Premium Only Content
Molecular robots work cooperatively in swarms Under UV Light
I believe this is what the UV/ Black light street lamps are all about!!!
They are trying to change us with light and frequencies!!
Studying Azobenzene-Modified DNA for Programmable Nanoparticle Assembly and Nucleic Acid Detection
DNA Nanostructures on Membranes as Tools for Synthetic Biology
https://www.cell.com/action/showPdf?pii=S0006-3495%2816%2930065-0
Azobenzene-Based Cross-Linked Small-Molecule Vesicles for Precise Oxidative Damage Treatments Featuring Controlled and Prompt Molecular Release
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.chemmater.1c01860
Conformational changes of DNA induced by a trans-azobenzene derivative via non-covalent interactions
https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2018/cp/c8cp03836h
A Light-Driven DNA Nanomachine for the Efficient Photoswitching of RNA Digestion
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.200907082
Journal of Biomedical Nanotechnology
Light-regulated host–guest interaction as a new strategy for intracellular PEG-detachable polyplexes to facilitate nuclear entry
https://pubs.rsc.org/en/Content/ArticleLanding/2012/CC/C2CC34768G
Conformational Switching of G-Quadruplex DNA by Photoregulation
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/anie.201002290
Photoregulated DNA Rotary System
https://www.chemistryviews.org/details/ezine/10501617/Photoregulated_DNA_Rotary_System.html
A Photoregulated DNA-Based Rotary System and Direct Observation of Its Rotational Movement
https://chemistry-europe.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/chem.201605616
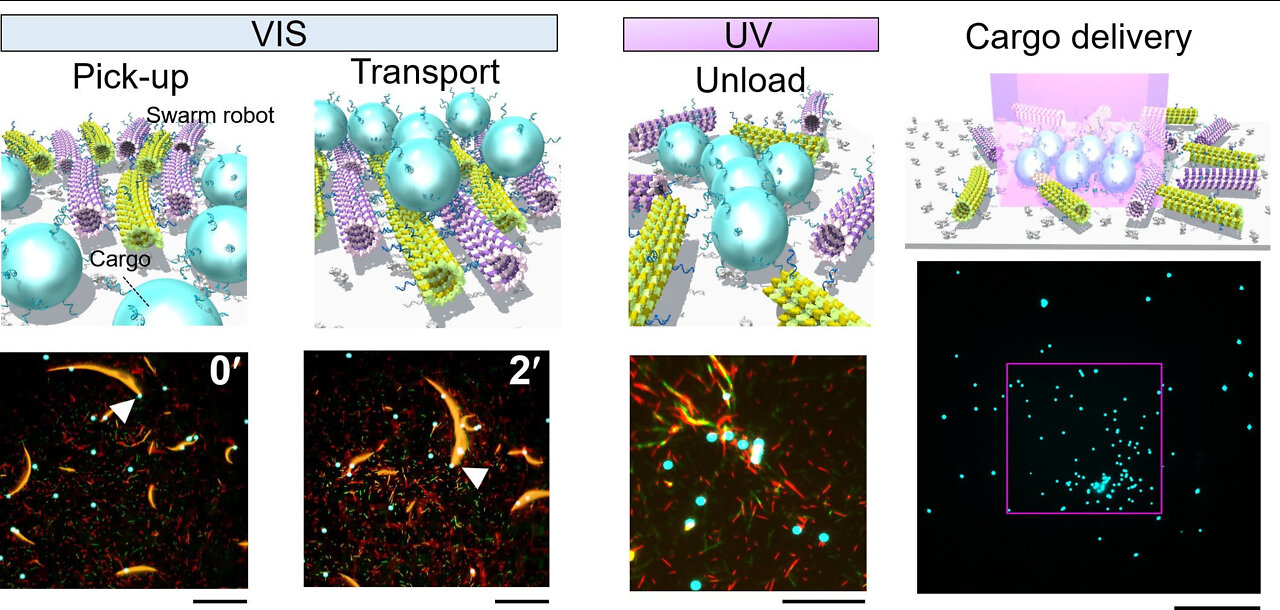
In a global first, scientists have demonstrated that molecular robots are able to accomplish cargo delivery by employing a strategy of swarming, achieving a transport efficiency five times greater than that of single robots.
