Premium Only Content
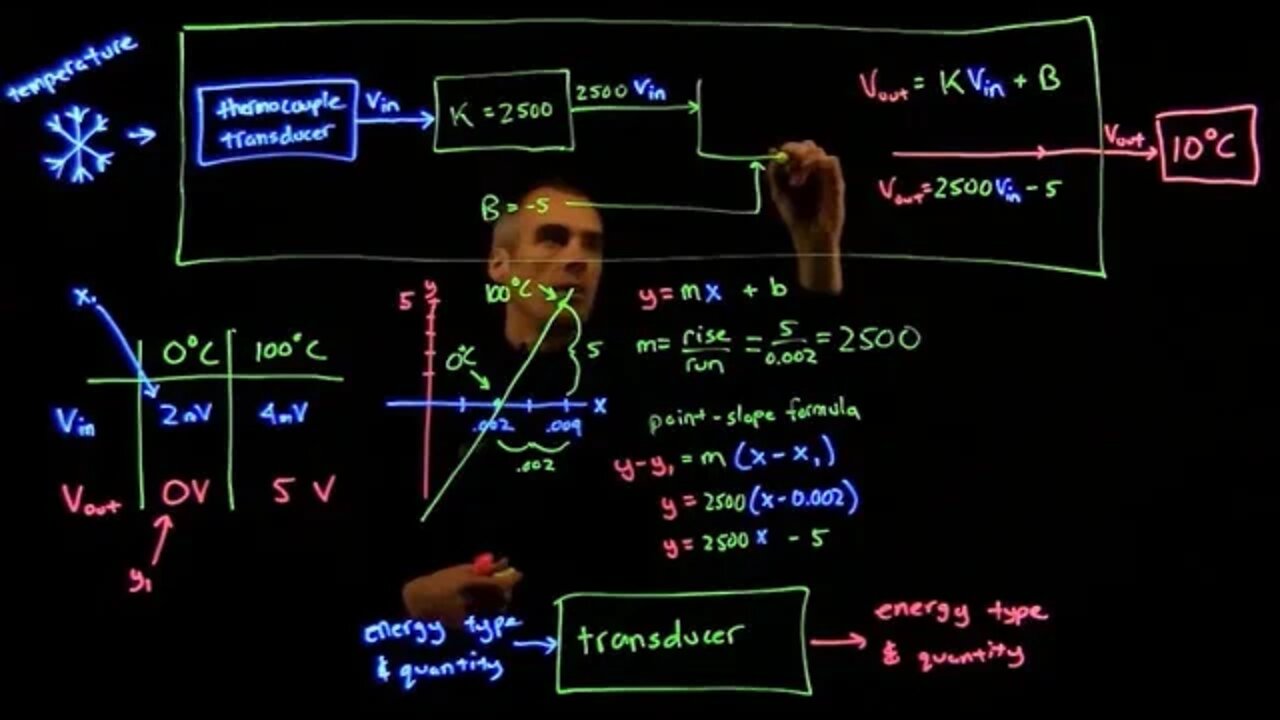
How to solve for amplification and gain in a transducer (thermometer example)
Basic introduction to transducers and a quick example of amplifying a microphone signal to a computer speaker.
Below is the basic format:
Sensor to electric signal -- amplify electric signal and change bias – thermometer output
thermocouple -- amplify electric signal and change bias – thermometer output
2 to 4 mV corresponds to 0 to 100 degrees Celsius -- amplify electric signal and change bias – thermometer output, 0 to 5 V corresponds to 0 to 100 degrees Celcius
Here we can't just multiply by K because, say it's 0 degrees and we needed to translate 2 mV to 0 V, we would have to multiply by 0, but of course then every temperature would give us 0 output voltage. So we have to introduce a bias as well.
To do this it may help to create a little table:
V_out = K V_in + B
So you may notice this looks like an equation for a line, y=mx+b and we can just consider this like a graph with V_in as my x and V_out as my y
So we have two points we need to connect
And you notice if we a draw a line through these two points we get an intersection on the x axis at our B value.
Two find this equation we can first find the slope as the rise/run
Rise = (V_out2-V_out1) = (y_2-y_1)= (5-0) = 5
Run = (V_in2 – V_in1) = (x_2-x_1) = 0.004-0.002= 0.002
So our slope will be 5/0.002 = 2500, which will be our b value
Then use our point-slope formula
Y-y_1= m (x-x_1)
Y-0 = 2500 (x-0.002)
Y=2500x-5
So our m value of 2500 is our K
And our b value of –5 is our big B
And our diagram for the transducer would look like this:
-

FreshandFit
6 hours agoAfter Hours w/ Girls
75.4K51 -
 2:33:58
2:33:58
TimcastIRL
9 hours agoDan Bongino ACCEPTS Deputy FBI Director, SECRET NSA CHATS EXPOSED w/Joey Mannarino | Timcast IRL
146K76 -
 1:09:33
1:09:33
Glenn Greenwald
13 hours agoMichael Tracey Reports from CPAC: Exclusive Interviews with Liz Truss, Steve Bannon & More | SYSTEM UPDATE #412
96K78 -
 56:02
56:02
Sarah Westall
9 hours agoBiohacking & Peptides: Weight loss, Anti-Aging & Performance – Myth vs Reality w/ Dr. Diane Kazer
45.3K14 -
 11:22
11:22
Bearing
19 hours ago"Anxious & Confused" Federal Workers FREAK OUT Over DOGE Efficiency Email 💥
64.2K64 -
 1:31:20
1:31:20
Flyover Conservatives
1 day agoUS STOCK MARKET: Sinking Ship - Dr. Kirk Elliott; How I Fought Back Against Woke Schools & Stopped Gender Bathrooms - Stacy Washington | FOC Show
67.7K1 -
 1:08:09
1:08:09
Donald Trump Jr.
14 hours agoFBI Dream Team, Plus Taking Your Questions Live! | Triggered Ep.219
208K279 -
 7:32:37
7:32:37
Akademiks
13 hours agoDrake and PartyNextDoor '$$$4U' Album Sells 250K first week. BIG AK IS BACK.
124K18 -
 3:12:08
3:12:08
MyronGainesX
12 hours ago $32.56 earnedDan Bongino Named FBI Deputy Director, Trump Meets Macron, And More!
100K29 -
 3:12:31
3:12:31
vivafrei
12 hours agoBarnes Live from Seattle - Defending Benshoof in a Case that is CRAY CRAY!
166K50