Premium Only Content
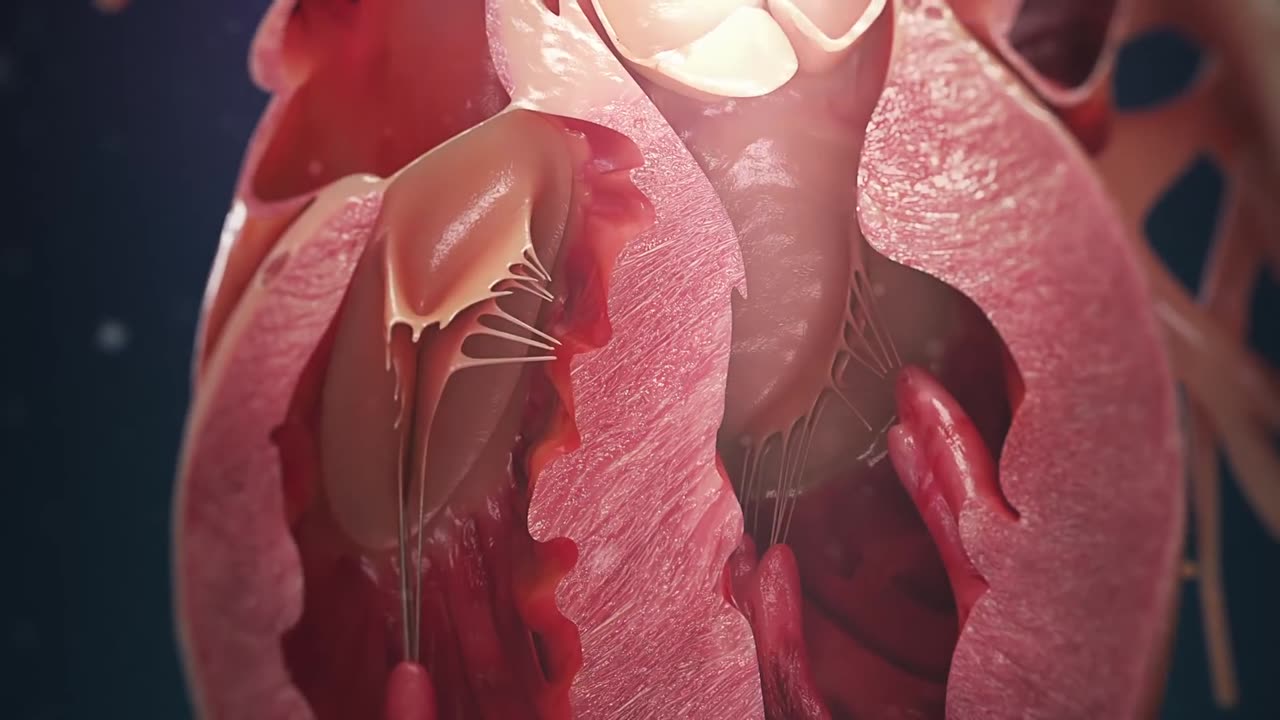
Human Circulatory System
The human circulatory system is a complex network of organs, vessels, and tissues that work together to transport blood, nutrients, and oxygen throughout the body. The circulatory system includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood.
The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood through the circulatory system. It is divided into four chambers: the right atrium, the right ventricle, the left atrium, and the left ventricle. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body and pumps it to the right ventricle, which then pumps it to the lungs to be oxygenated. The left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs and pumps it to the left ventricle, which then pumps it to the rest of the body.
Blood vessels are tubes that carry blood throughout the body. There are three types of blood vessels: arteries, veins, and capillaries. Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to the rest of the body, while veins carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart. Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels and connect arteries to veins. They are responsible for the exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products between the blood and the body's cells.
Blood is a fluid that carries oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body. It is composed of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Plasma is the liquid portion of blood that contains nutrients, hormones, and proteins. Red blood cells carry oxygen from the lungs to the body's cells, while white blood cells help fight infections and diseases. Platelets are responsible for clotting blood to stop bleeding.
Overall, the circulatory system plays a crucial role in maintaining the body's health and well-being by ensuring that oxygen and nutrients reach all of the body's cells, while waste products are removed.
-
 10:37
10:37
Russell Brand
2 days agoHow is this even allowed?
162K835 -
 1:37:26
1:37:26
Real Coffee With Scott Adams
6 hours agoEpisode 2701 CWSA 12/26/24
87.4K82 -
 2:58:58
2:58:58
Wendy Bell Radio
10 hours ago9 Steps Ahead
116K138 -
 2:03:46
2:03:46
LFA TV
19 hours agoTIME FOR A NEW SPEAKER! | LIVE FROM AMERICA 12.26.24 11am EST
66.9K41 -
 1:40:22
1:40:22
Game On!
16 hours ago $5.36 earnedNFL Thursday Night Football Seahawks at Bears EXPERT Picks!
50K9 -
 1:50:54
1:50:54
xBuRnTx
6 hours agoWho's Ready for New Years!
36.9K1 -
 12:09
12:09
Tactical Advisor
18 hours agoSmith & Wesson Shield Plus Carry Comp
30.3K2 -
 4:35:25
4:35:25
Father Russell
11 hours agoDelta Force | Not A Woman? | Mad Martigan Time
69.9K5 -
 3:29:42
3:29:42
BrookieMonster
18 hours ago $44.93 earnedChristmas Stream: Marvel Rivals with CallmeSeags 🎄
188K13 -
 LIVE
LIVE
TheSaf3Hav3n
4 days ago| RUMBLES FIRST SUBATHON IS HERE!!! | DAY 5 |
191 watching