Premium Only Content
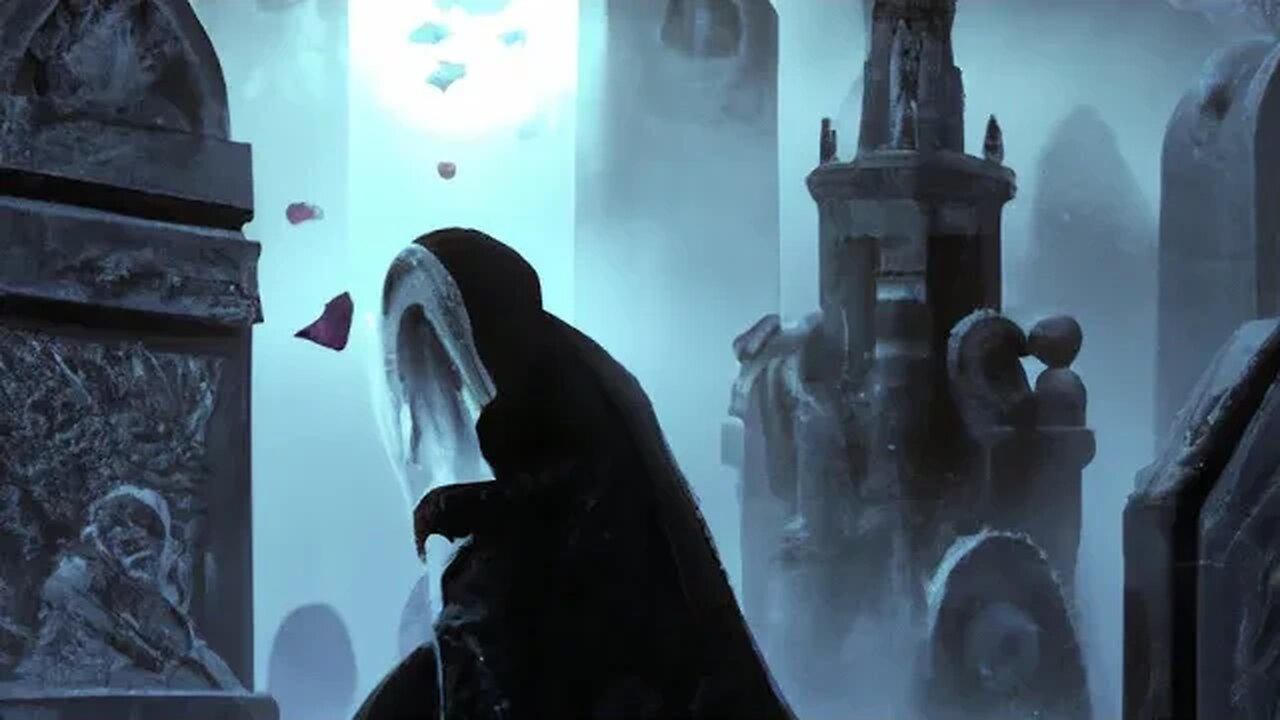

"Rising from the Dead: The Inspiring Story of a Woman's Battle with Cotard's Syndrome"
Cotard's syndrome, also known as Walking Corpse syndrome, is a rare and severe mental illness that affects the way a person perceives reality. It is characterized by the belief that one is dead, does not exist, or has lost their internal organs, along with depression, anxiety, and hallucinations. This condition can cause significant distress and disability, and can greatly impact a person's ability to function in daily life.
The exact causes of Cotard's syndrome are still not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to abnormal activity in certain areas of the brain. It is often seen in conjunction with other mental illnesses such as depression, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder. Some experts believe that a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors may contribute to the development of this condition.
The symptoms of Cotard's syndrome can vary from person to person, but typically include a pervasive feeling of being dead, along with a range of other symptoms such as anhedonia (lack of pleasure or interest in activities), apathy, and nihilistic delusions (beliefs that life has no meaning or purpose). In some cases, people with Cotard's syndrome may also experience hallucinations and delusions, and may engage in self-harm or suicidal behaviors.
Diagnosis of Cotard's syndrome can be challenging, as its symptoms can resemble those of other mental illnesses. A thorough medical and psychiatric evaluation is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis. This may include a physical examination, a review of medical history, and laboratory tests to rule out any underlying medical conditions. A mental health professional may also use diagnostic tools such as the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) and the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) to diagnose Cotard's syndrome.
There is currently no cure for Cotard's syndrome, but with proper treatment, patients can make significant progress in managing their symptoms and improving their quality of life. Treatment typically involves a combination of medications, therapy, and rehabilitation. Antidepressant and antipsychotic medications may be used to help manage symptoms of depression and anxiety, while cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and other forms of talk therapy can help patients develop coping skills and improve their overall outlook. Rehabilitation and support programs can also help patients reintegrate into society and resume normal activities.
Living with Cotard's syndrome can be challenging, but with the right help and support, patients can lead fulfilling lives. It is important for those affected by this condition to seek help from mental health professionals and to have a strong support system in place. Friends, family, and loved ones can play a critical role in helping patients manage their symptoms and providing emotional support.
In conclusion, Cotard's syndrome is a rare and complex condition that can cause significant distress and disability. While there is no cure, with proper treatment and support, people with this condition can make significant progress in managing their symptoms and improving their quality of life. It is important for those affected by Cotard's syndrome to seek help and for the wider public to be more aware of this debilitating condition.
-
 5:00:01
5:00:01
Pepkilla
8 hours agoHappy Thanksgiving ~ Wumble StwEeeem
36.4K5 -
 7:24:25
7:24:25
Rotella Games
1 day agoThanksgiving Side Missions & Hangout | GTA San Andreas
51.2K3 -
 4:07:31
4:07:31
MafiaTwin
7 hours agoFrist Stream On Rumble
36.7K -
 19:41
19:41
Neil McCoy-Ward
10 hours agoFinally! Some Good News Today... (& Happy Thanksgiving!)
23.2K14 -
 7:22:11
7:22:11
tacetmort3m
11 hours ago🔴 LIVE - (HAPPY THANKSGIVING!) BACK WITH MORE STALKER ACTION - STALKER 2 - PART 7
19.5K -
 58:05
58:05
The Tom Renz Show
7 hours agoThanksgiving In America 2024 - With Mark Sherwood
15.3K2 -
 1:13:41
1:13:41
DDayCobra
9 hours ago $1.24 earnedHappy Thanksgiving!
44.2K4 -
 42:24
42:24
Professor Nez
9 hours ago🚨Kamala's Staff CONFESSES to FRAUD! Trump is Already MAKING AMERICA GREAT AGAIN! 🇺🇸
77.7K134 -
 5:12:17
5:12:17
Akademiks
11 hours agoDrake Sues Universal Music Group over Kendrick Lamar 'Not Like Us' again!! Diddy Denied Bail!
89.5K13 -
 1:23:15
1:23:15
Viss
10 hours ago🔴LIVE - Thanksgiving PUBG (Short Stream)
41.5K29