Premium Only Content
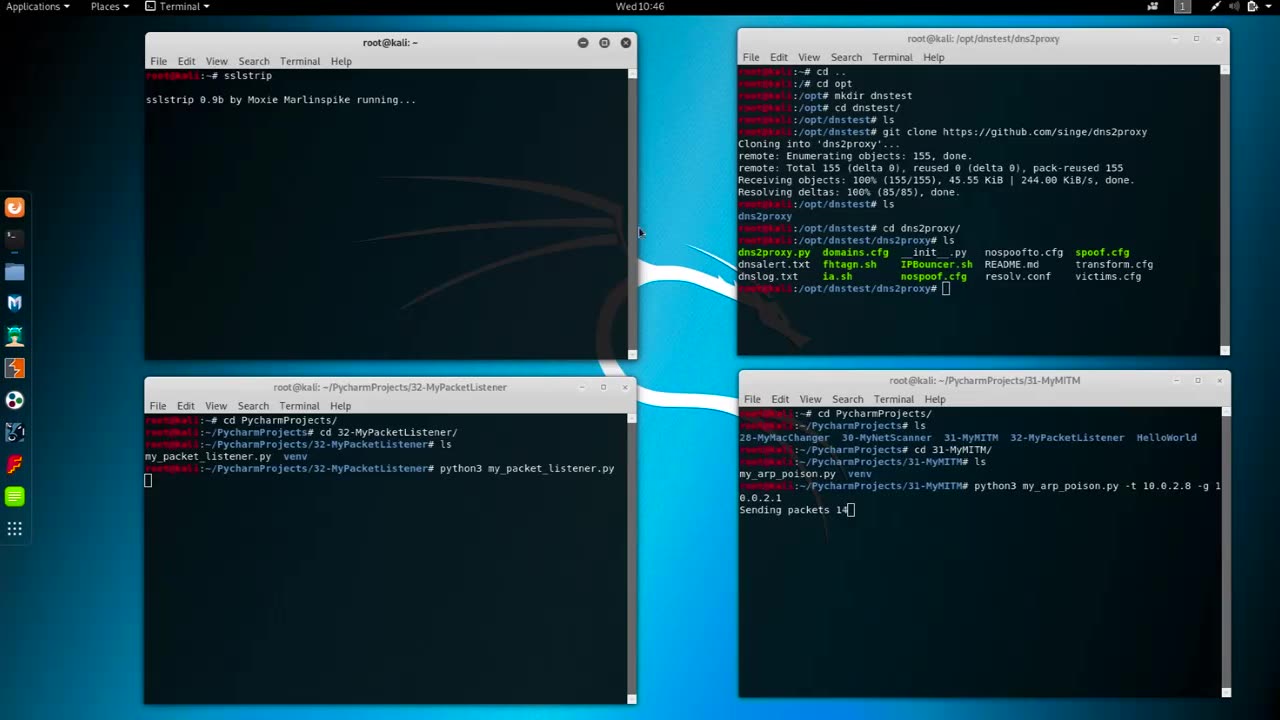
Chapter-36, LEC-6 | Downgrading HTTPS | #ethicalhacking #hacking #education
#ethicalhacking #hacking #rumble #virel #trending #education
Subscribe to our channel YouTube channel.❤️
/@thecybersecurityclassroom
Followe me on Rumble.💕
/@the1cybersequrityclassroom
Downgrading HTTPS, also known as HTTPS downgrade attack or SSL stripping, is a type of cyber attack where an attacker intercepts a secure HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) connection between a client (such as a web browser) and a server, and downgrades it to an insecure HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) connection. This attack can occur when a client tries to establish a secure connection with a website or web application, but the attacker intercepts the communication and manipulates it to remove the encryption, making it vulnerable to eavesdropping, data interception, and tampering.
