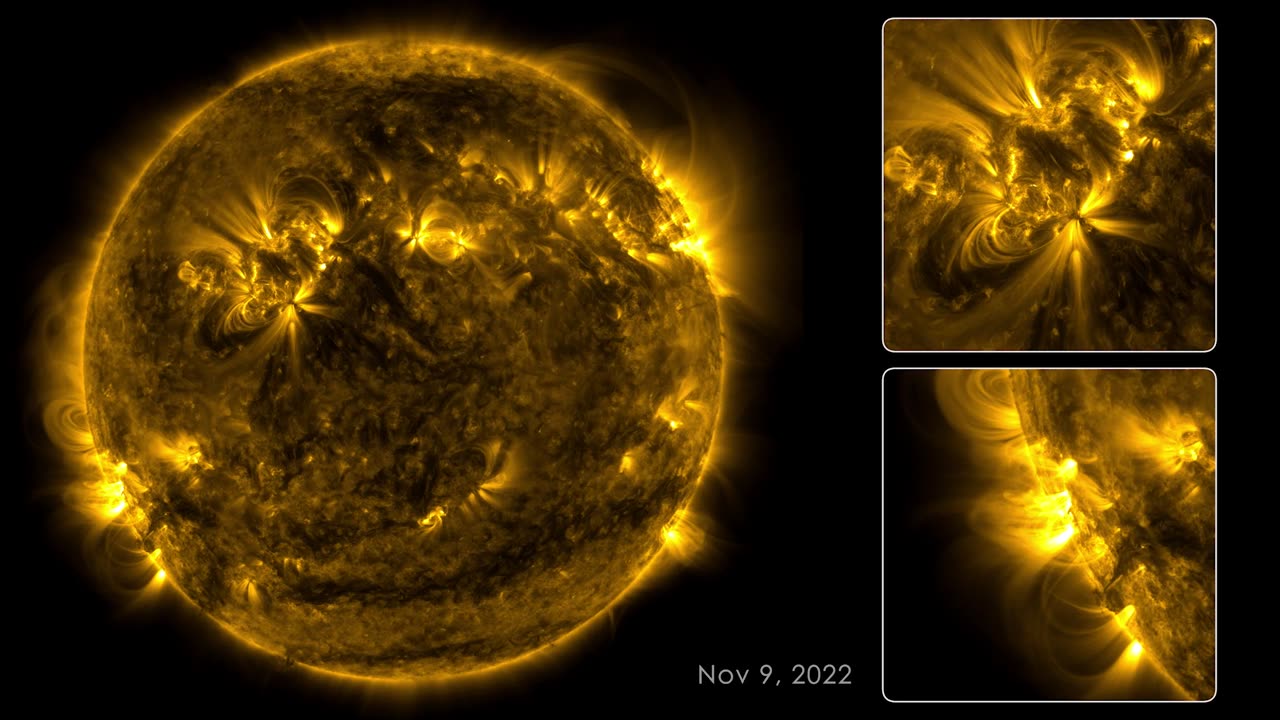
Sun (The Star):
The Sun is the central and most massive object in the solar system, accounting for more than 99% of its total mass.
It is a G-type main-sequence star, commonly referred to as a yellow dwarf, and is about 4.6 billion years old.
The Sun's energy is produced through nuclear fusion, primarily converting hydrogen into helium, which emits light and heat.
Planets:
There are eight recognized planets in the solar system, categorized into two main groups: terrestrial planets (inner planets) and gas giants (outer planets).
Terrestrial Planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars. These planets are relatively small, rocky, and have solid surfaces.
Gas Giants: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune. These planets are much larger and composed mainly of hydrogen and helium, with no solid surface.
Dwarf Planets:
Pluto was formerly classified as the ninth planet but was reclassified as a dwarf planet in 2006 by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Other notable dwarf planets include Eris, Haumea, Makemake, and Ceres.
Moons (Natural Satellites):
Moons orbit around planets, and some are quite large and geologically active, like Jupiter's moon Io and Saturn's moon Enceladus.
Earth's moon (Luna) is the fifth-largest natural satellite in the solar system and plays a significant role in Earth's tidal processes.
Asteroids and Comets:
Asteroids are rocky objects that orbit the Sun, primarily found in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.
Comets are icy bodies that often develop a glowing coma and a tail when they approach the Sun. They originate from the Kuiper Belt and the Oort Cloud.
Kuiper Belt and Oort Cloud:
The Kuiper Belt is a region beyond Neptune that contains icy objects, including Pluto and other dwarf planets. The Oort Cloud is a hypothetical region far beyond the Kuiper Belt, believed to contain a vast reservoir of comets.
Orbits and Distances:
The distance between the planets and the Sun varies greatly. Astronomical units (AU) are used to measure these distances, with 1 AU being the average distance between Earth and the Sun (about 93 million miles or 150 million kilometers).
Formation and Evolution:
The solar system likely formed from a giant molecular cloud of gas and dust. The Sun formed at its center, and the remaining material accreted into planets, moons, and other objects over millions of years.
The solar system continues to be a subject of scientific research and exploration, with ongoing missions to study and learn more about its various components and their interactions.
#Solar Observations
#Sun's Activity
#Solar Flares
#Sunspot Cycle
#Solar Dynamics
#Space Weather
#Solar Phenomena
#Solar Science
#Sun's Magnetic Field
#Solar Eruptions
#Solar Exploration
#Sunspot Observations
#Sun's Corona
#Solar Research
#Sunspot Analysis
#Solar Images
#Solar Activity Time-Lapse
#Sun's Surface
#Solar Flare Monitoring
#Sun's Energy
-
 3:18:47
3:18:47
DLDAfterDark
11 hours ago $8.35 earnedDLD Live! What's The "best" PDW?? Considerations For Trunk/Truck Gun & Gats in Bags & Backpacks
41.5K10 -
 DVR
DVR
saiyagamertv
7 hours agoIm ready to RUMBLE lets WIN!!
56 -
 15:25
15:25
Exploring With Nug
22 hours ago $25.25 earnedBag of Phones Found While Searching For Missing Man In River!
105K31 -
 3:58:27
3:58:27
fuzzypickles168
11 hours agoLate Nite Jam Session - Rock Band 4 | Was: EA Sports WRC | 1 John 2:1-17
39.8K -
![Nintendo Switch It UP Saturdays with The Fellas: LIVE - Episode #13 [Mario Kart 8 Deluxe]](https://1a-1791.com/video/fww1/97/s8/1/1/g/A/z/1gAzy.0kob-small-Nintendo-Switch-It-UP-Satur.jpg) 3:33:38
3:33:38
MoFio23!
21 hours agoNintendo Switch It UP Saturdays with The Fellas: LIVE - Episode #13 [Mario Kart 8 Deluxe]
76.2K2 -
 23:24
23:24
MYLUNCHBREAK CHANNEL PAGE
22 hours agoDams Destroyed Turkey
119K101 -
 7:24:43
7:24:43
SpartanTheDogg
14 hours agoPro Halo Player
79.7K2 -
 11:29
11:29
Tundra Tactical
14 hours ago $4.00 earnedGEN Z Brit 3D Prints a WORKING Gun Pt.3!
71.6K8 -
 8:07:55
8:07:55
AdmiralSmoothrod
16 hours agoark ascended - its dino time again
44.8K2 -
 2:08:21
2:08:21
The Illusion of Consensus
9 days agoFormer FDA Official Dr. Philip Krause On White House Pressure To Approve Covid Vaccines at the FDA
79K109