Swarm robotics is a new discipline, inspired by the cooperative behavior of living organisms, that focuses on the fabrication of robots and their utilization in swarms to accomplish complex tasks. A swarm is an orderly collective behavior of multiple individuals.
Macro-scale swarm robots have been developed and employed for a variety of applications, such as transporting and accumulating cargo, forming shapes, and building complex structures.
A team of researchers, led by Dr. Mousumi Akter and Associate Professor Akira Kakugo from the Faculty of Science at Hokkaido University,
has succeeded in developing the world's first working micro-sized machines utilizing the advantages of swarming.
The findings were published in the journal Science Robotics
("Cooperative cargo transportation by a swarm of molecular machines").
A swarm of cooperating robots gains a number of characteristics which are not found in individual robots—they can divide a workload,
respond to risks, and even create complex structures in response to changes in the environment.
Microrobots and machines at the micro- and nano-scale have very few practical applications due to their size; if they could cooperate in swarms, their potential uses would increase massively.
The team constructed about five million single molecular machines. These machines were composed of two biological components: microtubules linked to DNA,
Recruiting a microtubule-binding complex to DNA directs chromosome segregation in budding yeast
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2752306/
Binding of microtubule protein to DNA and chromatin: possibility of simultaneous linkage of microtubule to nucleic acid and assembly of the microtubule structure
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC326720/pdf/nar00397-0148.pdf
which allowed them to swarm; and kinesin, which were actuators capable of transporting the microtubules.
The DNA was combined with a light-sensitive compound called azobenzene
Azobenzene | C12H10N2 - PubChem
https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/azobenzene
that functioned as a sensor,
allowing for control of swarming.
When exposed to visible light, changes in the structure of azobenzene caused the DNA to form double strands and led to the microtubules forming swarms.
Exposure to UV light reversed this process.
The cargo used in the experiments consisted of polystyrene beads of diameters ranging from micrometers to tens of micrometers.
These beads were treated with azobenzene-linked DNA; thus, the cargo was loaded when exposed to visible light and unloaded when exposed to UV light. However,
the DNA and azobenzene used in the molecular machines and the cargo were different, so swarming could be controlled independently of cargo-loading.
Single machines are able to load and transport polystyrene beads up to 3 micrometers in diameter,
whereas swarms of machines could transport cargo as large as 30 micrometers in diameter.
Furthermore,
a comparison of transport distance and transport volume showed that the swarms were up to five times more efficient at transport compared to the single machines.
original link by Hokkaido Uni
-
 15:39
15:39
Watchman's Duty
11 days agoWhy Is Everything A Monthly Subscription Now...?
1.8K4 -
 1:57:48
1:57:48
The Charlie Kirk Show
2 hours agoTrump Gets His Cabinet + Killing the USAID Grift + Why Bud Light Collapsed | Frericks | 2.4.2025
136K29 -
 1:21:47
1:21:47
Simply Bitcoin
2 hours ago $1.56 earnedDid America JUST Change The Bitcoin Nation State Race Forever?! | EP 1175
12.5K1 -
 37:13
37:13
Grant Stinchfield
2 hours ago $1.21 earnedBill Gates is Making the Media Rounds Today to Push the Vax and Stop RFK Jr.
8.02K18 -
 53:03
53:03
TheAlecLaceShow
4 hours agoGuest: Rep. Burgess Owens | Trump Wins with Mexico & Canada | DNC Diversity | The Alec Lace Show
6.17K5 -
 1:00:28
1:00:28
The Dan Bongino Show
5 hours agoTrump’s Most Important Fight To Date (Ep. 2415) - 02/04/2025
603K1.19K -
 59:44
59:44
The Rubin Report
4 hours agoPress Gasps When Shown What USAID Spent Money On
77.3K120 -
 1:15:21
1:15:21
Bare Knuckle Fighting Championship
4 hours agoThe Bare Knuckle Show with Brian Soscia
13.7K3 -
 1:28:32
1:28:32
The Shannon Joy Show
5 hours ago🔥SHOCK Report - The COVID Dossier! A Coordinated Global Military Operation: Live EXCLUSIVE W/ Sasha Latypova & Debbie Lerman.🔥
12.8K2 -
 1:57:04
1:57:04
Steven Crowder
5 hours agoUSAID Exposed: Everything You Need to Know Featuring Mike Benz
363K219