The HTTPS protocol encrypts data exchanged between a client and a server using SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security) encryption, which ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of the communication. HTTPS is widely used to secure sensitive data, such as login credentials, credit card information, and personal data, transmitted over the internet, and is considered a fundamental security measure to protect users' privacy and sensitive information.
A HTTPS downgrade attack typically involves the following steps:
Intercepting the communication: The attacker positions themselves between the client and the server, intercepting the communication using techniques such as man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, DNS spoofing, or ARP spoofing.
Modifying the communication: The attacker manipulates the communication to remove the HTTPS encryption and downgrades it to HTTP. This can involve altering the client's request to the server or modifying the server's response to the client.
Tampering with data: Once the communication is downgraded to HTTP, the attacker can eavesdrop on the data exchanged between the client and the server, intercept sensitive information, and even modify the data to perform attacks such as injecting malware, redirecting traffic to malicious websites, or stealing credentials.
Downgrading HTTPS can be used as a stepping stone for other attacks, such as phishing, credential theft, or session hijacking, as it allows the attacker to intercept and manipulate the communication between the client and the server without the knowledge of the parties involved.
To protect against HTTPS downgrade attacks, it is important to use secure communication channels, such as HTTPS, whenever sensitive data is transmitted over the internet. Website owners should also implement best practices, such as HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) and certificate pinning, to prevent downgrade attacks and enforce the use of HTTPS. Additionally, users should be cautious when accessing websites, especially on public networks, and be vigilant for any signs of insecure connections, such as missing HTTPS indicators or warning messages from web browsers.
#hacking #growthhacking #biohacking #ethicalhacking #lifehacking #whacking #hackingout #happyhacking #brainhacking #travelhacking #househacking #brainhackingum #hackingtools
#bushwhacking #hacking_or_secutiy #porthacking#porthacking #belajarhacking #hackinginstagram #growthacking #biohackingsecrets #realityhacking #neurohacking #hackingnews #funnelhacking #mindhacking #funnelhackinglive #hackinglife #termuxhacking #learnhacking #bodyhacking #patternhacking #biohackingsuccess #ikeahacking #hackingorsecurity #russianhacking #traumahacking #shackingup #hackinghealth #growthhackingtips #wifihacking
-
 DVR
DVR
Flyover Conservatives
21 hours agoEczema, Brain Fog, B.O., and Gas… Eating Steak and Butter Creates Ultimate Health Hack - Bella, Steak and Butter Gal | FOC Show
15K -
 51:58
51:58
PMG
5 hours ago $0.04 earned"Can the Government Learn from Elon Musk’s 70% Labor Cut? A Deep Dive into Inefficient Agencies"
10.5K -
 LIVE
LIVE
Amish Zaku
5 hours agoRumble Spartans #10 - New Year New Maps
171 watching -
 1:04:58
1:04:58
In The Litter Box w/ Jewels & Catturd
1 day agoNo Tax On Tips! | In the Litter Box w/ Jewels & Catturd – Ep. 722 – 1/17/2025
136K31 -
 5:35:39
5:35:39
Dr Disrespect
11 hours ago🔴LIVE - DR DISRESPECT - WARZONE - CRAZY CHALLENGES
160K33 -
 1:16:30
1:16:30
Edge of Wonder
7 hours agoLA Fire Updates: Miracles Amidst the Devastation
35.3K8 -
 54:54
54:54
LFA TV
11 hours agoBanning Mystery of the Ages | TRUMPET DAILY 1.17.25 7pm
30.2K7 -
 1:47:13
1:47:13
2 MIKES LIVE
5 hours ago2 MIKES LIVE #168 Open Mike Friday!
26.6K2 -
 1:05:11
1:05:11
Sarah Westall
5 hours agoMysterious Fog and California Wildfires Both Contain Dangerous Elements w/ Dr Robert Young & Hazen
30.4K7 -
 1:40:48
1:40:48
Mally_Mouse
4 hours agoLet's Play!! -- Stardew Valley pt. 23!
26.8K