Premium Only Content
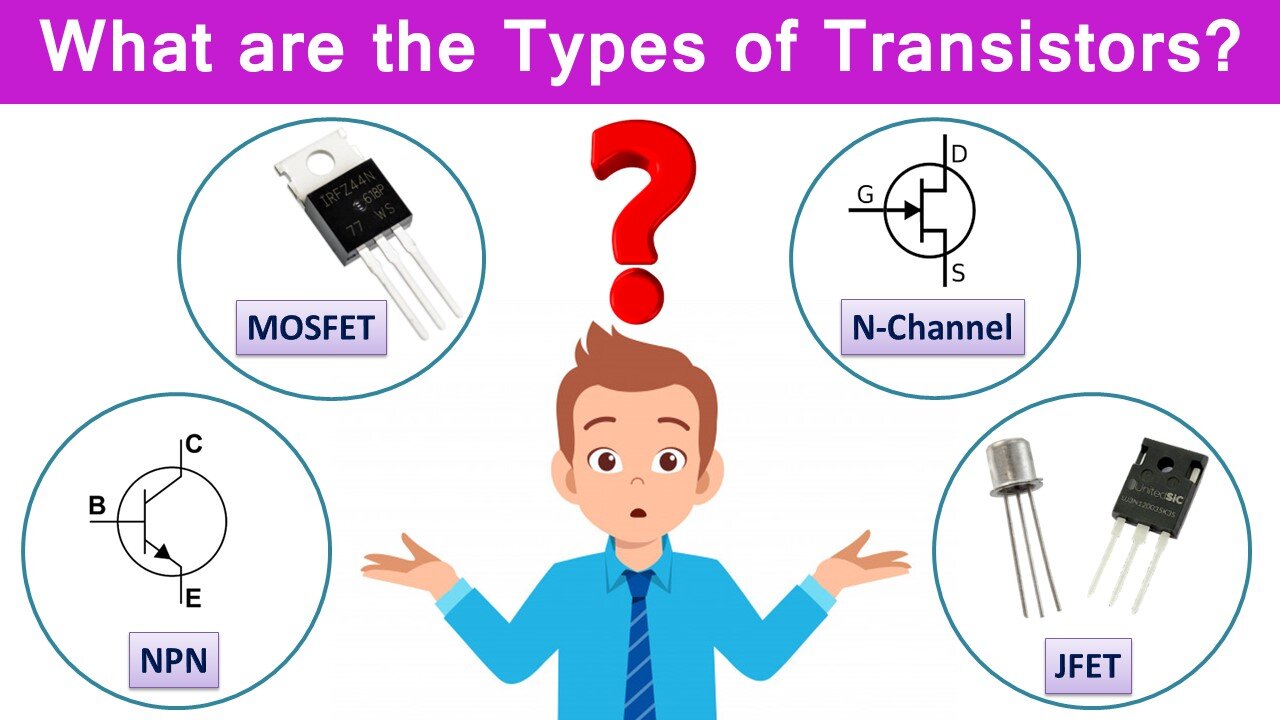
What are the Types of Transistors?
At the beginning of the 20th century, when computers began to be produced, they were gigantic. Today, however, there has been the discovery of transistors that make them small enough to take them on our knees and fit them in our palms with phones or tablets. In addition, thanks to transistors, processors that offer much faster operation have been developed. A transistor is an electronic circuit element that regulates current or voltage flow and acts as a switch or amplifier for electronic signals. It was invented in 1947 and quickly replaced the vacuum tube as an electronic signal conditioner. It consists of a layer of doped semiconductor materials such as silicon and germanium, each of which can carry a current. The subject of this video is not the structure and history of transistors, but after a small introduction about transistors, we can move on to our main topic.
You may know or have heard of transistors such as BJT, MOSFET, JFET, NPN, N-Channel and many more. But you may have trouble distinguishing them. If so, this lesson is for you. At the end of this video, we will basically learn that all three pins circuit elements are not transistors, how transistors are classified and how we can distinguish them.
Transistors are classified into two groups, BJT and FET. These expressions come from abbreviations formed from the initials of their English names. BJT comes from the acronym Bipolar Junction Transistor while FET comes from the abbreviation Field Effect Transistor. The task of both transistors is to provide current control or voltage amplification as a switch. If we talk briefly about the differences between them, BJTs control current and current, while FETs control voltage and current. BJTs are quickly affected by temperature, while FETs are less affected by temperature. As such, BJTs degrade quickly, while FETs are more durable and long-lasting. Therefore, BJTs are generally preferred in low-current hobby electronic applications, while FETs are mostly preferred in low-voltage commercial applications. Also, BJTs have a low switching speed, while FETs have a high switching speed.
-
 8:09
8:09
Electrical Electronics Applications
1 year agoSeries and Parallel Combination Circuits Explained | How to Solve Any Series and Parallel Circuit?
159 -
 1:18:01
1:18:01
Glenn Greenwald
7 hours agoWill Trump's Second Term Promote Economic Populism? Matt Stoller On Cabinet Picks To Fight Corporate Power; Should Liberals Cut Off Pro-Trump Friends & Family? | SYSTEM UPDATE #372
158K126 -
 2:26:30
2:26:30
WeAreChange
8 hours agoTrump To Subdue Deranged Opposition! ARRESTS Planned
126K51 -
 1:19:04
1:19:04
JustPearlyThings
8 hours agoWhy MODERN WOMEN Keep REJECTING The Redpill! | Pearl Daily
97.8K52 -
 1:15:03
1:15:03
Man in America
10 hours agoBig Pharma EXPOSED: The HIDDEN Cures They Tried to Bury
27.8K12 -
 2:18:12
2:18:12
VikingsOutlawsAndCowboys
10 hours agoVOC SHOW LIVE - #9
8.62K -
 43:22
43:22
PMG
1 day ago $3.25 earned"Sean Parnell Speaks Out for Tulsi Gabbard and Pete Hegseth; J6 Pardons Needed"
22.3K7 -
 1:14:23
1:14:23
Flyover Conservatives
1 day agoShifting Alliances: Tulsi, Musk, RFK, Rogan… CAN THEY BE TRUSTED? - Roger Stone | FOC Show
32.5K1 -
 39:01
39:01
The Why Files
8 days agoSymbols of Power: Deciphering the Language of the Secret Elite
114K64 -
 1:07:16
1:07:16
Edge of Wonder
10 hours agoWho Are the Men in Black? The CIA Connection
27.1K5