Premium Only Content
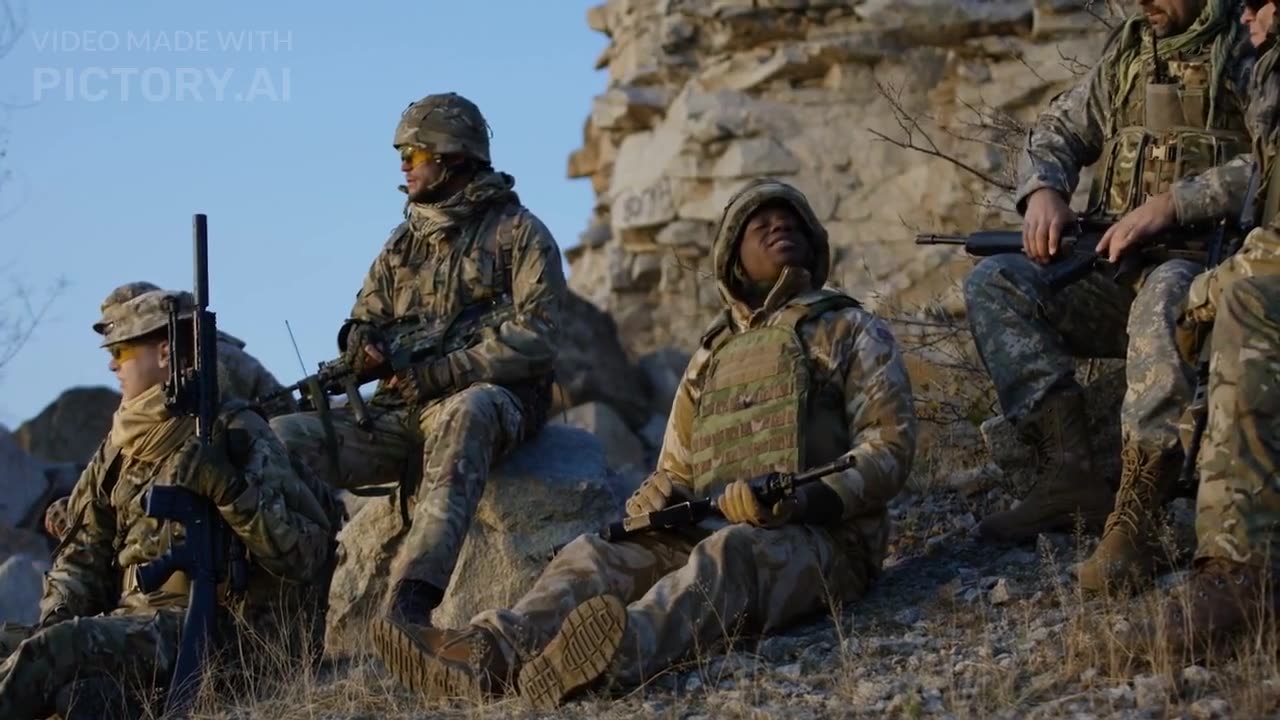

World War 1
World War 1, also known as the Great War, was a global conflict that took place from 1914 to 1918. It involved many of the world's major powers and was primarily centered in Europe. Here are some key points about World War 1:
Causes:
Nationalism: Intense patriotism and the desire for self-determination among various ethnic groups in Europe.
Imperialism: Rivalries over colonies and resources, particularly in Africa and Asia.
Militarism: The build-up of armed forces and a focus on military strength.
Alliances: The formation of rival alliances, such as the Triple Entente (France, Russia, and the United Kingdom) and the Central Powers (Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy).
Key Events:
Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand: On June 28, 1914, the heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne, Archduke Franz Ferdinand, was assassinated in Sarajevo by a Serbian nationalist, Gavrilo Princip. This event triggered a chain reaction of alliances and led to the outbreak of war.
Western Front: The war quickly turned into a stalemate on the Western Front, with both sides digging trenches and engaging in trench warfare.
Eastern Front: Fighting between Germany and Austria-Hungary against Russia took place on the Eastern Front, with significant battles like Tannenberg and the Brusilov Offensive.
U.S. Entry: The United States entered the war in 1917 on the side of the Allies (including France, the UK, and Russia) after German unrestricted submarine warfare and the revelation of the Zimmerman Telegram.
Armistice and Treaty of Versailles: The armistice was signed on November 11, 1918, marking the end of hostilities. The Treaty of Versailles, signed in 1919, officially ended the war and imposed harsh conditions on Germany, which would later contribute to World War II.
Consequences:
Casualties: The war resulted in millions of casualties, both military and civilian, due to combat, disease, and famine.
Redrawing of Boundaries: The Treaty of Versailles led to significant territorial changes, the collapse of empires (such as the Austro-Hungarian and Ottoman Empires), and the creation of new nations.
League of Nations: The League of Nations was established as an international organization to promote peace and prevent future conflicts. It was a precursor to the United Nations.
Economic Impact: The war caused severe economic disruptions and led to the reevaluation of global trade and financial systems.
Social and Political Changes: World War 1 had profound social and political effects, including the women's suffrage movement, disillusionment with traditional institutions, and the rise of communism and fascism in the interwar period.
World War 1 was a devastating conflict that reshaped the geopolitical landscape and set the stage for future conflicts and political developments in the 20th century.
-
 10:39
10:39
World War One Footage
1 year agoWorld War I Footage
27 -
 0:13
0:13
Mark Levin Show
1 year agoWorld War 3
9.1K8 -
 1:21:41
1:21:41
WARYAHZ
1 year agoWORLD WIDE WAR
7321 -
 1:10
1:10
HeppyIsland
1 year agoWorld war 2023
1 -
 30:48
30:48
Toni do Capri
1 year agoWORLD WAR Z #7 JERUSALÉM
-
 3:31
3:31
actuele Soemo
1 year agoWorld War 3?
27 -
 0:19
0:19
AmericanWoman711
1 year agoWORLD WAR 3
451 -
 0:25
0:25
ww3ready
1 year agoworld war 3
40 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Bannons War Room
1 year agoWarRoom Live
33,047 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
LFA TV
21 hours agoTARIFF TRADE WAR! | LIVE FROM AMERICA 2.3.25 11am
4,118 watching